Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2014 Sep;6(5):470-473. 10.4168/aair.2014.6.5.470.
Occupational Rhinoconjunctivitis due to Maize in a Snack Processor: A Cross-Reactivity Study Between Lipid Transfer Proteins From Different Cereals and Peach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy, Hospital La Paz Institute for Health Research (IdiPAZ), Madrid, Spain. dguillen27@gmail.com
- 2Unidad de Bioquimica, Departamento de Biotecnologia, E.T.S. Ingenieros Agronomos, UPM, Madrid, Spain.
- 3CIBER de Enfermedades Respiratorias CIBERES, Madrid, Spain.
- KMID: 2181086
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.5.470
Abstract
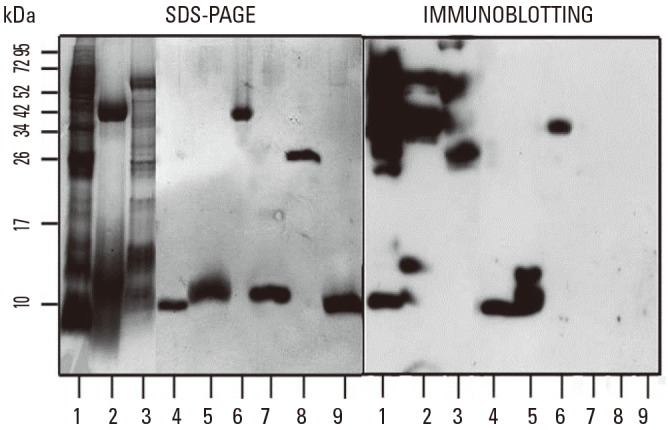
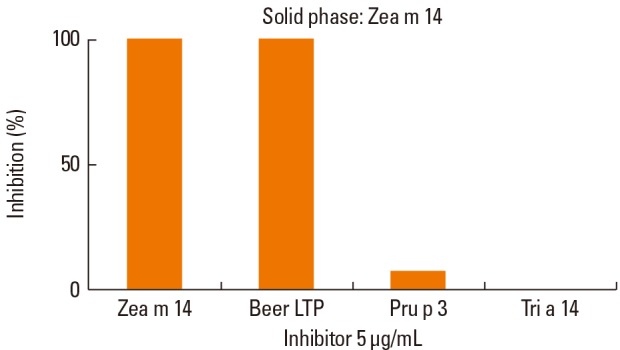
- We report the case of a snack processor who developed occupational rhinoconjunctivitis due to maize brand exposure during the extrusion process, and who experienced abdominal pain upon drinking beer. The allergens implicated and the cross-reactivity between non-specific lipid transfer proteins (LTPs) from different cereals and peach were investigated. Skin prick tests and specific IgE to cereal flours, pulmonary functions tests and specific conjunctival and inhalation challenges to maize extract were performed. In vitro studies included IgE immunoblotting and ELISA inhibition assays. Skin prick tests with maize flour, maize brand and wheat flour extracts were positive, whereas serum specific IgE was positive only to maize flour. Specific inhalation challenge (SIC) to maize flour did not elicit an asthmatic reaction; however, conjunctival challenge test with the same extract was positive. Patient's serum recognized IgE-binding bands in the maize and beer extracts corresponding to LTPs. In the ELISA inhibition assays, a significant degree of allergenic cross-reactivity was found between maize and beer LTPs, whereas no cross-reactivity was observed between maize LTP and wheat and peach LTPs.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Survey of IgE Reactivity to Nonbiting Midges in Korea and Identification of IgE-Binding Protein
Myung-hee Yi, Ju Yeong Kim, Kyoung Yong Jeong, Han-Il Ree, Tai-Soon Yong
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2019;11(5):644-654. doi: 10.4168/aair.2019.11.5.644.
Reference
-
1. Pasini G, Simonato B, Curioni A, Vincenzi S, Cristaudo A, Santucci B, Peruffo AD, Giannattasio M. IgE-mediated allergy to corn: a 50 kDa protein, belonging to the reduced soluble proteins, is a major allergen. Allergy. 2002; 57:98–106. PMID: 11929411.2. Maniu CM, Faupel U, Siebenhaar G, Hunzelmann N. Maize: a new occupational allergen in the pharmaceutical industry. Allergy. 2010; 65:930–931. PMID: 20180793.
Article3. Sung SY, Lee WY, Yong SJ, Shin KC, Park HS, Kim HM, Kim SH. A case of occupational rhinitis induced by maize pollen exposure in a farmer: detection of IgE-binding components. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2012; 4:49–51. PMID: 22211171.
Article4. Li LC, Bedinger PA, Volk C, Jones AD, Cosgrove DJ. Purification and characterization of four beta-expansins (Zea m 1 isoforms) from maize pollen. Plant Physiol. 2003; 132:2073–2085. PMID: 12913162.5. Petersen A, Dresselhaus T, Grobe K, Becker WM. Proteome analysis of maize pollen for allergy-relevant components. Proteomics. 2006; 6:6317–6325. PMID: 17080481.
Article6. Abelson MB, Chambers WA, Smith LM. Conjunctival allergen challenge. A clinical approach to studying allergic conjunctivitis. Arch Ophthalmol. 1990; 108:84–88. PMID: 2297337.7. Gonzalo-Garijo MA, Pérez-Calderón R, Muñoz-Rodríguez A, Tormo-Molina R, Silva-Palacios I. Hypersensitivity to maize pollen. Allergy. 2004; 59:365. PMID: 14982529.
Article8. Park HS, Nahm DH. Identification of IgE-binding components in occupational asthma caused by corn dust. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1997; 79:75–79. PMID: 9236505.
Article9. Cristaudo A, Simonato B, Pasini G, De Rocco M, Curioni A, Giannattasio M. Contact urticaria and protein contact dermatitis from corn in a patient with serum IgE specific for a salt-soluble corn protein of low molecular weight. Contact Dermatitis. 2004; 51:84–87. PMID: 15373849.
Article10. Scibilia J, Pastorello EA, Zisa G, Ottolenghi A, Ballmer-Weber B, Pravettoni V, Scovena E, Robino A, Ortolani C. Maize food allergy: a double-blind placebo-controlled study. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1943–1949. PMID: 18778272.
Article11. Pastorello EA, Farioli L, Pravettoni V, Ispano M, Scibola E, Trambaioli C, Giuffrida MG, Ansaloni R, Godovac-Zimmermann J, Conti A, Fortunato D, Ortolani C. The maize major allergen, which is responsible for food-induced allergic reactions, is a lipid transfer protein. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2000; 106:744–751. PMID: 11031346.
Article12. Weichel M, Vergoossen NJ, Bonomi S, Scibilia J, Ortolani C, Ballmer-Weber BK, Pastorello EA, Crameri R. Screening the allergenic repertoires of wheat and maize with sera from double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge positive patients. Allergy. 2006; 61:128–135. PMID: 16364168.
Article13. Fasoli E, Pastorello EA, Farioli L, Scibilia J, Aldini G, Carini M, Marocco A, Boschetti E, Righetti PG. Searching for allergens in maize kernels via proteomic tools. J Proteomics. 2009; 72:501–510. PMID: 19367736.
Article14. Palacin A, Quirce S, Armentia A, Fernández-Nieto M, Pacios LF, Asensio T, Sastre J, Diaz-Perales A, Salcedo G. Wheat lipid transfer protein is a major allergen associated with Baker's asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007; 120:1132–1138. PMID: 17716720.
Article15. Quirce S, Diaz-Perales A. Diagnosis and management of grain-induced asthma. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2013; 5:348–356. PMID: 24179680.
Article16. Tordesillas L, Pacios LF, Palacin A, Quirce S, Armentia A, Barber D, Salcedo G, Diaz-Perales A. Molecular basis of allergen cross-reactivity: non-specific lipid transfer proteins from wheat flour and peach fruit as models. Mol Immunol. 2009; 47:534–540. PMID: 19846220.
Article17. Bernardi ML, Giangrieco I, Camardella L, Ferrara R, Palazzo P, Panico MR, Crescenzo R, Carratore V, Zennaro D, Liso M, Santoro M, Zuzzi S, Tamburrini M, Ciardiello MA, Mari A. Allergenic lipid transfer proteins from plant-derived foods do not immunologically and clinically behave homogeneously: the kiwifruit LTP as a model. PLoS One. 2011; 6:e27856. PMID: 22114713.
Article18. García-Casado G, Crespo JF, Rodríguez J, Salcedo G. Isolation and characterization of barley lipid transfer protein and protein Z as beer allergens. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2001; 108:647–649. PMID: 11590395.
Article19. Pastorello EA, Farioli L, Pravettoni V, Scibilia J, Conti A, Fortunato D, Borgonovo L, Bonomi S, Primavesi L, Ballmer-Weber B. Maize food allergy: lipid-transfer proteins, endochitinases, and alpha-zein precursor are relevant maize allergens in double-blind placebo-controlled maize-challenge-positive patients. Anal Bioanal Chem. 2009; 395:93–102. PMID: 19669736.
Article20. Pastorello EA, Pompei C, Pravettoni V, Farioli L, Calamari AM, Scibilia J, Robino AM, Conti A, Iametti S, Fortunato D, Bonomi S, Ortolani C. Lipid-transfer protein is the major maize allergen maintaining IgE-binding activity after cooking at 100 degrees C, as demonstrated in anaphylactic patients and patients with positive double-blind, placebo-controlled food challenge results. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 112:775–783. PMID: 14564361.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Occupational Rhinitis Induced by Maize Pollen Exposure in a Farmer: Detection of IgE-Binding Components
- A case report of recurrent anaphylaxis in a 36-year-old female: Lipid transfer protein syndrome
- A Case of Rice Induced Food Allergy in an Adult Patient Presenting Multiple Food Allergies
- Mugwort Pollen-Related Food Allergy: Lipid Transfer Protein Sensitization and Correlation With the Severity of Allergic Reactions in a Chinese Population
- A case study of apple seed and grape allergy with sensitisation to nonspecific lipid transfer protein