J Adv Prosthodont.
2013 Nov;5(4):494-501. 10.4047/jap.2013.5.4.494.
Morphometric analysis of maxillary alveolar regions for immediate implantation
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Republic of Korea. donghoohan@yuhs.ac
- 2Department of Oral Maxillofacial Surgery, Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
- 3Division in Anatomy and Developmental Biology, Department of Oral Biology, Oral Science Research Center, Yonsei University College of Dentistry, Seoul, Republic of Korea. hjk776@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 2176544
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4047/jap.2013.5.4.494
Abstract
- PURPOSE
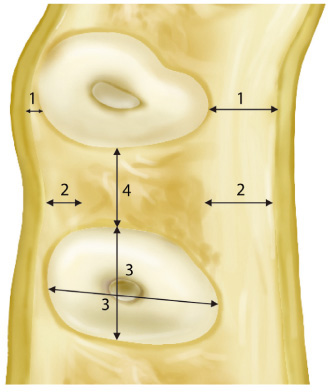
The purpose of this study was to provide an actual guideline in determining the shape, diameter, and position of the implant in immediate implantation by the measurement of the thickness of facial and palatal plate, the thickness of cortical bone on the facial and palatal plate, the diameter of the root, and the distance between the roots in the cadavers.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
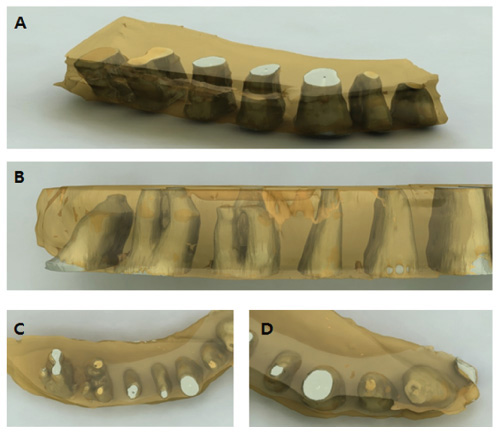
The horizontal sections of 20 maxillae were measured and analyzed to obtain the average values. Resin blocks were produced and cut serially at 1 mm intervals from the cervical line to the root apex. Images of each section were obtained and the following measurements were performed: The thickness of the facial and palatal residual bone at each root surface, the thickness of the facial and palatal cortical bone at the interdental region, the diameter of all roots of each section on the faciopalatal and mesiodistal diameter, and the interroot distance. Three specimens with measurements close to the average values were chosen and 3-dimensional images were reconstructed.
RESULTS
The thickness of the facial and palatal cortical bone at the interdental region in the maxilla, the buccal cortical bone was thicker in the posterior region compared to the anterior region. The interroot distance of the alveolar bone thickness between the roots increased from anterior to posterior region and from coronal to apical in the maxilla.
CONCLUSION
In this study, the limited results of the morphometric analysis of the alveolar ridge using the sections of maxilla in the cadavers may offer the useful information when planning and selecting optimal implant for immediate implantation in the maxilla.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Akimoto K, Becker W, Persson R, Baker DA, Rohrer MD, O'Neal RB. Evaluation of titanium implants placed into simulated extraction sockets: a study in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999; 14:351–360.2. Zarb GA, Schmitt A. The longitudinal clinical effectiveness of osseointegrated dental implants: the Toronto study. Part I: Surgical results. J Prosthet Dent. 1990; 63:451–457.3. Carlsson GE, Bergman B, Hedegård B. Changes in contour of the maxillary alveolar process under immediate dentures. A longitudinal clinical and x-ray cephalometric study covering 5 years. Acta Odontol Scand. 1967; 25:45–75.4. Lazzara RJ. Immediate implant placement into extraction sites: surgical and restorative advantages. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1989; 9:332–343.5. Parel SM, Triplett RG. Immediate fixture placement: a treatment planning alternative. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1990; 5:337–345.6. Denissen HW, Kalk W, Veldhuis HA, van Waas MA. Anatomic consideration for preventive implantation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1993; 8:191–196.7. Sclar A. Ridge Preservation for Optimum Esthetics and Function: The "Bio-Col" Technique. Postgrad Dent. 1999; 6:3–11.8. Watzek G, Haider R, Mensdorff-Pouilly N, Haas R. Immediate and delayed implantation for complete restoration of the jaw following extraction of all residual teeth: a retrospective study comparing different types of serial immediate implantation. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1995; 10:561–567.9. Koh RU, Rudek I, Wang HL. Immediate implant placement: positives and negatives. Implant Dent. 2010; 19:98–108.10. Oakley E, Rhyu IC, Karatzas S, Gandini-Santiago L, Nevins M, Caton J. Formation of the biologic width following crown lengthening in nonhuman primates. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1999; 19:529–541.11. Novaes AB Jr, Novaes AB. IMZ implants placed into extraction sockets in association with membrane therapy (Gengiflex) and porous hydroxyapatite: a case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1992; 7:536–540.12. Werbitt MJ, Goldberg PV. The immediate implant: bone preservation and bone regeneration. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1992; 12:206–217.13. Klokkevold PR, Han TJ, Camargo PM. Aesthetic management of extractions for implant site development: delayed versus staged implant placement. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1999; 11:603–610.14. Juodzbalys G. Instrument for extraction socket measurement in immediate implant installation. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2003; 14:144–149.15. Meredith N. Assessment of implant stability as a prognostic determinant. Int J Prosthodont. 1998; 11:491–501.16. Zarb GA, Schmitt A. Osseointegration and the edentulous predicament. The 10-year-old Toronto study. Br Dent J. 1991; 170:439–444.17. Akimoto K, Becker W, Persson R, Baker DA, Rohrer MD, O'Neal RB. Evaluation of titanium implants placed into simulated extraction sockets: a study in dogs. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 1999; 14:351–360.18. Paolantonio M, Dolci M, Scarano A, d'Archivio D, di Placido G, Tumini V, Piattelli A. Immediate implantation in fresh extraction sockets. A controlled clinical and histological study in man. J Periodontol. 2001; 72:1560–1571.19. Saadoun AP, Sullivan DY, Krischek M, Le Gall M. Single tooth implant-management for success. Pract Periodontics Aesthet Dent. 1994; 6:73–80.20. Salama H, Salama M. The role of orthodontic extrusive remodeling in the enhancement of soft and hard tissue profiles prior to implant placement: a systematic approach to the management of extraction site defects. Int J Periodontics Restorative Dent. 1993; 13:312–333.21. Block MS, Kent JN. Placement of endosseous implants into tooth extraction sites. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1991; 49:1269–1276.22. Araújo MG, Sukekava F, Wennström JL, Lindhe J. Ridge alterations following implant placement in fresh extraction sockets: an experimental study in the dog. J Clin Periodontol. 2005; 32:645–652.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Morphometrics of alveolar process and anatomical structures around inferior maxillary sinus for maxillary implantation
- A Case of Maxillary Sinusitis after Sinus Floor Augmentation
- Three-dimensional evaluation of maxillary anterior alveolar bone for optimal placement of miniscrew implants
- Implant Placement Using Alveolar Ridge Split in Atrophic Maxillary Alveolar Bone
- Morphometric Analysis of Maxillary Sinus Floor and Alveolar Process in Korean