Chonnam Med J.
2015 Apr;51(1):39-42. 10.4068/cmj.2015.51.1.39.
IgG4-Related Systemic Disease Can Be Easily Mistaken as a Uroepithelial Tumor
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Nephrology, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea. jyjung@gachon.ac.kr
- 2Department of Internal Medicine, Gachon University Gil Medical Center, Gachon University School of Medicine, Incheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2172146
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4068/cmj.2015.51.1.39
Abstract
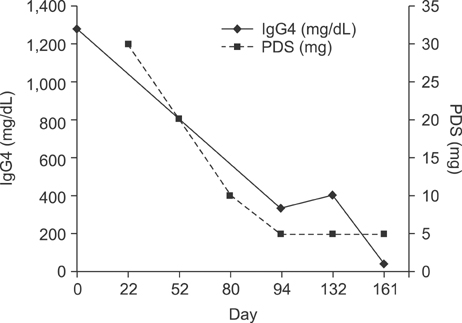
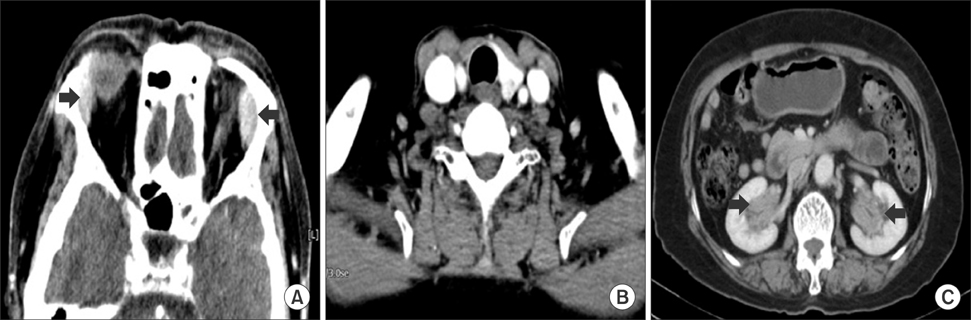
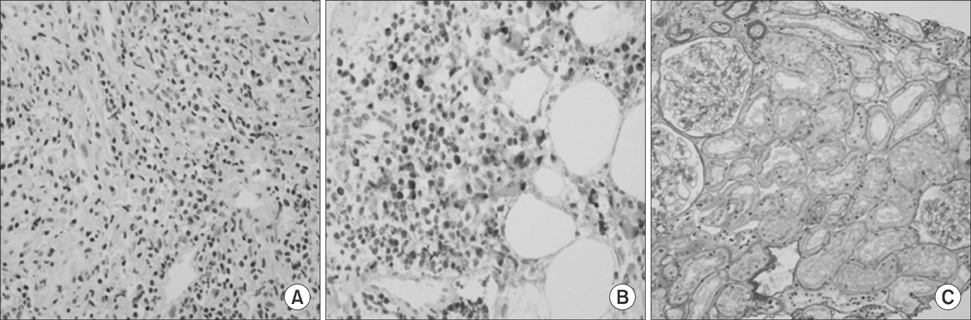
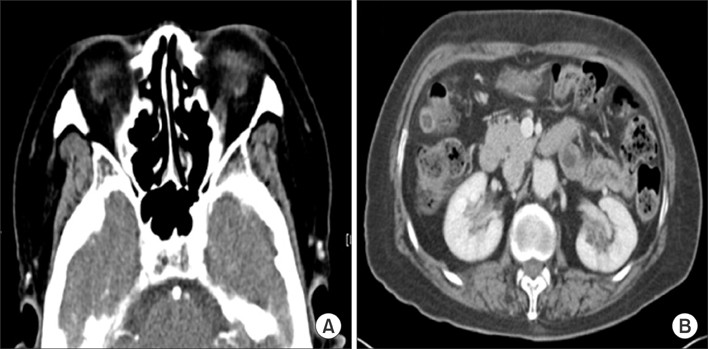
- Immunoglobulin G4-related disease (IgG4-RD) is a newly recognized systemic syndrome characterized by elevated serum IgG4 concentrations and tumefaction or tissue infiltration by IgG4-positive plasma cells. We experienced a case of IgG4-RD involving multiple organs in a 64-year-old female who was referred for a suspected uroepithelial tumor. A mass biopsy confirmed dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltration with an increased number of IgG4-positive plasma cells. We discuss this case and review the literature to bring IgG4-RD to the attention to clinicians because it responds dramatically well to steroid therapy and should be kept in mind as a differential diagnosis to avoid unnecessary surgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. Research Program for Intractable Disease by Ministry of Health, Labor and Welfare (MHLW) Japan G4 team. A novel clinical entity, IgG4-related disease (IgG4RD): general concept and details. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:1–14.
Article2. Umehara H, Okazaki K, Masaki Y, Kawano M, Yamamoto M, Saeki T, et al. Comprehensive diagnostic criteria for IgG4-related disease (IgG4-RD), 2011. Mod Rheumatol. 2012; 22:21–30.
Article3. Kamisawa T, Okamoto A. Autoimmune pancreatitis: proposal of IgG4-related sclerosing disease. J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:613–625.
Article4. Shoji S, Nakano M, Usui Y. IgG4-related inflammatory pseudotumor of the kidney. Int J Urol. 2010; 17:389–390.
Article5. Stone JH, Zen Y, Deshpande V. IgG4-related disease. N Engl J Med. 2012; 366:539–551.
Article6. Bissada NK, Finkbeiner AE. Idiopathic segmental ureteritis. Urology. 1978; 12:64–66.
Article7. Li Y, Nishihara E, Hirokawa M, Taniguchi E, Miyauchi A, Kakudo K. Distinct clinical, serological, and sonographic characteristics of hashimoto\'s thyroiditis based with and without IgG4-positive plasma cells. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2010; 95:1309–1317.
Article8. Kamisawa T, Shimosegawa T, Okazaki K, Nishino T, Watanabe H, Kanno A, et al. Standard steroid treatment for autoimmune pancreatitis. Gut. 2009; 58:1504–1507.
Article9. Kamisawa T, Chen PY, Tu Y, Nakajima H, Egawa N. Autoimmune pancreatitis metachronously associated with retroperitoneal fibrosis with IgG4-positive plasma cell infiltration. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:2955–2957.
Article10. Kawa S, Ito T, Watanabe T, Maruyama M, Hamano H, Maruyama M, et al. The Utility of Serum IgG4 Concentrations as a Biomarker. Int J Rheumatol. 2012; 2012:198314.
Article