Ann Dermatol.
2011 Feb;23(1):119-122. 10.5021/ad.2011.23.1.119.
Sorafenib (Nexavar(R), BAY 43-9006)-induced Hand-foot Skin Reaction with Facial Erythema
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mnkim@cau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2171970
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2011.23.1.119
Abstract
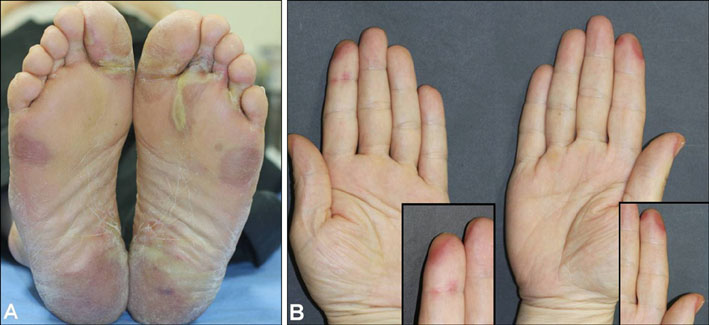
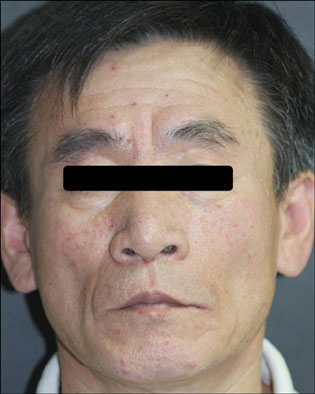
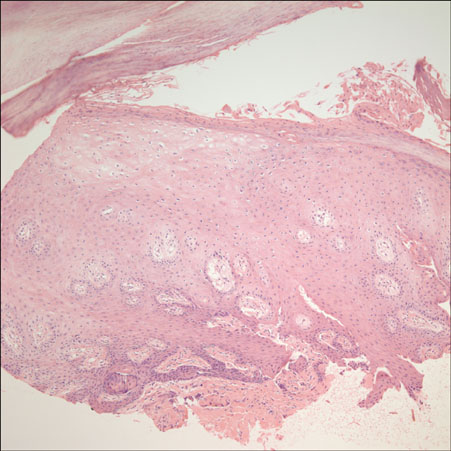
- Sorafenib (Nexavar(R), BAY 43-9006) is a novel, orally administered multi-kinase inhibitor that has recently been approved for the treatment of metastatic renal cell carcinoma. It is also used to delay disease progression in patients with advanced solid organ malignancies and metastatic melanoma. Sorafenib is associated with a relatively high incidence of dermatologic adverse events. The commonly occurring dermatologic adverse events associated with sorafenib include hand-foot skin reaction, facial erythema, splinter subungual hemorrhages, alopecia, pruritus and xerosis. We report here on a case of a 50-year-old man who was diagnosed with metastatic hepatocellular carcinoma. He developed both facial erythema and hand-foot skin reaction after the administration of sorafenib.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Kane RC, Farrell AT, Saber H, Tang S, Williams G, Jee JM, et al. Sorafenib for the treatment of advanced renal cell carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 2006. 12:7271–7278.
Article2. Llovet J, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Raoul J, Zeuzem S, et al. Randomized phase III trial of sorafenib versus placebo in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) [abstract]. J Clin Oncol. 2007. 25:LBA1.3. Ratain MJ, Eisen T, Stadler WM, Flaherty KT, Kaye SB, Rosner GL, et al. Phase II placebo-controlled randomized discontinuation trial of sorafenib in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. J Clin Oncol. 2006. 24:2505–2512.
Article4. Strumberg D, Awada A, Hirte H, Clark JW, Seeber S, Piccart P, et al. Pooled safety analysis of BAY 43-9006 (sorafenib) monotherapy in patients with advanced solid tumours: is rash associated with treatment outcome? Eur J Cancer. 2006. 42:548–556.
Article5. Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, et al. BAY 43-9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 2004. 64:7099–7109.
Article6. Ito Y, Sasaki Y, Horimoto M, Wada S, Tanaka Y, Kasahara A, et al. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinases/extracellular signal-regulated kinases in human hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology. 1998. 27:951–958.
Article7. Autier J, Escudier B, Wechsler J, Spatz A, Robert C. Prospective study of the cutaneous adverse effects of sorafenib, a novel multikinase inhibitor. Arch Dermatol. 2008. 144:886–892.
Article8. Susser WS, Whitaker-Worth DL, Grant-Kels JM. Mucocutaneous reactions to chemotherapy. J Am Acad Dermatol. 1999. 40:367–398.
Article9. Lacouture ME, Wu S, Robert C, Atkins MB, Kong HH, Guitart J, et al. Evolving strategies for the management of hand-foot skin reaction associated with the multitargeted kinase inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib. Oncologist. 2008. 13:1001–1011.
Article10. Chu D, Lacouture ME, Fillos T, Wu S. Risk of hand-foot skin reaction with sorafenib: a systematic review and metaanalysis. Acta Oncol. 2008. 47:176–186.
Article11. Lee WJ, Lee JL, Chang SE, Lee MW, Kang YK, Choi JH, et al. Cutaneous adverse effects in patients treated with the multitargeted kinase inhibitors sorafenib and sunitinib. Br J Dermatol. 2009. 161:1045–1051.
Article12. Park JH, Kim S, Choi SC, Lee ES, Yang JM. Cutaneous adverse effects associated with sorafenib therapy (Nexavar®, BAY 43-9006). Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:141–143.13. Kim HJ, Kim JH, Kim JB, Kim HK, Ko YS, Joh OJ, et al. A case of leukocytoclastic vasculitis after use of sorafenib (Nexavar®). Korean J Dermatol. 2008. 46:648–651.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Cutaneous Adverse Effects Associated with Sorafenib Therapy (Nexavar(R), BAY 43-9006)
- Multiple Epidermal Cysts in a Hepatocellular Carcinoma Patient Taking Nexavar®
- A Case of Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis after Use of Sorafenib (Nexavar(R))
- A Case of Drug Eruption Similar to Erythema Multiforme Induced by Sorafenib
- Scrotal Erythema Associated with Sorafenib Therapy in a Patient with Hepatocellular Carcinoma