Infect Chemother.
2013 Sep;45(3):331-334. 10.3947/ic.2013.45.3.331.
Emphysematous Pyelonephritis Caused by Citrobacter freundii in a Patient with Type 2 Diabetes and Neurogenic Bladder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea. hka1114@eulji.ac.kr
- 2Department of Radiology, Eulji General Hospital, Eulji University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2170433
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2013.45.3.331
Abstract
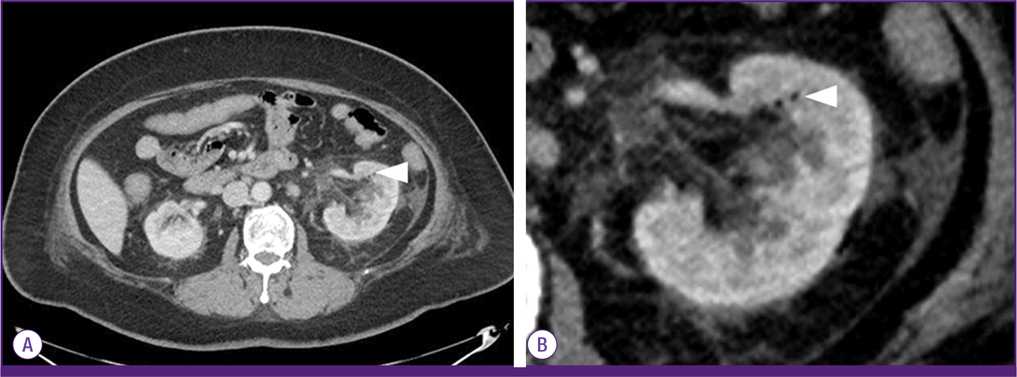
- Emphysematous pyelonephritis (EPN) is a rare, life-threatening complication of upper urinary tract infections that is characterized by the presence of gas in the renal parenchyma and perirenal space. It commonly occurs in diabetic patients. Escherichia coli are the most common causative organisms, with few reports implicating Citrobacter freundii as the etiologic agent in EPN. A 57-year-old woman with diabetes and neurogenic bladder visited at our department with confused mentality, myalgia, and general weakness. Further investigation revealed that the patient suffered from unilateral EPN with sepsis caused by C. freundii. The patient's condition was improved considerably with percutaneous drainage and use of intravenous antibiotics for several weeks. However, renal function eventually deteriorated to permanent renal failure, which required hemodialysis. In conclusion, C. freundii may be the causative pathogen of EPN in a patient with type 2 diabetes and neurogenic bladder.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huang JJ, Tseng CC. Emphysematous pyelonephritis: clinicoradiological classification, management, prognosis, and pathogenesis. Arch Intern Med. 2000; 160:797–805.2. Ubee SS, McGlynn L, Fordham M. Emphysematous pyelonephritis. BJU Int. 2011; 107:1474–1478.
Article3. Wang JM, Lim HK, Pang KK. Emphysematous pyelonephritis. Scand J Urol Nephrol. 2007; 41:223–229.
Article4. Abdul-Halim H, Kehinde EO, Abdeen S, Lashin I, Al-Hunayan AA, Al-Awadi KA. Severe emphysematous pyelonephritis in diabetic patients: diagnosis and aspects of surgical management. Urol Int. 2005; 75:123–128.
Article5. Patterson JE, Andriole VT. Bacterial urinary tract infections in diabetes. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 1997; 11:735–750.
Article6. Bjurlin MA, Hurley SD, Kim DY, Cohn MR, Jordan MD, Kim R, Divakaruni N, Hollowell CM. Clinical outcomes of nonoperative management in emphysematous urinary tract infections. Urology. 2012; 79:1281–1285.
Article7. Dubey IB, Agrawal V, Jain BK. Five patients with emphysematous pyelonephritis. Iran J Kidney Dis. 2011; 5:204–206.8. Farrell DJ, Morrissey I, De Rubeis D, Robbins M, Felmingham D. A UK multicentre study of the antimicrobial susceptibility of bacterial pathogens causing urinary tract infection. J Infect. 2003; 46:94–100.
Article9. Kofteridis DP, Papadimitraki E, Mantadakis E, Maraki S, Papadakis JA, Tzifa G, Samonis G. Effect of diabetes mellitus on the clinical and microbiological features of hospitalized elderly patients with acute pyelonephritis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2009; 57:2125–2128.
Article10. Lin SY, Ho MW, Yang YF, Liu JH, Wang IK, Lin SH, Huang CC. Abscess caused by Citrobacter koseri infection: three case reports and a literature review. Intern Med. 2011; 50:1333–1337.
Article11. Williams RD, Simmons RL. Citrobacter perinephric abscess presenting as pneumoscrotum in transplant recipient. Urology. 1974; 3:478–480.
Article12. Fischer C, Kallerhoff M, Weidner W, Ringert RH. Citrobacter emphysematous pyelonephritis in a tuberculous kidney caused by citrobacter A case report in a diabetic patient. Ann Urol (Paris). 1996; 30:108–111.13. Khaira A, Gupta A, Rana DS, Gupta A, Bhalla A, Khullar D. Retrospective analysis of clinical profile prognostic factors and outcomes of 19 patients of emphysematous pyelonephritis. Int Urol Nephrol. 2009; 41:959–966.
Article14. Mohanty S, Singhal R, Sood S, Dhawan B, Kapil A, Das BK. Citrobacter infections in a tertiary care hospital in Northern India. J Infect. 2007; 54:58–64.
Article15. Samonis G, Karageorgopoulos DE, Kofteridis DP, Matthaiou DK, Sidiropoulou V, Maraki S, Falagas ME. Citrobacter infections in a general hospital: characteristics and outcomes. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2009; 28:61–68.
Article