Cancer Res Treat.
2014 Jan;46(1):48-54.
Dose KRAS Mutation Status Affect on the Effect of VEGF Therapy in Metastatic Colon Cancer Patients?
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. yhk0215@korea.ac.kr
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
Mutations affecting the KRAS gene are an established negative predictor for anti-epidermal growth factor receptor (anti-EGFR) therapies in metastatic colorectal cancer (CRC). However, the role of KRAS mutation as a biomarker for anti-vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) remains controversial.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
We analyzed retrospective data from 32 CRC patients who were available for KRAS mutation status and received cytotoxic chemotherapy plus bevacizumab as a first-line therapy. Six of 32 patients received anti-EGFR therapies. We used KRAS mutation status as a predictive or prognostic factor in CRC patients receiving bevacizumab.
RESULTS
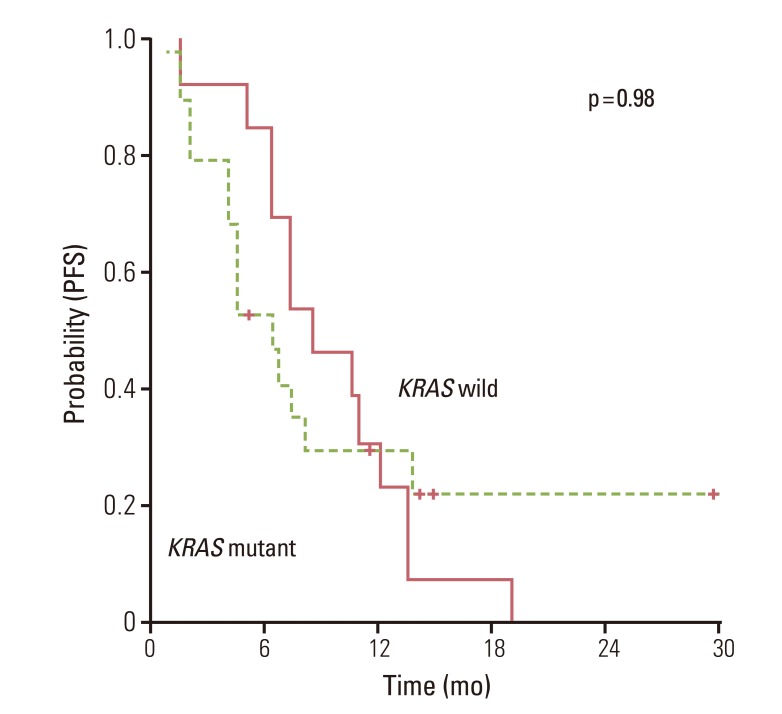
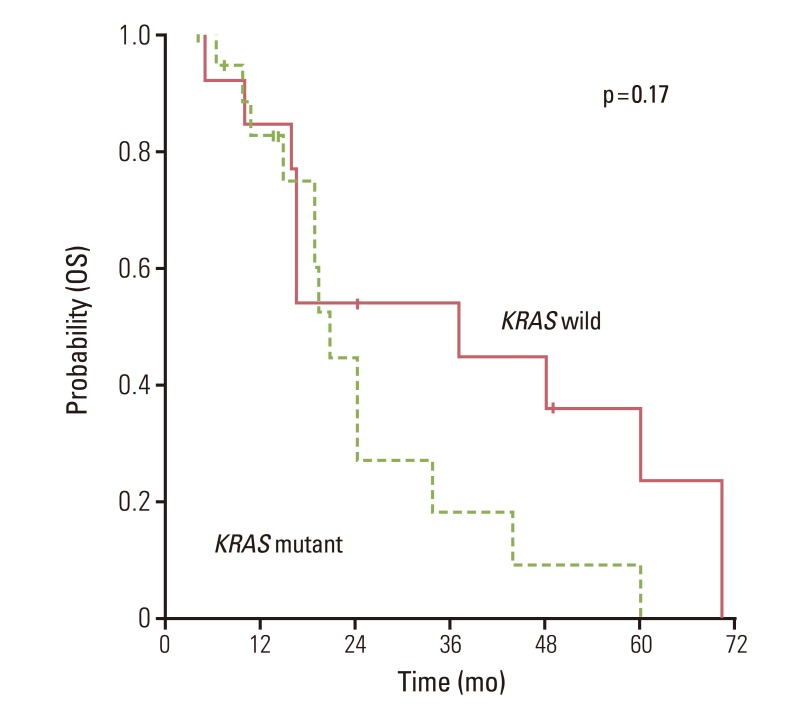
We observed mutations in KRAS in 59.4% of patients. Bevacizumab was used in combination with oxaliplatin based regimens. There was no significant difference for progression free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) in patients with oxaliplatin based cytotoxic chemotherapy plus bevacizumab according to the status of KRAS mutation. After first-line therapy, 28 patients (87.5%) received second-line therapy. In univariate analysis, KRAS mutations did not have a major prognostic value for PFS (hazard ratio, 1.007; 95% confidence interval [CI], 0.469 to 2.162; p>0.05) or OS (hazard ratio, 0.548; 95% CI, 0.226 to 1.328; p>0.05). In addition, anti-EGFR therapies did not affect the impact on OS.
CONCLUSION
KRAS mutation is neither a predictive for bevacizumab nor a prognostic for OS in CRC patients receiving anti-VEGF therapy.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90. PMID: 21296855.
Article2. Comella P, Casaretti R, Sandomenico C, Avallone A, Franco L. Capecitabine, alone and in combination, in the management of patients with colorectal cancer: a review of the evidence. Drugs. 2008; 68:949–961. PMID: 18457461.3. de Gramont A, Louvet C, Andre T, Tournigand C, Krulik M. A review of GERCOD trials of bimonthly leucovorin plus 5-fluorouracil 48-h continuous infusion in advanced colorectal cancer: evolution of a regimen. Groupe d'Etude et de Recherche sur les Cancers de l'Ovaire et Digestifs (GERCOD). Eur J Cancer. 1998; 34:619–626. PMID: 9713264.4. Capdevila J, Elez E, Peralta S, Macarulla T, Ramos FJ, Tabernero J. Oxaliplatin-based chemotherapy in the management of colorectal cancer. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 2008; 8:1223–1236. PMID: 18699761.
Article5. Borgstrom P, Hillan KJ, Sriramarao P, Ferrara N. Complete inhibition of angiogenesis and growth of microtumors by anti-vascular endothelial growth factor neutralizing antibody: novel concepts of angiostatic therapy from intravital videomicroscopy. Cancer Res. 1996; 56:4032–4039. PMID: 8752175.6. Kim KJ, Li B, Winer J, Armanini M, Gillett N, Phillips HS, et al. Inhibition of vascular endothelial growth factor-induced angiogenesis suppresses tumour growth in vivo. Nature. 1993; 362:841–844. PMID: 7683111.
Article7. Blick SK, Scott LJ. Cetuximab: a review of its use in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck and metastatic colorectal cancer. Drugs. 2007; 67:2585–2607. PMID: 18034592.8. McCormack PL, Keam SJ. Bevacizumab: a review of its use in metastatic colorectal cancer. Drugs. 2008; 68:487–506. PMID: 18318567.9. Amado RG, Wolf M, Peeters M, Van Cutsem E, Siena S, Freeman DJ, et al. Wild-type KRAS is required for panitumumab efficacy in patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:1626–1634. PMID: 18316791.10. Karapetis CS, Khambata-Ford S, Jonker DJ, O'Callaghan CJ, Tu D, Tebbutt NC, et al. K-ras mutations and benefit from cetuximab in advanced colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008; 359:1757–1765. PMID: 18946061.11. Shankaran V, Luu TH, Nonzee N, Richey E, McKoy JM, Graff Zivin J, et al. Costs and cost effectiveness of a health care provider-directed intervention to promote colorectal cancer screening. J Clin Oncol. 2009; 27:5370–5375. PMID: 19826133.
Article12. Hurwitz H, Fehrenbacher L, Novotny W, Cartwright T, Hainsworth J, Heim W, et al. Bevacizumab plus irinotecan, fluorouracil, and leucovorin for metastatic colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2004; 350:2335–2342. PMID: 15175435.
Article13. Jubb AM, Pham TQ, Hanby AM, Frantz GD, Peale FV, Wu TD, et al. Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor, hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, and carbonic anhydrase IX in human tumours. J Clin Pathol. 2004; 57:504–512. PMID: 15113858.14. Kim SJ, Uehara H, Karashima T, Shepherd DL, Killion JJ, Fidler IJ. Blockade of epidermal growth factor receptor signaling in tumor cells and tumor-associated endothelial cells for therapy of androgen-independent human prostate cancer growing in the bone of nude mice. Clin Cancer Res. 2003; 9:1200–1210. PMID: 12631626.15. Ellis LM. Epidermal growth factor receptor in tumor angiogenesis. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 2004; 18:1007–1021. PMID: 15474332.
Article16. Chin L, Tam A, Pomerantz J, Wong M, Holash J, Bardeesy N, et al. Essential role for oncogenic Ras in tumour maintenance. Nature. 1999; 400:468–472. PMID: 10440378.
Article17. Rak J, Mitsuhashi Y, Bayko L, Filmus J, Shirasawa S, Sasazuki T, et al. Mutant ras oncogenes upregulate VEGF/VPF expression: implications for induction and inhibition of tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Res. 1995; 55:4575–4580. PMID: 7553632.18. Watnick RS, Cheng YN, Rangarajan A, Ince TA, Weinberg RA. Ras modulates Myc activity to repress thrombospondin-1 expression and increase tumor angiogenesis. Cancer Cell. 2003; 3:219–231. PMID: 12676581.
Article19. Jubb AM, Harris AL. Biomarkers to predict the clinical efficacy of bevacizumab in cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2010; 11:1172–1183. PMID: 21126687.
Article20. Rak J, Mitsuhashi Y, Sheehan C, Tamir A, Viloria-Petit A, Filmus J, et al. Oncogenes and tumor angiogenesis: differential modes of vascular endothelial growth factor up-regulation in ras-transformed epithelial cells and fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 2000; 60:490–498. PMID: 10667605.21. Price TJ, Hardingham JE, Lee CK, Weickhardt A, Townsend AR, Wrin JW, et al. Impact of KRAS and BRAF gene mutation status on outcomes from the Phase III AGITG MAX Trial of capecitabine alone or in Combination with bevacizumab and mitomycin in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011; 29:2675–2682. PMID: 21646616.
Article22. Reinacher-Schick A, Schulmann K, Modest DP, Bruns N, Graeven U, Jaworska M, et al. Effect of KRAS codon13 mutations in patients with advanced colorectal cancer (advanced CRC) under oxaliplatin containing chemotherapy: results from a translational study of the AIO colorectal study group. BMC Cancer. 2012; 12:349. PMID: 22876876.
Article23. Andreyev HJ, Norman AR, Cunningham D, Oates J, Dix BR, Iacopetta BJ, et al. Kirsten ras mutations in patients with colorectal cancer: the 'RASCAL II' study. Br J Cancer. 2001; 85:692–696. PMID: 11531254.24. Leslie A, Pratt NR, Gillespie K, Sales M, Kernohan NM, Smith G, et al. Mutations of APC, K-ras, and p53 are associated with specific chromosomal aberrations in colorectal adenocarcinomas. Cancer Res. 2003; 63:4656–4661. PMID: 12907646.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Impact of KRAS Mutation Status on Outcomes in Metastatic Colon Cancer Patients without Anti-Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor Therapy
- Can Serum be Used for Analyzing the KRAS Mutation Status in Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer?
- Systemic Therapy for Advanced and Metastatic Colon Cancer
- Magnetic Resonance-Based Texture Analysis Differentiating KRAS Mutation Status in Rectal Cancer
- Noonan Syndrome Confirmed to KRAS Gene Mutation: A Case of KRAS Gene Mutation