Cancer Res Treat.
2011 Sep;43(3):154-159.
Efficacy and Safety of Oxaliplatin, 5-Fluorouracil, and Folinic Acid Combination Chemotherapy as First-Line Treatment in Metastatic or Recurrent Gastric Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Cheonan Hospital, Cheonan, Korea.
- 2Divisions of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Bucheon Hospital, Bucheon, Korea. dshong@schmc.ac.kr
- 3Division of Hematology and Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Soonchunhyang University Seoul Hospital, Soonchunhyang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
We retrospectively determined the efficacy and safety of the combination of oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU), and folinic acid (FA) as first-line chemotherapy for patients with metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between January 2006 and August 2009, 39 patients with histologically-confirmed, metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer underwent chemotherapy, and the results were retrospectively investigated. The chemotherapy regimen consisted of oxaliplatin (100 mg/m2) and FA (200 mg/m2; 2-hour infusion), then 5-FU (2,400 mg/m2; 46-hour continuous infusion) every 2 weeks.
RESULTS
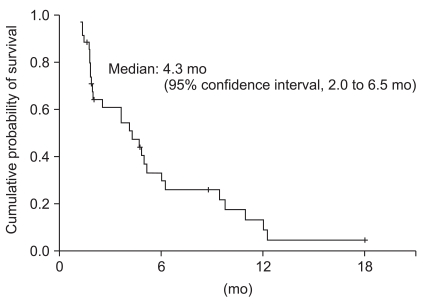
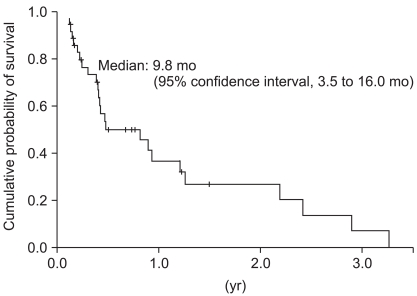
Thirty-nine patients received a total of 210 treatment cycles. The median number of cycles was 6 (range, 1 to 16). Of the 32 evaluable patients, zero patients achieved a complete response and 11 patients achieved a partial response (response rate, 28.2%). The median time-to-progression and overall survival were 4.3 months (95% confidence interval [CI], 2.0 to 6.5 months) and 9.8 months (95% CI, 3.5 to 16.0 months), respectively. The main hematologic toxicity was anemia, which was observed in 119 cycles (56.7%). Grade 3/4 neutropenia was observed in 32 cycles (15.2%). The main non-hematologic toxicity was constipation, which was observed in 91 cycles (46.2%). Peripheral neuropathy occurred in 71 cycles (33.8%); all cases were grade 1 or 2. No treatment-related deaths were reported.
CONCLUSION
This study showed that combination chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, 5-FU, and FA is an active and well-tolerated regimen as first-line treatment in patients with metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Pisters PW, Kelsen DP, Powell SM, Tepper JE. De Vita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer of the stomach. Cancer: principles and practice of oncology. 2005. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins;p. 909–944.2. Glimelius B, Ekström K, Hoffman K, Graf W, Sjödén PO, Haglund U, et al. Randomized comparison between chemotherapy plus best supportive care with best supportive care in advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 1997; 8:163–168. PMID: 9093725.
Article3. Ohtsu A. Chemotherapy for metastatic gastric cancer: past, present, and future. J Gastroenterol. 2008; 43:256–264. PMID: 18458840.
Article4. Waters JS, Norman A, Cunningham D, Scarffe JH, Webb A, Harper P, et al. Long-term survival after epirubicin, cisplatin and fluorouracil for gastric cancer: results of a randomized trial. Br J Cancer. 1999; 80:269–272. PMID: 10390007.
Article5. Vanhoefer U, Rougier P, Wilke H, Ducreux MP, Lacave AJ, Van Cutsem E, et al. Final results of a randomized phase III trial of sequential high-dose methotrexate, fluorouracil, and doxorubicin versus etoposide, leucovorin, and fluorouracil versus infusional fluorouracil and cisplatin in advanced gastric cancer: a trial of the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer Gastrointestinal Tract Cancer Cooperative Group. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:2648–2657. PMID: 10894863.
Article6. Arnould S, Hennebelle I, Canal P, Bugat R, Guichard S. Cellular determinants of oxaliplatin sensitivity in colon cancer cell lines. Eur J Cancer. 2003; 39:112–119. PMID: 12504667.
Article7. Marchetti P, Galla DA, Russo FP, Ricevuto E, Flati V, Porzio G, et al. Apoptosis induced by oxaliplatin in human colon cancer HCT15 cell line. Anticancer Res. 2004; 24:219–226. PMID: 15015600.8. Ravaioli A, Marangolo M, Pasquini E, Rossi A, Amadori D, Cruciani G, et al. Bolus fluorouracil and leucovorin with oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in metastatic colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:2545–2550. PMID: 12011134.
Article9. Extra JM, Espie M, Calvo F, Ferme C, Mignot L, Marty M. Phase I study of oxaliplatin in patients with advanced cancer. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1990; 25:299–303. PMID: 2295116.
Article10. Woynarowski JM, Faivre S, Herzig MC, Arnett B, Chapman WG, Trevino AV, et al. Oxaliplatin-induced damage of cellular DNA. Mol Pharmacol. 2000; 58:920–927. PMID: 11040038.
Article11. Schmidt W, Chaney SG. Role of carrier ligand in platinum resistance of human carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1993; 53:799–805. PMID: 8428361.12. Mamenta EL, Poma EE, Kaufmann WK, Delmastro DA, Grady HL, Chaney SG. Enhanced replicative bypass of platinum-DNA adducts in cisplatin-resistant human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res. 1994; 54:3500–3505. PMID: 8012973.13. Cunningham D, Starling N, Rao S, Iveson T, Nicolson M, Coxon F, et al. Capecitabine and oxaliplatin for advanced esophagogastric cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008; 358:36–46. PMID: 18172173.
Article14. Al-Batran SE, Hartmann JT, Probst S, Schmalenberg H, Hollerbach S, Hofheinz R, et al. Phase III trial in metastatic gastroesophageal adenocarcinoma with fluorouracil, leucovorin plus either oxaliplatin or cisplatin: a study of the Arbeitsgemeinschaft Internistische Onkologie. J Clin Oncol. 2008; 26:1435–1442. PMID: 18349393.
Article15. Louvet C, André T, Tigaud JM, Gamelin E, Douillard JY, Brunet R, et al. Phase II study of oxaliplatin, fluorouracil, and folinic acid in locally advanced or metastatic gastric cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 2002; 20:4543–4548. PMID: 12454110.
Article16. Al-Batran SE, Atmaca A, Hegewisch-Becker S, Jaeger D, Hahnfeld S, Rummel MJ, et al. Phase II trial of biweekly infusional fluorouracil, folinic acid, and oxaliplatin in patients with advanced gastric cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:658–663. PMID: 14966088.
Article17. Kim DY, Kim JH, Lee SH, Kim TY, Heo DS, Bang YJ, et al. Phase II study of oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in previously platinum-treated patients with advanced gastric cancer. Ann Oncol. 2003; 14:383–387. PMID: 12598342.
Article18. Chao Y, Yeh KH, Chang CJ, Chen LT, Chao TY, Wu MF, et al. Phase II study of weekly oxaliplatin and 24-h infusion of high-dose 5-fluorouracil and folinic acid in the treatment of advanced gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004; 91:453–458. PMID: 15226770.
Article19. Lordick F, Lorenzen S, Stollfuss J, Vehling-Kaiser U, Kullmann F, Hentrich M, et al. Phase II study of weekly oxaliplatin plus infusional fluorouracil and folinic acid (FUFOX regimen) as first-line treatment in metastatic gastric cancer. Br J Cancer. 2005; 93:190–194. PMID: 16012522.
Article20. Therasse P, Arbuck SG, Eisenhauer EA, Wanders J, Kaplan RS, Rubinstein L, et al. New guidelines to evaluate the response to treatment in solid tumors. European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer, National Cancer Institute of the United States, National Cancer Institute of Canada. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2000; 92:205–216. PMID: 10655437.21. Choi IS, Oh DY, Kim BS, Lee KW, Kim JH, Lee JS. Oxaliplatin, 5-FU, folinic acid as first-line palliative chemotherapy in elderly patients with metastatic or recurrent gastric cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2007; 39:99–103. PMID: 19746224.
Article22. Extra JM, Marty M, Brienza S, Misset JL. Pharmacokinetics and safety profile of oxaliplatin. Semin Oncol. 1998; 25(2 Suppl 5):13–22. PMID: 9609104.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Oxaliplatin, 5-FU, Folinic Acid as First-line Palliative Chemotherapy in Elderly Patients with Metastatic or Recurrent Gastric Cancer
- A Case of Autoimmune Hemolytic Anemia Caused by Repeated Administration of Oxaliplatin
- Chemotherapy for Colorecal Cancer
- A Retrospective Study of First-Line Combination Chemotherapy in Advanced Colorectal Cancer: A Korean Single-Center Experience
- Hypersensitivity Reactions to Oxaliplatin