Variability of Offending Allergens of Allergic Rhinitis According to Age: Optimization of Skin Prick Test Allergens
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Chosun University College of Medicine, Gwangju, Korea.
- 2Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. csrhee@snu.ac.kr
- 3Department of Otorhinolaryngology, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- 4Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Institute of Allergy and Clinical Immunology, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 6Sensory Organ Research Center, Seoul National University Medical Research Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 7Graduate School of Immunology, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2166931
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2014.6.1.47
Abstract
- PURPOSE
This study evaluates offending allergens in patients with allergic rhinitis (AR) according to age that establish a minimal panel for skin prick test (SPT) allergens required to identify if a patient is sensitized.
METHODS
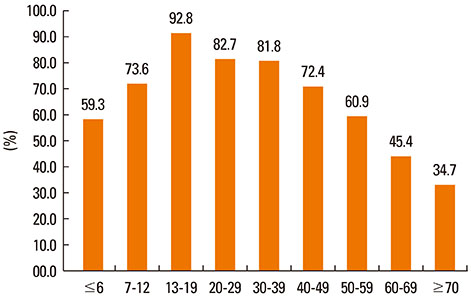
We retrospectively analyzed SPT results according to age to determine the minimum test battery panel necessary to screen at least 93%-95% of AR patients. Allergic skin tests (common airborne indoor and outdoor allergens) were performed on 7,182 patients from January 2007 to June 2011. All patients were classified into 9 groups according to age; subsequently, we investigated offending allergens by age group.
RESULTS
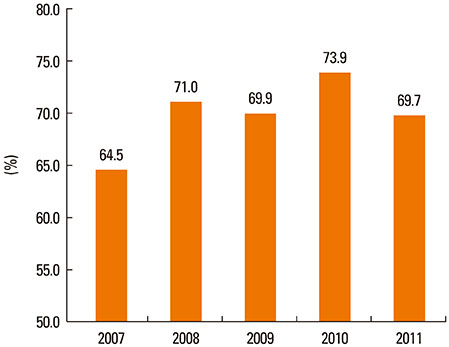
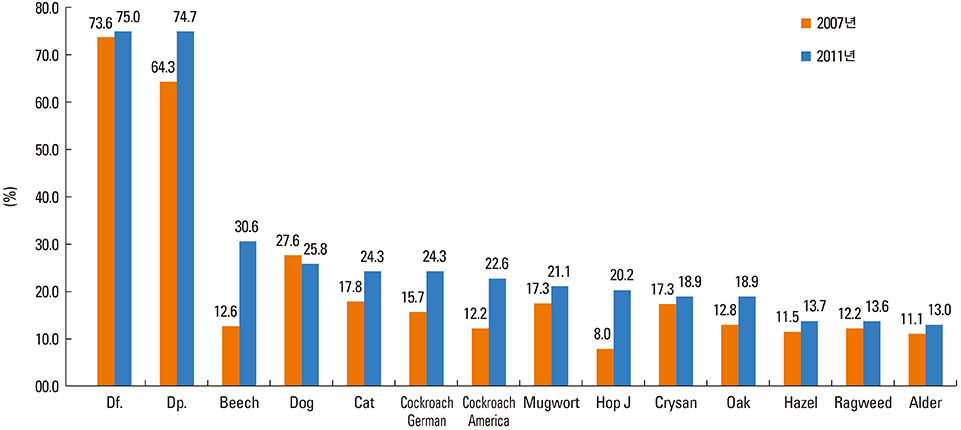
A total of 5,032 (70.1%) patients were found sensitized to at least one of the 55 aeroallergen extracts tested. The annual ranking of offending allergens was not significantly different from each other over the past 5 years. House dust mites (HDM) were the most prevalent allergens ranked from first to third for all 5 years. The allergens in the minimum test panel differed slightly among all age groups; in addition, the types of sensitized allergen sources were more diverse in the older versus younger age group. HDM covered a larger proportion of the sensitized allergens in the younger age group versus the older age group. Testing with 5 allergens (Dermatophagoides farinae, Tetranychus urticae, oak, mugwort and cockroach) adequately identified over 90% of the sensitized patients.
CONCLUSIONS
A SPT with around 5-7 allergens adequately detected most of the sensitization in the majority of the age groups in Korea. However, this study suggests that physicians perform the SPT with appropriately selected allergens in each age category for the screening of AR.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 10 articles
-
Clinical diagnostic guidelines for allergic rhinitis: diagnosis
Young Hyo Kim, Hyeon-Jong Yang, Jeong-Hee Choi, Dong-Kyu Kim, Young Yoo, Bora Lee, Mi-Ae Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Won-Young Kim, Jeong Hee Kim, Yang Park, So Yeon Park, Woo Yong Bae, Keejae Song, Min-Suk Yang, Sang Min Lee, Young-Mok Lee, Hyun Jong Lee, Jae-Hong Cho, Hye Mi Jee, Young-Il Koh,
J Korean Med Assoc. 2017;60(1):81-88. doi: 10.5124/jkma.2017.60.1.81.Identification of IgE binding components of two major weed pollens, ragweed and mugwort
Moon-Gyung Yoon, Mi-Ae Kim, Hyun-Jung Jin, Yoo-Seob Shin, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2014;2(5):337-343. doi: 10.4168/aard.2014.2.5.337.Clinical features of allergic rhinitis in Korean children
Jae Sook Kim, Hee Suk Kang, Hae Ji Jang, Jeong Hee Kim, Dae Hyun Lim, Byong Kwan Son
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(2):116-123. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.2.116.Changes in skin reactivity and associated factors in patients sensitized to house dust mites after 1 year of allergen-specific immunotherapy
Jeong-Yeop Son, Mann-Hong Jung, Kwang-Wook Koh, Eun-Kee Park, Jeong-Hoon Heo, Gil-Soon Choi, Hee-Kyoo Kim
Asia Pac Allergy. 2017;7(2):82-91. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2017.7.2.82.Unmet Primary Physicians' Needs for Allergic Rhinitis Care in Korea
Hyeon-Jong Yang, Young Hyo Kim, Bora Lee, Do Youn Kong, Dong-Kyu Kim, Mi-Ae Kim, Bong-Seong Kim, Won-young Kim, Jeong Hee Kim, Yang Park, So Yeon Park, Woo Yong Bae, Keejae Song, Min Suk Yang, Sang Min Lee, Young-Mok Lee, Hyun Jong Lee, Jae-Hong Cho, Hye Mi Jee, Jeong-Hee Choi, Young Yoo, Young-Il Koh,
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(3):265-271. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.3.265.Patterns of Inhalant Allergen Sensitization and Geographical Variation in Korean Adults: A Multicenter Retrospective Study
Min-Gyu Kang, Mi-Yeong Kim, Woo-Jung Song, Sujeong Kim, Eun-Jung Jo, Seung-Eun Lee, Jae-Woo Kwon, Sang-Min Lee, Chan-Sun Park, Hye-Kyung Park, Heung-Woo Park, Yoon-Seok Chang, Jaechun Lee, Young-Min Lee, Young-Koo Jee, Jong-Myung Lee, Inseon S. Choi, Sang-Heon Cho
Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2017;9(6):499-508. doi: 10.4168/aair.2017.9.6.499.Cross-allergenicity between dandelion and major weed pollens
Ji Hye Kim, Moon-Kyung Yoon, Mi-Ae Kim, Yoo-Seob Shin, Young Min Ye, Hae-Sim Park
Allergy Asthma Respir Dis. 2015;3(5):358-364. doi: 10.4168/aard.2015.3.5.358.The Relationship between the Causative Allergens of Allergic Diseases and Environments in Korea Over a 8-Year-Period: Based on Skin Prick Test from 2006 to 2015
Chan-Soon Park, Boo-Young Kim, Soo Whan Kim, Joo Hyung Lee, Soo Kweon Koo, Kyung-Su Kim, Seon Tae Kim, Yong-Dae Kim, Jeong Hong Kim, Jin Kook Kim, Chang Hoon Kim, Hyun Jun Kim, Hyo Yeol Kim, Ki-Sang Rha, Hwan-Jung Roh, Dong-Joon Park, Seung-Heon Shin, Sang-Chul Lim, Jae-Hoon Lee, Heung Man Lee, Heung Gu Lee, Young Ha Kim, Jin Hee Cho
J Rhinol. 2018;25(2):91-98. doi: 10.18787/jr.2018.25.2.91.Optimization of Allergen Panels for Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis
Jieun Lee, Jin Kook Kim, Kyung Soo Kim, Chae-Seo Rhee
Korean J Otorhinolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2019;62(11):609-616. doi: 10.3342/kjorl-hns.2019.00451.Long-term Breastfeeding in the Prevention of Allergic Rhinitis: Allergic Rhinitis Cohort Study for Kids (ARCO-Kids Study)
Doo Hee Han, Jae-Min Shin, Seokyung An, Jong Seung Kim, Dong-Young Kim, Sungji Moon, Jung-Soo Kim, Joong Saeng Cho, Si Whan Kim, Young Hyo Kim, Hwan-Jung Roh, Woo Sub Shim, Ki-Sang Rha, Sang-Wook Kim, Seung-Sin Lee, Dae Woo Kim, Kyu-Sup Cho, Hyo Jin Yim, Sue K. Park, Chae-Seo Rhee
Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol. 2019;12(3):301-307. doi: 10.21053/ceo.2018.01781.
Reference
-
1. Bousquet PJ, Burbach G, Heinzerling LM, Edenharter G, Bachert C, Bindslev-Jensen C, Bonini S, Bousquet-Rouanet L, Demoly P, Bresciani M, Bruno A, Gjomarkaj M, Canonica GW, Darsow U, Durham S, Fokkens WJ, Giavi S, Gramiccioni C, Papadopoulos NG, Haahtela T, Kowalski ML, Magyar P, Muraközi G, Orosz M, Röhnelt C, Stingl G, Todo-Bom A, von Mutius E, Wiesner A, Wöhrl S, Bousquet J, Zuberbier T. GA2LEN skin test study III: minimum battery of test inhalent allergens needed in epidemiological studies in patients. Allergy. 2009; 64:1656–1662.2. Bousquet PJ, Hooper R, Kogevinas M, Jarvis D, Burney P. Number of allergens to be tested to assess allergenic sensitization in epidemiologic studies: results of the European Community Respiratory Health Survey I. Clin Exp Allergy. 2007; 37:780–787.3. Heinzerling LM, Burbach GJ, Edenharter G, Bachert C, Bindslev-Jensen C, Bonini S, Bousquet J, Bousquet-Rouanet L, Bousquet PJ, Bresciani M, Bruno A, Burney P, Canonica GW, Darsow U, Demoly P, Durham S, Fokkens WJ, Giavi S, Gjomarkaj M, Gramiccioni C, Haahtela T, Kowalski ML, Magyar P, Muraközi G, Orosz M, Papadopoulos NG, Röhnelt C, Stingl G, Todo-Bom A, von Mutius E, Wiesner A, Wöhrl S, Zuberbier T. GA(2)LEN skin test study I: GA(2)LEN harmonization of skin prick testing: novel sensitization patterns for inhalant allergens in Europe. Allergy. 2009; 64:1498–1506.4. Bousquet PJ, Chatzi L, Jarvis D, Burney P. Assessing skin prick tests reliability in ECRHS-I. Allergy. 2008; 63:341–346.5. Burney PG, Luczynska C, Chinn S, Jarvis D. The European Community Respiratory Health Survey. Eur Respir J. 1994; 7:954–960.6. Zureik M, Neukirch C, Leynaert B, Liard R, Bousquet J, Neukirch F. European Community Respiratory Health Survey. Sensitisation to airborne moulds and severity of asthma: cross sectional study from European Community Respiratory Health Survey. BMJ. 2002; 325:411–414.7. Eun YG, Kim SW, Lee IY, Cho JS. Cockroach allergic rhinitis in the urban area in Korea: sensitivity and diagnosis. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 2004; 47:747–750.8. Bang JH, Kim YJ, Shin HS, Lee BJ. Clinical analysis of allergic rhinitis in Seoul. Korean J Rhinol. 1996; 3:130–134.9. Ko YH, Park SY, Lee JH, Koo GJ, Koo SK, Lee SH, Kim SW. A clinical statistics on the offending allergens of allergic rhinitis. Korean J Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg. 1998; 41:42–47.10. Şahiner UM, Civelek E, Yavuz ST, Büyüktiryaki AB, Tuncer A, Şekerel BE. Skin prick testing to aeroallergen extracts: what is the optimal panel in children and adolescents in Turkey? Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2012; 157:391–398.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Allergic Skin Prick Test and FAST System in Patients with Allergic Rhinitis
- A Clinical Statistics on the Offending Allergens of Allergic Rhinitis
- Correlation between MAST, the skin prick test, and the nasal provocation test in patients with allergic rhinitis
- Comparison of MAST Chemiluminescent Assay(MAST-CLA) with Skin Prick, Test in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis
- Optimization of Allergen Panels for Diagnosis of Allergic Rhinitis