Healthc Inform Res.
2015 Oct;21(4):283-291. 10.4258/hir.2015.21.4.283.
Fifteen-year Experience with Telemedicine Services in Gangwon Province in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Emergency Medicine, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea. mooeob@gmail.com
- 2Gangwon Telemedicine Center, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 3Department of Emergency Medicine, Graduate School, Hallym University, Chuncheon, Korea.
- 4Department of Physical Medicine and Rehabilitation, Hallym University Chuncheon Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Chuncheon, Korea.
- KMID: 2166878
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4258/hir.2015.21.4.283
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
This study attempted to identify the factors that contribute to successful telemedicine service. This was done by analyzing the operational state of successful telemedicine services offered in Gangwon Province of Korea and their outcome for the last fifteen years.
METHODS
A comparative analysis was made based on reports and a thesis on the satisfaction rate of patients and providers, patient compliance to treatment, and economic assessment of Gangwon telemedicine service, which were carried out in three periods: the years 2006, 2010, and 2012.
RESULTS
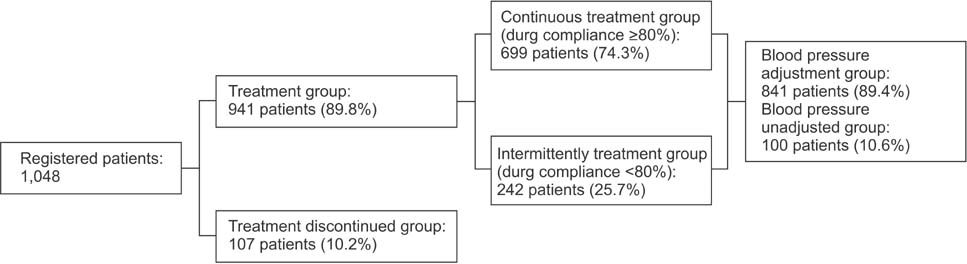
The satisfaction surveys in all three periods showed similar results for patients (4.46+/-0.70 point) and healthcare practitioners, including nurses (3.82+/-0.62 point) and physicians (3.60+/-0.56 point), in decreasing order from the year 2012. Through the survey of patients' compliance with treatment, it was confirmed that telemedicine services increased patients' compliance with drug administration, facilitated improvement of lifestyle habits, improved glycated hemoglobin for patients with diabetes mellitus, and enhanced the rate of blood pressure control. In the survey conducted on patients' willingness to pay for telemedicine services in 2007, it was found that those patients were willing to pay about $3.5 for services.
CONCLUSIONS
The telemedicine services of Gangwon Province increased patients' compliance with drug administration, improved blood glucose control, enhanced blood pressure control for patients with hypertension, and provided economic advantage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
High Time to Discuss Future-Oriented Telemedicine
In Ho Kwon
Healthc Inform Res. 2015;21(4):211-212. doi: 10.4258/hir.2015.21.4.211.
Reference
-
1. Gangwon Province. 6th Gangwon regional health plan. Gangwon, Korea: Gangwon Province;2014.2. Ahn ME, Park KS, Han JH, Shin SG. The guide of Gangwon Telemedicine System. Gangwon, Korea: Health Policy Department;2015.3. Ahn ME, Han JH. The operational performance of the Gangwon u-health service. Gangwon, Korea: Hallym University Telemedicine Center;2013.4. Ryu SW, Rhee HS, Lee KH, Yoon JY. The evaluation of situation and performance of Gangwon Telemedicine System. Seoul, Korea: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs;2006.5. Lee YT, Park JS, Kwak MS, Kim JY, Park SB, Lee KI. A pilot project comprehensive assessment for the application of the u-Health service in 2010. Seoul, Korea: Korea Health Industry Development Institute;2010.6. Jang MH. The influence of telemedicine service system on diabetes care [dissertation]. Chuncheon, Korea: Hallym University;2008.7. Kim KH, Lee MO, Lee JK, Ryu SW. Compliance of hypertensive patients registered in primary health care posts implementing the Gangwon telemedicine service system. J Korean Soc Health Inf Health Stat. 2008; 33:59–76.8. Kim SJ, Moon OR, Ahn ME, Ryu SW. Estimating the willingness-to-pay for telehealth services of chronic disease in rural area. J Korean Soc Health Inf Health Stat. 2007; 32(1):17–31.9. Lee YT, Park JS, Kang DW, Kim SY, Ryu SW, Park DK, et al. A pilot project comprehensive assessment for the application of the u-Health service. Seoul, Korea: Korea Health Industry Development Institute;2009.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Satisfaction Survey of Telemedicine Services for the Patients With Dementia in the Vulnerable Area for Medical Service
- Survey study of telemedicine-experienced physicians on the acceptability of telemedicine: using propensity score matching method
- A debate about telemedicine in South Korea
- Changes in Public Health Perceptios after the Outbreak of Coronavirus Disease-19 among the Gangwon Province Residents Focusing on the Results of the Gangwon Province Residents’ Panel Survey 2019-2020
- The general public’s perspectives on telemedicine during the COVID-19 pandemic in Korea: analysis of a nationwide survey