Cancer Res Treat.
2004 Aug;36(4):240-245.
Prognostic Significance of Immunohistochemical Expression of EGFR and C-erbB-2 Oncoprotein in Curatively Resected Gastric Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. shs7436@dsmc.or.kr
- 2Department of General Surgery, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea.
Abstract
- PURPOSE
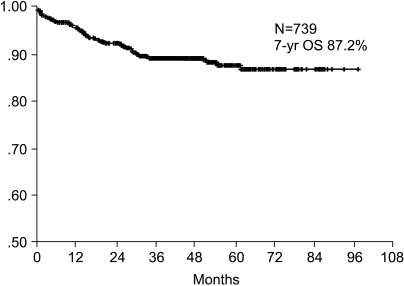
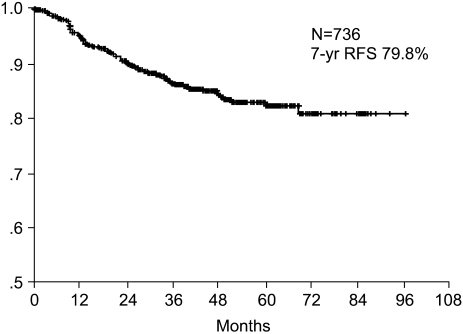
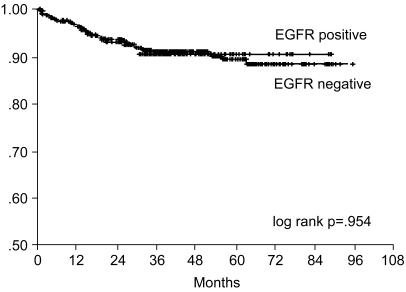
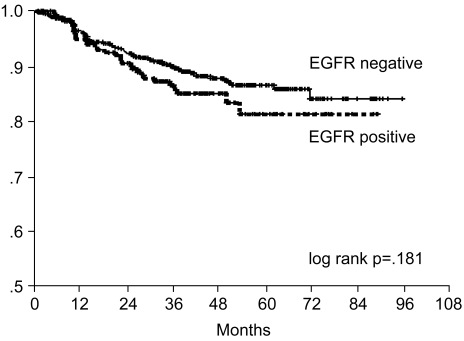
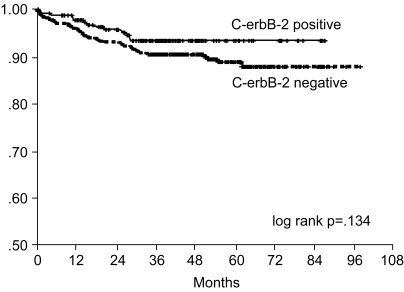
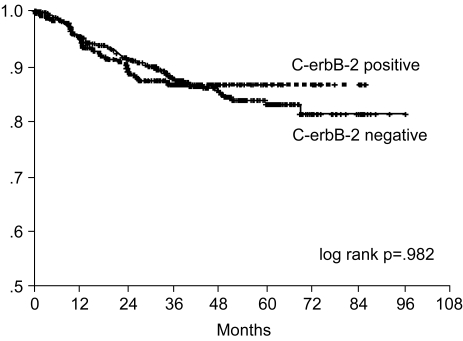
The purpose of this study was to investigate the prognostic significance of the expression of EGFR and C-erbB-2 gene products by immunohistochemical analysis for curatively resected gastric adenocarcinoma. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Between January 1996 and December 2001, 739 patients with curatively resected gastric cancer patients underwent Immunohistochemical staining for EGFR and C-erbB-2 proteins, and we retro spectively analyzed their correlation with the clinical outcome. RESULTS: The overexpressions of EGFR and C-erbB-2 were 25.4% and 26.2%, respectively. The overexpressions of EGFR was associated with the more poorly differentiated tumor (p=0.000) and with neuronal invasion (p=0.03). Overexpression of C-erbB-2 was associated with less vascular invasion (p=0.001). Tumor depth or node metastasis was not related to the overexpression of EGFR or C-erbB-2. The seven-year overall survival and relapse-free survival rates were 87.2% and 75.8%, respectively. Upon multivariate Cox regression analysis, the tumor stage, tumor size and patient age were important prognostic factors for overall survival, and tumor stage was the important factor for relapse-free survival. Overexpressions of EGFR or c-erbB-2 were not significant prognostic factors. CONCLUSION: Immunohistochemical staining of EGFR and C-erbB-2 gene products were not independent prognostic factors for predicting the overall survival and the relapse-free survival in curatively resected gastric cancer.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Korea National Statistical Office. Annual report on the cause of death statistics (based on vital registration). 2001. p. 14–15.2. Lee CW, Lee MY, Lim HS, Sohn SS, Jeon JK. Cancer incidence in Daegu in 1997-1998: the first results of the SDaegu Cancer Registry. J Korean Cancer Assoc. 2001; 33:136–148.3. Cancer registry system in Korea. Headquarter of Korea Central Cancer Registry. Available from: URL:http://www.ncc.re.kr.4. Garcia I, Vizoso F, Andicoechea A, Raigoso P, Verez P, Alexandre E, Garcia-Muniz JL, Allende MT. Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor receptor content in gastric cancer. Int J Biol Markers. 2001; 16:183–188. PMID: 11605731.
Article5. Kopp R, Ruge M, Rothbauer E, Cramer C, Kraemling HJ, Wiebeck B, Schildberg FW, Pfeiffer A. Impact of epifermal growth factor (EGF) radioreceptor analysis on long-term survival of gastric cancer patients. Anticancer Res. 2002; 22:1161–1167. PMID: 12168918.6. Takehara T, Kunitomo K, Kono K, Kitahara F, Lizuka H, Matsumoto Y, Fujino MA, Ooi A. Status of c-erbB-2 in gastric adenocarcinoma: a comparative study of immunohistochemistry, fluorescence in situ hybridization and enzyme- linked immunosorbennt assay. Int J Cancer. 2002; 98:833–837. PMID: 11948459.7. Baselga J, Tripathy D, Mendelsohn J, Baughman S, Benz CC, Dantis L, Sklarin NT, Seidman AD, Hudis CA, Moore J, Rose PP, Twaddell T, Henderson IC, Norton L. Phase II study of weekly intravenous trastuzumab (Herceptin) in patients with HER2/neu-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Semin Oncol. 1999; 26:78–83. PMID: 10482197.8. American Joint Committee on Cancer. AJCC cancer staging manual. 1997. 5th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;p. 71–76.9. Kaplan EL, Meier P. Nonparametric estimation for incomplete observations. J Am Statist Assoc. 1958; 53:457–481.10. Mantel N, Haenszel W. Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of disease. J Nat Cancer Inst. 1959; 22:719–748. PMID: 13655060.11. Cox DR. Regression models and life tables. J Roy Stat Soc. 1972; 34:187–220.12. Tokunaga A, Onda M, Okuda T, Teramoto T, Fujita I, Mizutani T, Kiyama T, Yoshiyuki T, Nishi K, Mtsukura N. Clinical significance of epidermal growth factor (EGF), EGF receptor, and c-erbB-2 in human gastric cancer. Cancer. 1995; 75:1418–1425. PMID: 7889468.
Article13. Bae CD, Juhnn YS, Park JB. Post-translational control of c-erb B-2 overexpression in stomach cancer cells. Exp Mol Med. 2001; 33:15–19. PMID: 11322480.14. Lemoine NR, Jain S, Silvestre F, Lopes C, Huches CM, McLelland E, Gullick WJ, Filipe MI. Amplification and overexpression of the EGF receptor and C-erbB-2 proto- oncogenes in human stomach cancer. Br J Cancer. 1991; 64:79–83. PMID: 1677259.15. Shun CT, Wu MS, Lin JT, Chen SY, Wang HP, Lee WJ, Wang TH, Chuang SM. Relationship of p53 and c-erbB-2 expression to histological features. Helicobacter pylori infec tion and prognosis in gastric cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997; 44:604–609. PMID: 9164544.16. Yonemura Y, Ninomiya I, Yamaguchi A, Fushida S, Kimura H, Ohoyama S, Miyazaki I, Endou Y, Tanaka M, Sasaki T. Evaluation of immunoreactivity for erbB-2 protein as a marker of poor short term prognosis in gastric cancer. Cancer Res. 1991; 51:1034–1038. PMID: 1670998.17. Santoro E, Carboni M, Catarci M, Carlini M, Carboni F, Zupi G, Vecchione A, D'Agnano I, Giannarelli D, Santoro R, Farofalo A. DNA ploidy, proliferative index and EGF-R status in 130 cases of resected gastric cancer- a multivariate analysis. Hepatogastroenterology. 1997; 44:826–837. PMID: 9222700.18. Falck VG, Gullick WJ. c-erbB-2 oncogene product staining in gastric adenocarcinoma. An immunohistochemical study. J Pathol. 1989; 159:107–111. PMID: 2572685.
Article19. Yokota J, Yamamoto T, Miyajima N, Toyoshima K, Nomura N, Sakamoto H, Yoshida T, Terada M, Sugimura T. Genetic alterations of the c-erb2 oncogene occur frequently in tubular adenocarcinoma of the stomach and are often accompanied by amplification of the v-erbA homologue. Oncogene. 1988; 2:283–287. PMID: 3281095.20. Motojima K, Furui J, Kohara N, Izawa K, Kanematsu T, Shiku H. erbB-2 expression in well-differentiated adenocarcinoma of the stomach predicts shorter survival after curative resection. Surgery. 1994; 115:349–354. PMID: 7907434.21. Koullias GJ, Kouraklis GP, Raftopoulos IS, Davaris PS, Papadopoulos SA, Golematis BC. Increased estrogen receptor and epidermal growth factor receptor gene product co- expression in surgically resected gastric adenocarcinomas. J Surg Oncol. 1996; 63:166–171. PMID: 8944060.22. Sanz-Ortega J, Steinberg SM, Moro E, Saez M, Lopez JA, Sierra E, Sanz-Esponera J, Merino MJ. Comparative study of tumor angiogenesis and immunohistochemistry for p53, c-ErbB2, c-myc and EGFr as prognostic factors in gastric cancer. Histol Histopathol. 2000; 15:455–462. PMID: 10809364.23. Mizutani T, Onda M, Tokunaga A, Yamanaka N, Sugisaki Y. Relationship of C-erbB-2 protein expression and gene amplification to invasion and metastasis in human gastric cancer. Cancer. 1993; 72:2083–2088. PMID: 8397058.
Article24. Kim JP, Oh ST, Hwang TS, Chi JG. The prognostic significance of c-erbB-2 and p53 protein expressions in gastric carcinoma-a multivariate analysis of prognostic factors. J Korean Med Sci. 1994; 9:248–253. PMID: 7993593.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Study of the Correlation between Expression of c-erbB-2 Oncoprotein and Various Clinicopathological Prognostic Factors in Breast Carcinoma
- c-erbB-2 Oncoprotein Expression in Ductal Carcinoma in situ and Paget's Disease of the Breast
- The Significance of C-erbB-2 Oncoprotein Expression as a Prognostic Predictor in Human Breast Cancer
- Rarity of EGFR and c-ErbB-2 Overexpressions in Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Immunohistochemical Study
- Comparison of c-erbB-2 Oncoprotein Expression in Serum and Tissue of Gastric Cancer Patients