Cancer Res Treat.
2005 Oct;37(5):284-289.
Combination Chemotherapy of Oxaliplatin, 5-Fluorouracil and Low Dose Leucovorin in Patients with Advanced Colorectal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chungbuk National University College of Medicine, Cheongju, Korea. kihlee@chungbuk. ac.kr
Abstract
- PURPOSE
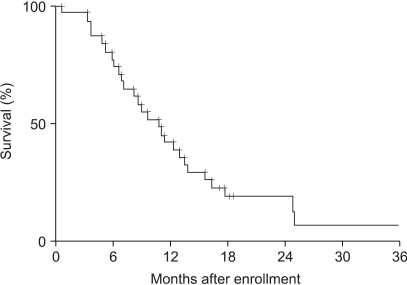
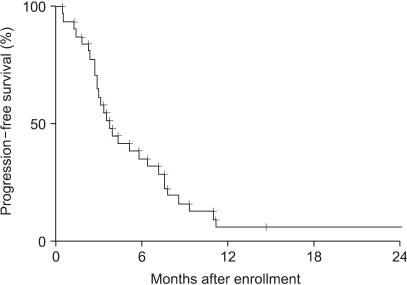
The aim of this study was to evaluate the efficacy and tolerability of the oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil (5-FU) and low dose leucovorin (LV) combination in patients with advanced colorectal cancer. MATERIALS AND METHODS: Patients with unresectable or recurrent colorectal carcinomas were prospectively accrued. Up to one prior chemotherapy regimen was allowed. Patients received oxaliplatin, 85 mg/m2, administered as a 2-hour infusion on day 1, followed by LV, 20 mg/m2, as a bolus and 5-FU, 1, 500 mg/m2, via continuous infusion for 24 hours on days 1 and 2. Treatment was repeated every 2 weeks until disease progression or adverse effects prohibited further therapy. RESULTS: Between August 1999 and May 2004, 31 patients were enrolled in this study. Of the patients enrolled, 24 and 31 were evaluable for tumor response and survival analysis, respectively. The patients' characteristics included a median age of 59, with 6 (19%) having had prior chemotherapy. No patient achieved a complete response, but nine (38%) attained a partial response. Seven (29%) patients maintained a stable disease and 8 (33%) experienced increasing disease. The median duration of the response was 6 months. After a median follow-up of 9.6 months, the median time to progression was 3.8 months, with a median survival of 10.7 months. The hematological toxicities were mild to moderate, with no treatment-related mortality or infection. The major non-hematological toxicity was gastrointestinal toxicity. CONCLUSIONS: The combination chemotherapy of oxaliplatin, low dose LV and continuous infusion of 5-FU is safe and has a cost-benefit, but is a moderately effective regimen in advanced colorectal cancer. A randomized trial comparing low and high dosages of leucovorin in the FOLFOX regimen is warranted.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Parkin DM, Bray F, Ferlay J, Pisani P. Global cancer statistics, 2002. CA Cancer J Clin. 2005; 55:74–108. PMID: 15761078.
Article2. Bae JM, Won YJ, Jung KW, Park JG. Annual report of the Korean central cancer registry program 2000: Based on registered data from 131 hospitals. Cancer Res Treat. 2002; 34:77–83.3. American Cancer Society. Cancer facts and figures: 1995. 1995. Atlanta, GA: American Cancer Society.4. Cunningham D, Pyrhonen S, James RD, Punt CJ, Hickish TF, Heikkila R, et al. Randomised trial of irinotecan plus supportive care versus supportive care alone after fluorouracil failure for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Lancet. 1998; 352:1413–1418. PMID: 9807987.
Article5. Palliative chemotherapy for advanced or metastatic colorectal cancer: Colorectal Meta-analysis Collaboration. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2000; 2:CD001545. PMID: 10796809.6. Park JY, Kim SY, Lee JJ, Yoon HJ, Cho KS. The efficacy of a modified chronomodulated infusion of oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin in advanced colorectal cancer (preliminary data). Cancer Res Treat. 2004; 36:199–204.
Article7. Thirion P, Michiels S, Pignon JP, Buyse M, Braud AC, Carlson RW, et al. Modulation of fluorouracil by leucovorin in patients with advanced colorectal cancer: An updated meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2004; 22:3766–3775. PMID: 15365073.8. Pendyala L, Creaven PJ. In vitro cytotoxicity, protein binding, red blood cell partitioning, and biotransformation of oxaliplatin. Cancer Res. 1993; 53:5970–5976. PMID: 8261411.9. Mathe G, Kidani Y, Segiguchi M, Eriguchi M, Fredj G, Peytavin G, et al. Oxalato-platinum or I-OHP, a third generation platinum complex: An experimental and clinical appraisal and preliminary comparison with cisplatinum and carboplatinum. Biomed Pharmacother. 1989; 43:237–250. PMID: 2675999.10. Levi F, Perpoint B, Garufi C, Focan C, Chollet P, Depres-Brummer P, et al. Oxaliplatin activity against metastatic colorectal cancer: A phase II study of 5-day continuous venous infusion at circadian rhythm modulated rate. Eur J Cancer. 1993; 29:1280–1284. PMID: 8343268.
Article11. Becouarn Y, Ychou M, Ducreux M, Borel C, Bertheault-Cvitkovic F, Seitz JF, et al. Digestive Group of French Federation of Cancer Centers. Phase II trial of oxaliplatin as first-line chemotherapy in metastatic colorectal cancer patients. J Clin Oncol. 1998; 16:2739–2744. PMID: 9704726.12. Diaz-Rubio E, Sastre J, Zaniboni A, Labianca R, Cortes-Funes H, de Braud F, et al. Oxaliplatin as a single agent in previously untreated colorectal carcinoma patients: A phase II multicentric study. Ann Oncol. 1998; 9:105–108. PMID: 9541691.13. Kim SY. Oxaliplatin: Is it a new standard weapon for colorectal cancer? Cancer Res Treat. 2004; 36:91–92.
Article14. Food and Drug Administration. Eloxatin: New or modified indication. 2004. Washington, DC: US Food and Drug Administration.15. Maindrault-Goebel F, de Gramont A, Louvet C, Andre T, Carola E, Mabro M, et al. High-dose intensity oxaliplatin added to the simplified bimonthly leucovorin and 5-fluorouracil regimen as second-line therapy for metastatic colorectal cancer (FOLFOX 7). Eur J Cancer. 2001; 37:1000–1005. PMID: 11334725.16. Meyerhardt JA, Mayer RJ. Systemic therapy for colorectal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2005; 352:476–487. PMID: 15689586.
Article17. QUASAR Collaborative Group. Comparison of flourouracil with additional levamisole, higher-dose folinic acid, or both, as adjuvant chemotherapy for colorectal cancer: a randomised trial. Lancet. 2000; 355:1588–1596. PMID: 10821362.18. Libutti SK, Saltz LB, Rustgi AK, Tepper JE. DeVita VT, Hellman S, Rosenberg SA, editors. Cancer of the colon. Cancer, Principles and practice of oncology. 2005. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Lippincott-Raven;p. 1061–1109.19. de Gramont A, Figer A, Seymour M, Homerin M, Hmissi A, Cassidy J, et al. Leucovorin and fluorouracil with or without oxaliplatin as first-line treatment in advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2000; 18:2938–2947. PMID: 10944126.
Article20. Goldstein D, Mitchell P, Micael M, Beale P, Friedlander M, Zalcber J, et al. Australian experience of a modified schedule of FOLFOX with high activity and tolerability and improved convenience in untreated metastatic colorectal cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2005; 92:832–837. PMID: 15756253.
Article21. Buroker TR, O'Connell MJ, Wieand HS, Krook JE, Gerstner JB, Mailliard JA, et al. Randomized comparison of two schedules of fluorouracil and leucovorin in the treatment of advanced colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 1994; 12:14–20. PMID: 7677801.
Article22. Leichman CG, Fleming TR, Muggia FM, Tangen CM, Ardalan B, Doroshow JH, et al. Phase II study of fluorouracil and its modulation in advanced colorectal cancer: a Southwest Oncology Group study. J Clin Oncol. 1995; 13:1303–1311. PMID: 7751875.
Article23. Sobrero AF, Aschele C, Bertino JR. Fluorouracil in colorectal cancer: A tale of two drugs-implications for biochemical modulation. J Clin Oncol. 1997; 15:368–381. PMID: 8996164.24. Kwon HC, Kim KT, Lee SA, Park JS, Kim SH, Kim JS, et al. Oxaliplatin with biweekly, low dose leucovorin and bolus and continuous infusion 5-fluorouracil (modified FOLFOX 4) as first-line therapy for patients with metastatic colorectal cancer. Cancer Res Treat. 2004; 36:115–120.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- 5-fluorouracil and low dose leucovorin combination chemotherapy for metastatic or recurrent colorectal cancer
- Diffuse alveolar damage during chemotherapy with oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil and leucovorin
- Pulmonary Fibrosis Under Chemotherapy with Oxaliplatin, 5-fluorouracil, and Leucovorin
- 5-fluorouracil and low dose leucovorin in advanced colorectal carcinoma
- Oxaliplatin/5-FU without Leucovorin Chemotherapy in Metastatic Colorectal Cancer