Ann Rehabil Med.
2013 Apr;37(2):191-201. 10.5535/arm.2013.37.2.191.
Effect of Medial Branch Block in Chronic Facet Joint Pain for Osteoporotic Compression Fracture: One Year Retrospective Study
- Affiliations
-
- 1Deaprement of Rehabilitation Medicine, Gil Hospital, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Health & Fitness Management, Namseoul University, Cheonan, Korea.
- 3Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Roihospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, SRC Hospital, Gwangju, Korea.
- 5Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, National Health Insurance Corporation Ilsan Hospital, Goyang, Korea.
- 6Department of Rehabilitation Medicine, Inje University Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. swc328@naver.com
- KMID: 2165770
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5535/arm.2013.37.2.191
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
To evaluate the outcomes of medial branch block in facet joint pain for osteoporotic compression fracture and utilize multiple regression, the relationship between their impact on treatment outcome and other factor, such as the radiologic finding, clinical parameters was analyze.
METHODS
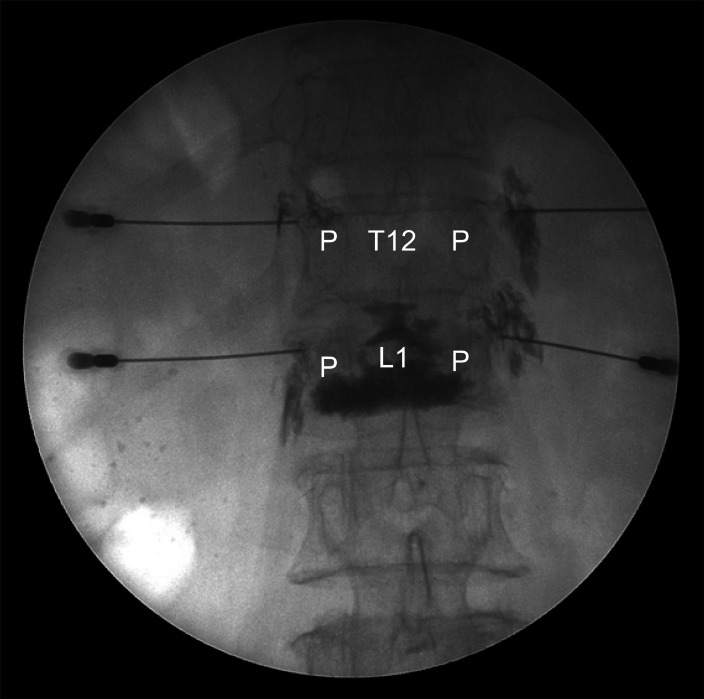
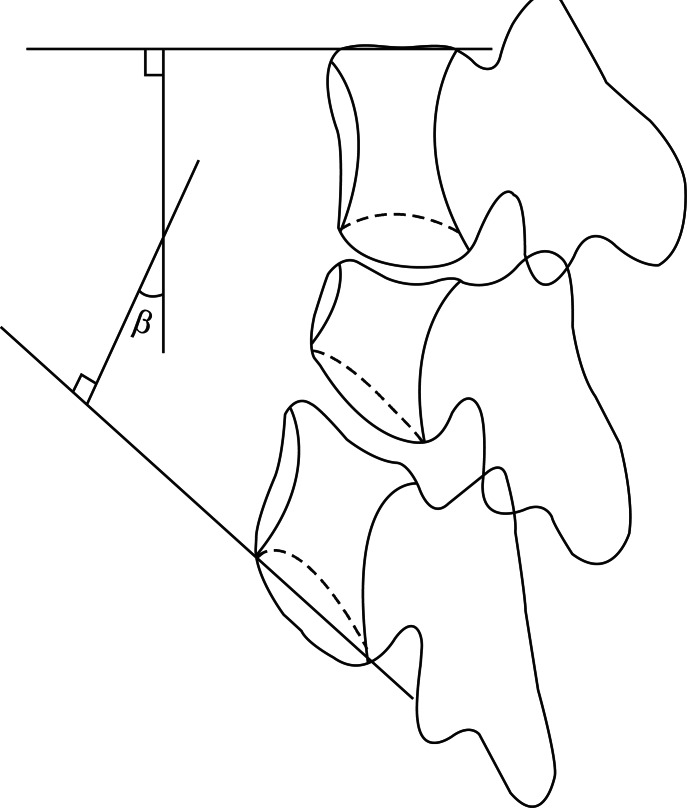
Fifty-three patients with axial back pain from osteoporotic compression fracture were enrolled. The clinical outcomes were measured by Verbal Numeric Rating Scale (VNS) and Oswestry Disability Index (ODI) before treatment, 2 weeks, 3 months, and 12 months after the medial branch block. Radiographic analysis included measurement of overall sagittal alignment, collapsed vertebral height, and vertebral kyphotic angle. After 12 months, patients' satisfaction was classified to five categories: excellent, good, fair, poor or fail. Statistical analysis of both radiographic and clinical parameters along with treatment outcome was performed to determine any significant correlations between the two.
RESULTS
VNS and ODI was improved 2 weeks after the injection and continued to improve until 12 months. Significant improvement with significant pain relief (>40%), functional improvement (>20%), and the patients rated their satisfaction level as "excellent" or "good" at 12 months after the first injection were observed in 78.9%. The radiographic and clinical parameters were not significantly correlated with treatment outcome.
CONCLUSION
Our retrospective study demonstrated that the medial branch block provided significant pain relief and functional recovery to the patients with osteoporotic spinal compression fractures complaining of continuous facet joint pain after vertebroplasty or conservative treatment. A placebo-controlled prospective randomized double-blind study should be conducted in the future to evaluate the treatment effects.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
The Validation of Ultrasound-Guided Target Segment Identification in Thoracic Spine as Confirmed by Fluoroscopy
Ju-Yeong Heo, Ji-Won Lee, Cheol-Hwan Kim, Sang-Min Lee, Yong-Soo Choi
Clin Orthop Surg. 2017;9(4):472-479. doi: 10.4055/cios.2017.9.4.472.
Reference
-
1. Bernstein J, Lane JM. Rothman RH, Siemone FA, editors. Metabolic disorders of the spine. The spine. 1992. 3rd ed. Philadelphia: WB Saunders;p. 1393–1394.2. Rapado A. General management of vertebral fractures. Bone. 1996; 18(3 Suppl):191S–196S. PMID: 8777087.
Article3. Watts NB, Harris ST, Genant HK. Treatment of painful osteoporotic vertebral fractures with percutaneous vertebroplasty or kyphoplasty. Osteoporos Int. 2001; 12:429–437. PMID: 11446557.
Article4. Garfin SR, Yuan HA, Reiley MA. New technologies in spine: kyphoplasty and vertebroplasty for the treatment of painful osteoporotic compression fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001; 26:1511–1515. PMID: 11462078.5. Mitra R, Do H, Alamin T, Cheng I. Facet pain in thoracic compression fractures. Pain Med. 2010; 11:1674–1677. PMID: 21029349.
Article6. Georgy BA. Interventional techniques in managing persistent pain after vertebral augmentation procedures: a retrospective evaluation. Pain Physician. 2007; 10:673–676. PMID: 17876364.7. Bogduk N. Evidence-informed management of chronic low back pain with facet injections and radiofrequency neurotomy. Spine J. 2008; 8:56–64. PMID: 18164454.
Article8. Bogduk N. Practice guidelines for spinal diagnostic and treatment procedures. 2004. 1st ed. San Francisco: International Spinal Intervention Society;p. 47–65.9. Bogduk N, Wilson AS, Tynan W. The human lumbar dorsal rami. J Anat. 1982; 134(Pt 2):383–397. PMID: 7076562.10. Bogduk N. The innervation of the lumbar spine. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1983; 8:286–293. PMID: 6226119.
Article11. Boswell MV, Shah RV, Everett CR, Sehgal N, McKenzie Brown AM, Abdi S, et al. Interventional techniques in the management of chronic spinal pain: evidence-based practice guidelines. Pain Physician. 2005; 8:1–47. PMID: 16850041.12. Manchikanti L, Staats PS, Singh V, Schultz DM, Vilims BD, Jasper JF, et al. Evidence-based practice guidelines for interventional techniques in the management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2003; 6:3–81. PMID: 16878163.13. Manchikanti L, Manchikanti KN, Manchukonda R, Pampati V, Cash KA. Evaluation of therapeutic thoracic medial branch block effectiveness in chronic thoracic pain: a prospective outcome study with minimum 1-year follow up. Pain Physician. 2006; 9:97–105. PMID: 16703969.14. Kim KT, Lee SH, Suk KS, Lee JH, Im YS, Seo EM. Loss of sagittal balance and clinical outcomes following corrective osteotomy for lumbar degenerative kyphosis. J Korean Orthop Assoc. 2009; 44:83–92.
Article15. Fairbank JC, Couper J, Davies JB, O'Brien JP. The Oswestry low back pain disability questionnaire. Physiotherapy. 1980; 66:271–273. PMID: 6450426.16. Lee IS, Kim SH, Lee JW, Hong SH, Choi JY, Kang HS, et al. Comparison of the temporary diagnostic relief of transforaminal epidural steroid injection approaches: conventional versus posterolateral technique. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 28:204–208. PMID: 17296980.17. Ng L, Chaudhary N, Sell P. The efficacy of corticosteroids in periradicular infiltration for chronic radicular pain: a randomized, double-blind, controlled trial. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005; 30:857–862. PMID: 15834326.18. Campbell WI, Kendrick RW. Pre-emptive analgesia using local anaesthesia: a study in bilaterally symmetrical surgery. Br J Anaesth. 1997; 79:657–659. PMID: 9422907.
Article19. Nam HS, Park YB. Effects of transforaminal injection for degenerative lumbar scoliosis combined with spinal stenosis. Ann Rehabil Med. 2011; 35:514–523. PMID: 22506167.
Article20. Ledlie JT, Renfro M. Balloon kyphoplasty: one-year outcomes in vertebral body height restoration, chronic pain, and activity levels. J Neurosurg. 2003; 98(1 Suppl):36–42. PMID: 12546386.
Article21. Beaman DN, Graziano GP, Glover RA, Wojtys EM, Chang V. Substance P innervation of lumbar spine facet joints. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1993; 18:1044–1049. PMID: 7690159.
Article22. Kim TK, Kim KH, Kim CH, Shin SW, Kwon JY, Kim HK, et al. Percutaneous vertebroplasty and facet joint block. J Korean Med Sci. 2005; 20:1023–1028. PMID: 16361816.
Article23. Manchikanti L, Singh V, Falco FJ, Cash KA, Pampati V. Lumbar facet joint nerve blocks in managing chronic facet joint pain: one-year follow-up of a randomized, double-blind controlled trial: Clinical Trial NCT00355914. Pain Physician. 2008; 11:121–132. PMID: 18354721.24. Lee HM, Weinstein JN, Meller ST, Hayashi N, Spratt KF, Gebhart GF. The role of steroids and their effects on phospholipase A2: an animal model of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998; 23:1191–1196. PMID: 9636970.25. Johansson A, Hao J, Sjolund B. Local corticosteroid application blocks transmission in normal nociceptive C-fibres. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1990; 34:335–338. PMID: 2167604.
Article26. Arner S, Lindblom U, Meyerson BA, Molander C. Prolonged relief of neuralgia after regional anesthetic blocks: a call for further experimental and systematic clinical studies. Pain. 1990; 43:287–297. PMID: 1705693.
Article27. Benzon HT. Epidural steroid injections for low back pain and lumbosacral radiculopathy. Pain. 1986; 24:277–295. PMID: 3008063.
Article28. Lavoie PA, Khazen T, Filion PR. Mechanisms of the inhibition of fast axonal transport by local anesthetics. Neuropharmacology. 1989; 28:175–181. PMID: 2469989.
Article29. Katz WA, Rothenberg R. Section 3: The nature of pain: pathophysiology. J Clin Rheumatol. 2005; 11(2 Suppl):S11–S15. PMID: 16357723.30. Cassuto J, Sinclair R, Bonderovic M. Anti-inflammatory properties of local anesthetics and their present and potential clinical implications. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 2006; 50:265–282. PMID: 16480459.
Article31. Weinstein JN, Collalto P, Lehmann TR. Thoracolumbar "burst" fractures treated conservatively: a long-term follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1988; 13:33–38. PMID: 3381135.
Article32. Willen J, Lindahl S, Nordwall A. Unstable thoracolumbar fractures: a comparative clinical study of conservative treatment and Harrington instrumentation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1985; 10:111–122. PMID: 4002035.33. Reid DC, Hu R, Davis LA, Saboe LA. The nonoperative treatment of burst fractures of the thoracolumbar junction. J Trauma. 1988; 28:1188–1194. PMID: 3411642.
Article34. Day B, Kokan P. Compression fractures of the thoracic and lumbar spine from compensable injuries. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1977; (124):173–176. PMID: 598072.
Article35. Aglietti P, Di Muria GV, Taylor TK, Ruff SJ, Marcucci M, Novembri A, et al. Conservative treatment of thoracic and lumbar vertebral fractures. Ital J Orthop Traumatol. 1983; 9(Suppl):83–105. PMID: 6679850.36. Shin BJ, Kim SK, Lee BI, Kim YI, Rah SK, Choi CU. Posterior column injuries in thoracolumbar and lumbar burst fractures. J Korean Soc Spine Surg. 1997; 4:67–73.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effectiveness of Facet Joint Injection for Treatment of Acute Osteoporotic Vertebral Compression Fracture
- Ultrasound Guided Therapeutic Medial Branch Block for the Facet Joint Pain
- Effect of Ultrasound-guided Lumbar Medial Branch Block in Chronic Low Back Pain
- Value of Bone Scintigraphy and Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) in Lumbar Facet Disease and Prediction of Short-term Outcome of Ultrasound Guided Medial Branch Block with Bone SPECT
- The Effects of Facet Joint Injection in Osteoporotic Spinal Compression Fractures