Clin Endosc.
2013 Sep;46(5):506-514.
Pancreatic Fluid Collection Drainage by Endoscopic Ultrasound: An Update
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Digestive and Liver Diseases, Columbia University Medical Center, New York, NY, USA.
- 2Division of Gastroenterology and Hepatology, New York Presbyterian Hospital, Weill Cornell Medical College, New York, NY, USA. mkahaleh@gmail.com
Abstract
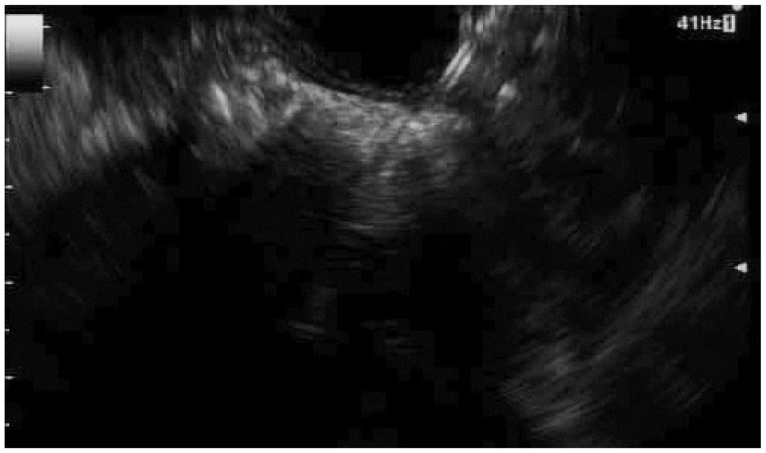
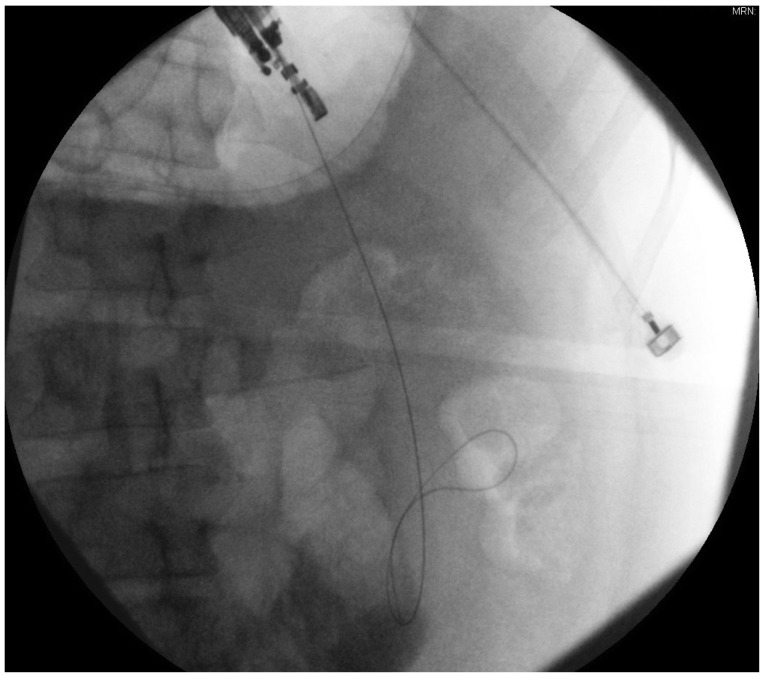
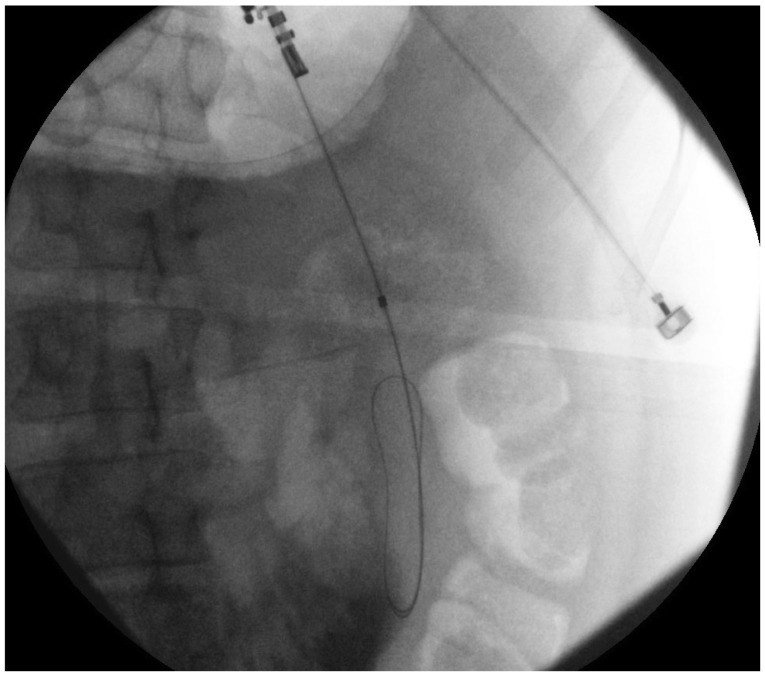
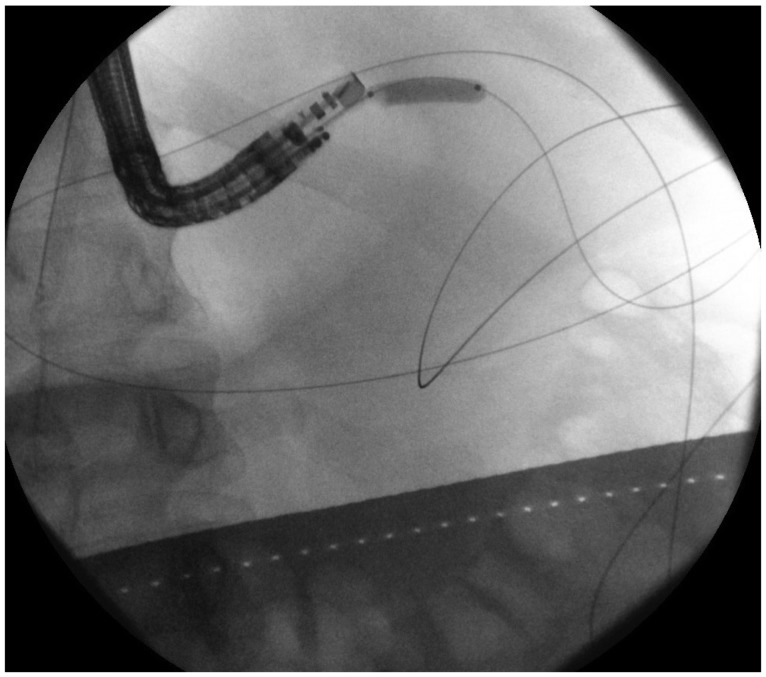
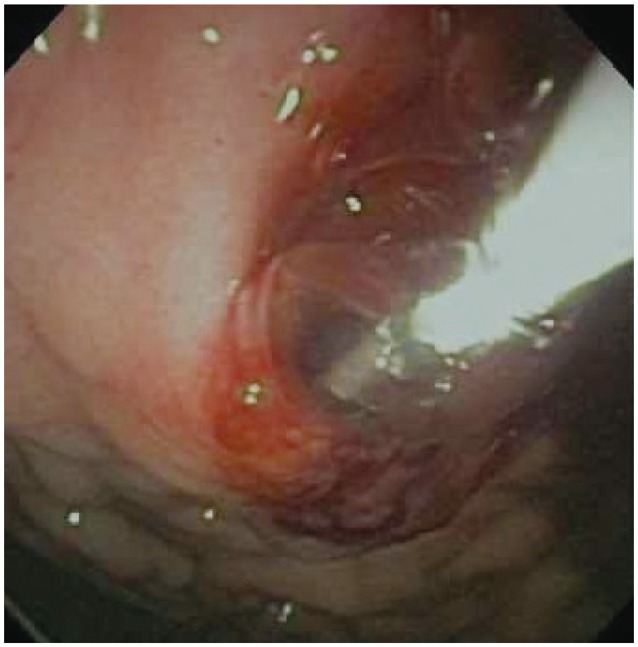
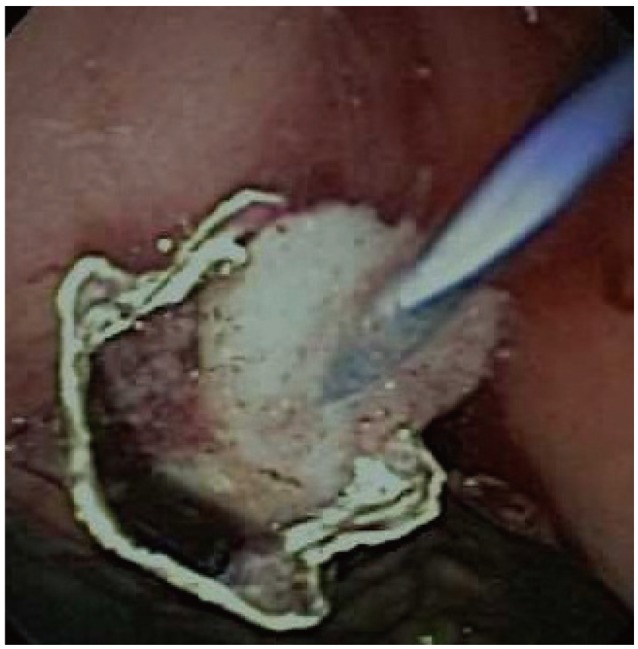
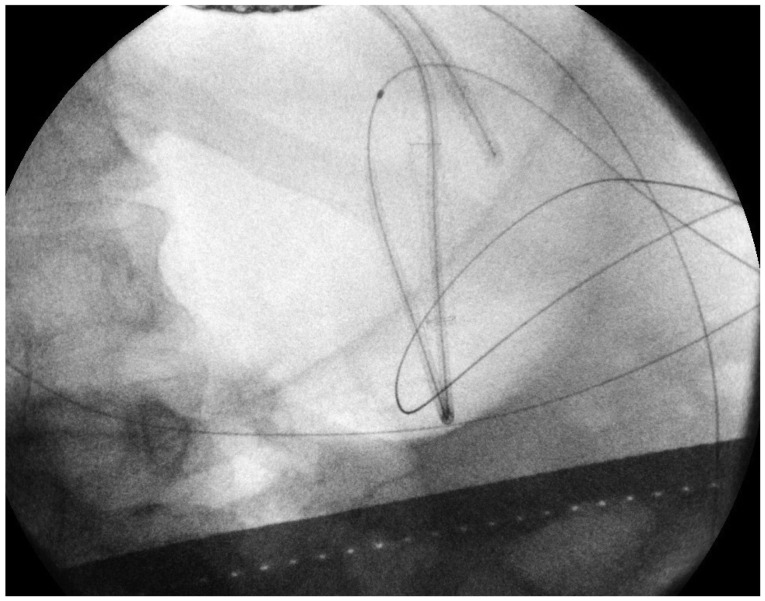
- Endoscopic management of symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections (PFCs) is now considered to be first line therapy. Expanded use of endoscopic ultrasound (EUS) techniques has resulted in increased applicability, safety, and efficacy of endoscopic transluminal PFC drainage. Steps include EUS-guided trangastric or transduodenal fistula creation into the PFC followed by stent placement or nasocystic drain deployment in order to decompress the collection. With the remarkable improvement in the available accessories and stents and development of exchange free access device; EUS drainage techniques have become simpler and less time consuming. The use of self-expandable metal stents with modifications to drain PFC has helped in overcoming some previously encountered challenges. PFCs considered suitable for endoscopic drainage include collection present for greater than 4 weeks, possessing a well-formed wall, position accessible endoscopically and located within 1 cm of the duodenal or gastric walls. Indications for EUS-guided drainage have been increasing which include unusual location of the collection, small window of entry, nonbulging collections, coagulopathy, intervening varices, failed conventional transmural drainage, indeterminate adherence of PFC to the luminal wall or suspicion of malignancy. In this article, we present a review of literature to date and discuss the recent developments in EUS-guided PFC drainage.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Baron TH, Thaggard WG, Morgan DE, Stanley RJ. Endoscopic therapy for organized pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology. 1996; 111:755–764. PMID: 8780582.
Article2. Baillie J. Pancreatic pseudocysts (Part I). Gastrointest Endosc. 2004; 59:873–879. PMID: 15173808.
Article3. Yeo CJ, Cameron JL, Sohn TA, et al. Six hundred fifty consecutive pancreaticoduodenectomies in the 1990s: pathology, complications, and outcomes. Ann Surg. 1997; 226:248–257. PMID: 9339931.4. Arvanitakis M, Delhaye M, Chamlou R, et al. Endoscopic therapy for main pancreatic-duct rupture after Silastic-ring vertical gastroplasty. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:143–151. PMID: 15990839.
Article5. Klöppel G. Pseudocysts and other non-neoplastic cysts of the pancreas. Semin Diagn Pathol. 2000; 17:7–15. PMID: 10721803.6. Bradley EL 3rd. A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, Ga, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg. 1993; 128:586–590. PMID: 8489394.7. Baron TH, Harewood GC, Morgan DE, Yates MR. Outcome differences after endoscopic drainage of pancreatic necrosis, acute pancreatic pseudocysts, and chronic pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:7–17. PMID: 12085029.
Article8. Baron TH, Morgan DE. The diagnosis and management of fluid collections associated with pancreatitis. Am J Med. 1997; 102:555–563. PMID: 9217671.9. Yeo CJ, Bastidas JA, Lynch-Nyhan A, Fishman EK, Zinner MJ, Cameron JL. The natural history of pancreatic pseudocysts documented by computed tomography. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1990; 170:411–417. PMID: 2326721.10. Bradley EL, Clements JL Jr, Gonzalez AC. The natural history of pancreatic pseudocysts: a unified concept of management. Am J Surg. 1979; 137:135–141. PMID: 758840.
Article11. Gouyon B, Lévy P, Ruszniewski P, et al. Predictive factors in the outcome of pseudocysts complicating alcoholic chronic pancreatitis. Gut. 1997; 41:821–825. PMID: 9462217.
Article12. Warshaw AL, Rattner DW. Timing of surgical drainage for pancreatic pseudocyst. Clinical and chemical criteria. Ann Surg. 1985; 202:720–724. PMID: 4073984.13. Bradley EL 3rd. A fifteen year experience with open drainage for infected pancreatic necrosis. Surg Gynecol Obstet. 1993; 177:215–222. PMID: 8356492.14. Boerma D, van Gulik TM, Obertop H, Gouma DJ. Internal drainage of infected pancreatic pseudocysts: safe or sorry? Dig Surg. 1999; 16:501–505. PMID: 10805550.
Article15. vanSonnenberg E, Wittich GR, Casola G, et al. Percutaneous drainage of infected and noninfected pancreatic pseudocysts: experience in 101 cases. Radiology. 1989; 170(3 Pt 1):757–761. PMID: 2644662.
Article16. Ahearne PM, Baillie JM, Cotton PB, Baker ME, Meyers WC, Pappas TN. An endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography (ERCP)-based algorithm for the management of pancreatic pseudocysts. Am J Surg. 1992; 163:111–115. PMID: 1733357.
Article17. Adams DB, Harvey TS, Anderson MC. Percutaneous catheter drainage of infected pancreatic and peripancreatic fluid collections. Arch Surg. 1990; 125:1554–1557. PMID: 2244807.
Article18. Neff R. Pancreatic pseudocysts and fluid collections: percutaneous approaches. Surg Clin North Am. 2001; 81:399–403. PMID: 11392426.19. Binmoeller KF, Seifert H, Walter A, Soehendra N. Transpapillary and transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 1995; 42:219–224. PMID: 7498686.
Article20. Cahen D, Rauws E, Fockens P, Weverling G, Huibregtse K, Bruno M. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts: long-term outcome and procedural factors associated with safe and successful treatment. Endoscopy. 2005; 37:977–983. PMID: 16189770.
Article21. Hookey LC, Debroux S, Delhaye M, Arvanitakis M, Le Moine O, Devière J. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic-fluid collections in 116 patients: a comparison of etiologies, drainage techniques, and outcomes. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:635–643. PMID: 16564865.
Article22. Delhaye M, Matos C, Devière J. Endoscopic management of chronic pancreatitis. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 2003; 13:717–742. PMID: 14986795.
Article23. Giovannini M. EUS-guided pancreatic pseudocyst drainage. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 9:32–38.
Article24. Howell DA, Holbrook RF, Bosco JJ, Muggia RA, Biber BP. Endoscopic needle localization of pancreatic pseudocysts before transmural drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 1993; 39:693–698. PMID: 8224695.
Article25. Antillon MR, Shah RJ, Stiegmann G, Chen YK. Single-step EUS-guided transmural drainage of simple and complicated pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:797–803. PMID: 16650541.
Article26. Sanchez Cortes E, Maalak A, Le Moine O, et al. Endoscopic cystenterostomy of nonbulging pancreatic fluid collections. Gastrointest Endosc. 2002; 56:380–386. PMID: 12196776.27. Arvanitakis M, Delhaye M, Bali MA, et al. Pancreatic-fluid collections: a randomized controlled trial regarding stent removal after endoscopic transmural drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 65:609–619. PMID: 17324413.
Article28. Baron TH. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. J Gastrointest Surg. 2008; 12:369–372. PMID: 17906903.
Article29. Giovannini M, Pesenti C, Rolland AL, Moutardier V, Delpero JR. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts or pancreatic abscesses using a therapeutic echo endoscope. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:473–477. PMID: 11437038.
Article30. Azar RR, Oh YS, Janec EM, Early DS, Jonnalagadda SS, Edmundowicz SA. Wire-guided pancreatic pseudocyst drainage by using a modified needle knife and therapeutic echoendoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:688–692. PMID: 16564874.
Article31. Krüger M, Schneider AS, Manns MP, Meier PN. Endoscopic management of pancreatic pseudocysts or abscesses after an EUS-guided 1-step procedure for initial access. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:409–416. PMID: 16500388.
Article32. Kahaleh M, Shami VM, Conaway MR, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound drainage of pancreatic pseudocyst: a prospective comparison with conventional endoscopic drainage. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:355–359. PMID: 16680634.
Article33. Lopes CV, Pesenti C, Bories E, Caillol F, Giovannini M. Endoscopic-ultrasound-guided endoscopic transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts and abscesses. Scand J Gastroenterol. 2007; 42:524–529. PMID: 17454865.34. Varadarajulu S, Wilcox CM, Tamhane A, Eloubeidi MA, Blakely J, Canon CL. Role of EUS in drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections not amenable for endoscopic transmural drainage. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007; 66:1107–1119. PMID: 17892874.
Article35. Barthet M, Lamblin G, Gasmi M, Vitton V, Desjeux A, Grimaud JC. Clinical usefulness of a treatment algorithm for pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:245–252. PMID: 18226686.
Article36. Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Tamhane A, Drelichman ER, Wilcox CM. Prospective randomized trial comparing EUS and EGD for transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:1102–1111. PMID: 18640677.
Article37. Bakker OJ, van Santvoort HC, van Brunschot S, et al. Endoscopic transgastric vs surgical necrosectomy for infected necrotizing pancreatitis: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2012; 307:1053–1061. PMID: 22416101.
Article38. Seewald S, Ang TL, Richter H, et al. Long-term results after endoscopic drainage and necrosectomy of symptomatic pancreatic fluid collections. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24:36–41. PMID: 22211410.
Article39. Fabbri C, Luigiano C, Cennamo V, et al. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided transmural drainage of infected pancreatic fluid collections with placement of covered self-expanding metal stents: a case series. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:429–433. PMID: 22382852.
Article40. Itoi T, Binmoeller KF, Shah J, et al. Clinical evaluation of a novel lumenapposing metal stent for endosonography-guided pancreatic pseudocyst and gallbladder drainage (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:870–876. PMID: 22301347.
Article41. Berzosa M, Maheshwari S, Patel KK, Shaib YH. Single-step endoscopic ultrasonography-guided drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections with a single self-expandable metal stent and standard linear echoendoscope. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:543–547. PMID: 22407382.
Article42. Penn DE, Draganov PV, Wagh MS, Forsmark CE, Gupte AR, Chauhan SS. Prospective evaluation of the use of fully covered self-expanding metal stents for EUS-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:679–684. PMID: 22732874.
Article43. Mangiavillano B, Arcidiacono PG, Masci E, et al. Single-step versus two-step endo-ultrasonography-guided drainage of pancreatic pseudocyst. J Dig Dis. 2012; 13:47–53. PMID: 22188916.
Article44. Weilert F, Binmoeller KF, Shah JN, Bhat YM, Kane S. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections with indeterminate adherence using temporary covered metal stents. Endoscopy. 2012; 44:780–783. PMID: 22791588.
Article45. Gornals JB, De la Serna-Higuera C, Sánchez-Yague A, Loras C, Sánchez-Cantos AM, Pérez-Miranda M. Endosonography-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections with a novel lumen-apposing stent. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:1428–1434. PMID: 23232994.
Article46. Binmoeller KF, Weilert F, Shah JN, Bhat YM, Kane S. Endosonography-guided transmural drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts using an exchange-free access device: initial clinical experience. Surg Endosc. 2013; 27:1835–1839. PMID: 23299130.
Article47. Andrén-Sandberg A, Dervenis C. Pancreatic pseudocysts in the 21st century. Part II: natural history. JOP. 2004; 5:64–70. PMID: 15007187.48. Jacobson BC, Baron TH, Adler DG, et al. ASGE guideline: the role of endoscopy in the diagnosis and the management of cystic lesions and inflammatory fluid collections of the pancreas. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 61:363–370. PMID: 15758904.
Article49. Varadarajulu S, Bang JY, Phadnis MA, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Endoscopic transmural drainage of peripancreatic fluid collections: outcomes and predictors of treatment success in 211 consecutive patients. J Gastrointest Surg. 2011; 15:2080–2088. PMID: 21786063.
Article50. Seifert H, Dietrich C, Schmitt T, Caspary W, Wehrmann T. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided one-step transmural drainage of cystic abdominal lesions with a large-channel echo endoscope. Endoscopy. 2000; 32:255–259. PMID: 10718392.
Article51. Seifert H, Faust D, Schmitt T, Dietrich C, Caspary W, Wehrmann T. Transmural drainage of cystic peripancreatic lesions with a new large-channel echo endoscope. Endoscopy. 2001; 33:1022–1026. PMID: 11740644.
Article52. Giovannini M, Bernardini D, Seitz JF. Cystogastrotomy entirely performed under endosonography guidance for pancreatic pseudocyst: results in six patients. Gastrointest Endosc. 1998; 48:200–203. PMID: 9717789.
Article53. Baron TH. Endoscopic drainage of pancreatic pseudocysts, abscesses and organized (walled-off) necrosis. In : Baron TH, Kozarek RA, Carr-Locke DL, editors. ERCP. Philadelphia: Saunders/Elsevier;2008. p. 475–491.54. Wiersema MJ. Endosonography-guided cystoduodenostomy with a therapeutic ultrasound endoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 1996; 44:614–617. PMID: 8934175.
Article55. Binmoeller KF, Soehendra N. Endoscopic ultrasonography in the diagnosis and treatment of pancreatic pseudocysts. Gastrointest Endosc Clin N Am. 1995; 5:805–816. PMID: 8535629.
Article56. Puri R, Mishra SR, Thandassery RB, Sud R, Eloubeidi MA. Outcome and complications of endoscopic ultrasound guided pancreatic pseudocyst drainage using combined endoprosthesis and naso-cystic drain. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2012; 27:722–727. PMID: 22313377.
Article57. Zheng M, Qin M. Endoscopic ultrasound guided transgastric stenting for the treatment of traumatic pancreatic pseudocyst. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011; 58:1106–1109. PMID: 21937358.
Article58. Varadarajulu S, Christein JD, Wilcox CM. Frequency of complications during EUS-guided drainage of pancreatic fluid collections in 148 consecutive patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2011; 26:1504–1508. PMID: 21575060.
Article59. Will U, Wanzar C, Gerlach R, Meyer F. Interventional ultrasound-guided procedures in pancreatic pseudocysts, abscesses and infected necroses: treatment algorithm in a large single-center study. Ultraschall Med. 2011; 32:176–183. PMID: 21259182.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Drainage of Pancreatic Fluid Collections (with Video)
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-Guided Management of Pancreatic Pseudocysts and Walled-Off Necrosis
- Endoscopic Management in Patients with Acute Pancreatitis
- Endoscopic Management of Pancreatic Fluid Collections in Children
- Endoscopic Ultrasound-guided Drainage in Pancreatobiliary Diseases