Clin Endosc.
2014 Sep;47(5):398-403. 10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.398.
Complications Related to Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection and Their Managements
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, The University of Tokyo Faculty of Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan. mtfujish-kkr@umin.ac.jp
- 2Department of Endoscopy and Endoscopic Surgery, The University of Tokyo Faculty of Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- 3Department of Epidemiology and Preventive Medicine, The University of Tokyo Faculty of Medicine, Graduate School of Medicine, Tokyo, Japan.
- KMID: 2165369
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.398
Abstract
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for early gastric cancer is a well-established procedure with the advantage of resection in an en bloc fashion, regardless of the size, shape, coexisting ulcer, and location of the lesion. However, gastric ESD is a more difficult and meticulous technique, and also requires a longer procedure time, than conventional endoscopic mucosal resection. These factors naturally increase the risk of various complications. The two most common complications accompanying gastric ESD are bleeding and perforation. These complications are known to occur both intraoperatively and postoperatively. However, there are other rare but serious complications related to gastric ESD, including aspiration pneumonia, stenosis, venous thromboembolism, and air embolism. Endoscopists should have sufficient knowledge about such complications and be prepared to deal with them appropriately, as successful management of complications is necessary for the successful completion of the entire ESD procedure.
MeSH Terms
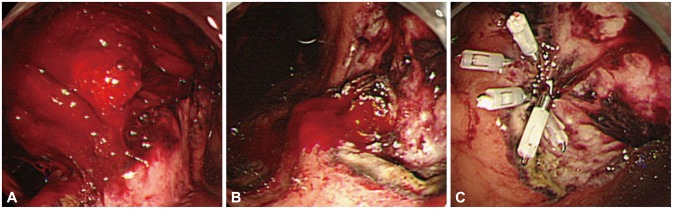
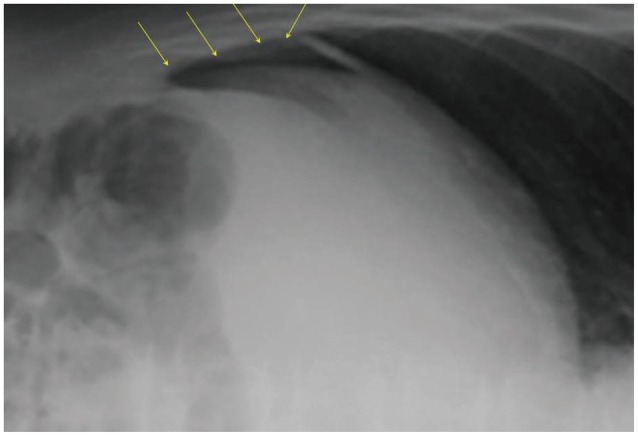
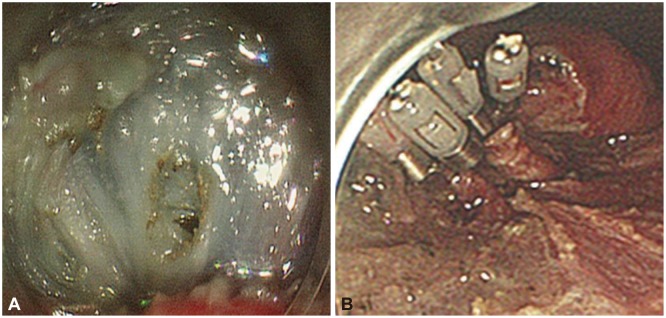
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Pneumothorax Following Gastric Endoscopic Mucosal Resect
Myeongseok Koh, Jin Seok Jang, Jae Hwang Cha
Korean J Gastroenterol. 2020;76(2):83-87. doi: 10.4166/kjg.2020.76.2.83.International Digestive Endoscopy Network 2014: Turnpike to the Future
Eun Young Kim, Kwang An Kwon, Il Ju Choi, Ji Kon Ryu, Ki Baik Hahm
Clin Endosc. 2014;47(5):371-382. doi: 10.5946/ce.2014.47.5.371.
Reference
-
1. Fujishiro M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for stomach neoplasms. World J Gastroenterol. 2006; 12:5108–5112. PMID: 16937520.
Article2. Goda K, Fujishiro M, Hirasawa K, et al. How to teach and learn endoscopic submucosal dissection for upper gastrointestinal neoplasm in Japan. Dig Endosc. 2012; 24(Suppl 1):136–142. PMID: 22533770.
Article3. Oda I, Gotoda T, Hamanaka H, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer: technical feasibility, operation time and complications from a large consecutive series. Dig Endosc. 2005; 17:54–58.
Article4. Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, et al. Management of bleeding concerning endoscopic submucosal dissection with the flex knife for stomach neoplasm. Dig Endosc. 2006; 18(Suppl 1):S119–S122.
Article5. Toyonaga T, Nishino E, Hirooka T, Ueda C, Noda K. Intraoperative bleeding in endoscopic submucosal dissection in the stomach and strategy for prevention and treatment. Dig Endosc. 2006; 18(Suppl 1):S123–S127.
Article6. Mannen K, Tsunada S, Hara M, et al. Risk factors for complications of endoscopic submucosal dissection in gastric tumors: analysis of 478 lesions. J Gastroenterol. 2010; 45:30–36. PMID: 19760133.
Article7. Tsuji Y, Ohata K, Ito T, et al. Risk factors for bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric lesions. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:2913–2917. PMID: 20556838.
Article8. Chung IK, Lee JH, Lee SH, et al. Therapeutic outcomes in 1000 cases of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: Korean ESD Study Group multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:1228–1235. PMID: 19249769.
Article9. Fujishiro M, Chiu PW, Wang HP. Role of antisecretory agents for gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Dig Endosc. 2013; 25(Suppl 1):86–93. PMID: 23368844.
Article10. Koh R, Hirasawa K, Yahara S, et al. Antithrombotic drugs are risk factors for delayed postoperative bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasms. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:476–483. PMID: 23622974.
Article11. Lim JH, Kim SG, Kim JW, et al. Do antiplatelets increase the risk of bleeding after endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric neoplasms? Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:719–727. PMID: 22317881.
Article12. Ryu HY, Kim JW, Kim HS, et al. Second-look endoscopy is not associated with better clinical outcomes after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: a prospective, randomized, clinical trial analyzed on an as-treated basis. Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 78:285–294. PMID: 23531425.
Article13. Fujishiro M, Abe N, Endo M, et al. Current managements and outcomes of peptic and artificial ulcer bleeding in Japan. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22(Suppl 1):S9–S14. PMID: 20590780.
Article14. Watari J, Tomita T, Toyoshima F, et al. Clinical outcomes and risk factors for perforation in gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection: a prospective pilot study. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2013; 5:281–287. PMID: 23772265.
Article15. Nonaka K, Kita H. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. J Cancer Ther. 2013; 4:26–32.
Article16. Watari J, Tomita T, Toyoshima F, et al. The incidence of "silent" free air and aspiration pneumonia detected by CT after gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 76:1116–1123. PMID: 23164512.
Article17. Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Nakamura M, et al. Successful outcomes of a novel endoscopic treatment for GI tumors: endoscopic submucosal dissection with a mixture of high-molecular-weight hyaluronic acid, glycerin, and sugar. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 63:243–249. PMID: 16427929.
Article18. Nonaka S, Saito Y, Takisawa H, Kim Y, Kikuchi T, Oda I. Safety of carbon dioxide insufflation for upper gastrointestinal tract endoscopic treatment of patients under deep sedation. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1638–1645. PMID: 20108154.
Article19. Fujishiro M, Yahagi N, Kakushima N, et al. Successful nonsurgical management of perforation complicating endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastrointestinal epithelial neoplasms. Endoscopy. 2006; 38:1001–1006. PMID: 17058165.
Article20. Ikezawa K, Michida T, Iwahashi K, et al. Delayed perforation occurring after endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Gastric Cancer. 2012; 15:111–114. PMID: 21948482.
Article21. Hanaoka N, Uedo N, Ishihara R, et al. Clinical features and outcomes of delayed perforation after endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancer. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:1112–1115. PMID: 21120780.
Article22. Park CH, Kim H, Kang YA, et al. Risk factors and prognosis of pulmonary complications after endoscopic submucosal dissection for gastric neoplasia. Dig Dis Sci. 2013; 58:540–546. PMID: 22996790.
Article23. Onozato Y, Kakizaki S, Ishihara H, et al. Feasibility of endoscopic submucosal dissection for elderly patients with early gastric cancer and adenomas. Dig Endosc. 2008; 20:12–16.24. Iizuka H, Kakizaki S, Sohara N, et al. Stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric cancers and adenomas. Dig Endosc. 2010; 22:282–288. PMID: 21175480.
Article25. Tsunada S, Ogata S, Mannen K, et al. Case series of endoscopic balloon dilation to treat a stricture caused by circumferential resection of the gastric antrum by endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 67:979–983. PMID: 18440388.
Article26. Shoji H, Yamaguchi N, Isomoto H, et al. Oral prednisolone and triamcinolone injection for gastric stricture after endoscopic submucosal dissection. Ann Transl Med. 2014; 2:22.27. Kusunoki M, Miyake K, Shindo T, et al. The incidence of deep vein thrombosis in Japanese patients undergoing endoscopic submucosal dissection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:798–804. PMID: 21855867.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Gastric wall abscess after endoscopic submucosal dissection
- Pathological Interpretation of Gastric Tumors in Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- The Clinical Accuracy of Endoscopic Ultrasonography and White Light Imaging in Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Perforation of a Gastric Tear during Esophageal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection under General Anesthesia
- History and Development of Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection