Ann Dermatol.
2016 Jun;28(3):344-351. 10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.344.
CSP0510 Lotion as a Novel Moisturizer Containing Citric Acid and Trisodium Phosphate Relieves Objective and Subjective Symptoms of Atopic Dermatitis
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Chonnam National University Medical School, Gwangju, Korea. schul@jnu.ac.kr
- 2Department of Microbiology, School of Medicine, Chosun University, Gwangju, Korea.
- KMID: 2164642
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2016.28.3.344
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Moisturizers with anti-inflammatory or anti-itch activity should be developed for the safe and effective management of atopic dermatitis (AD).
OBJECTIVE
This study evaluated the efficacy of a newly developed moisturizer, CSP0510 lotion (Twolines Inc., Korea), containing citric acid (CA) and trisodium phosphate (TSP) as active ingredients, in mild to moderate AD.
METHODS AND RESULTS
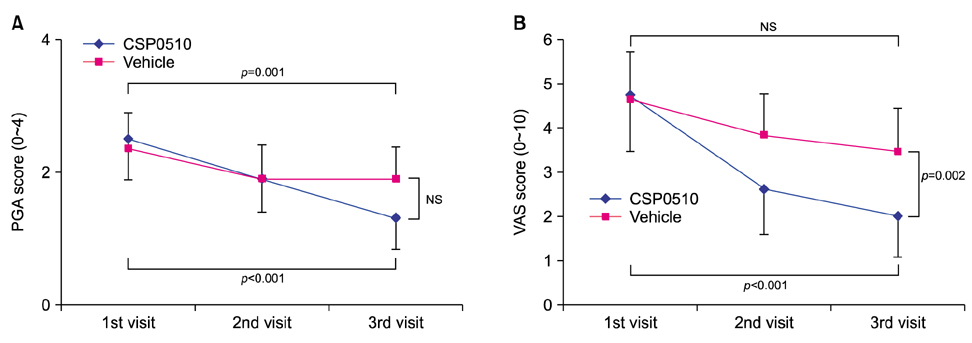
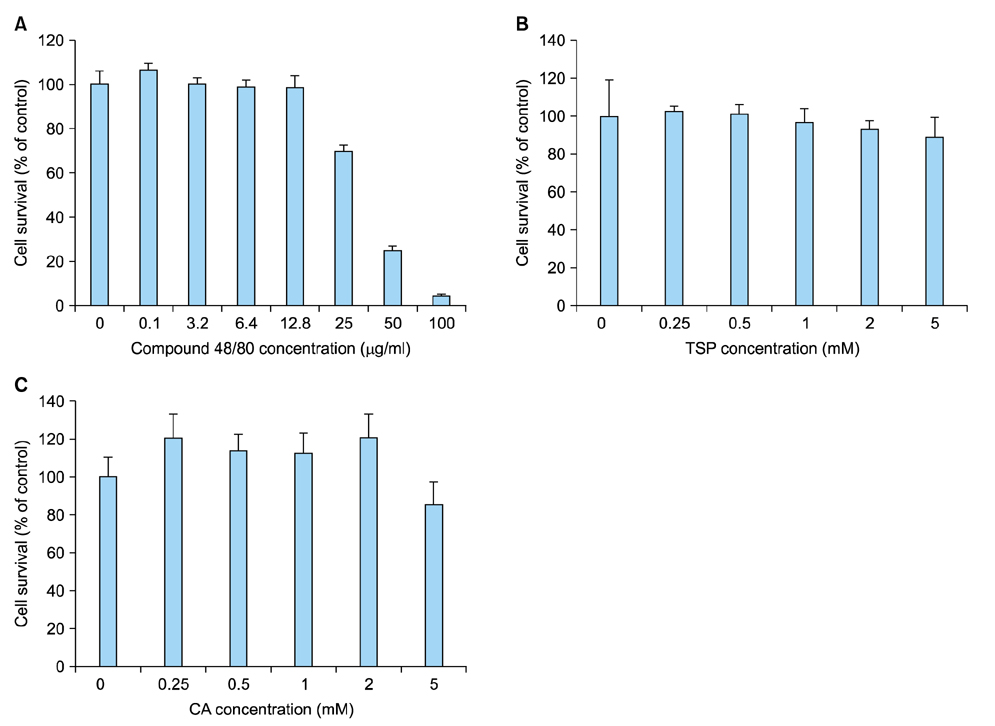
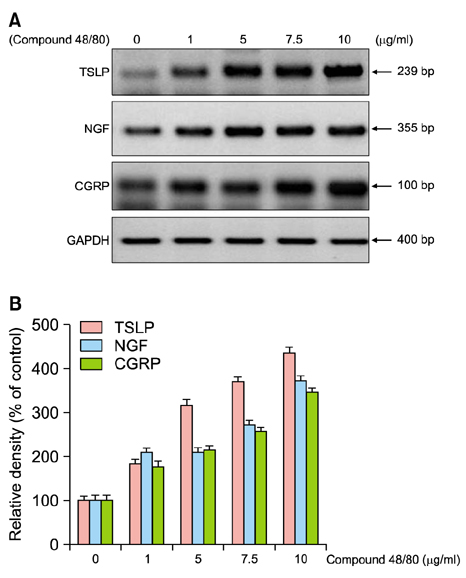
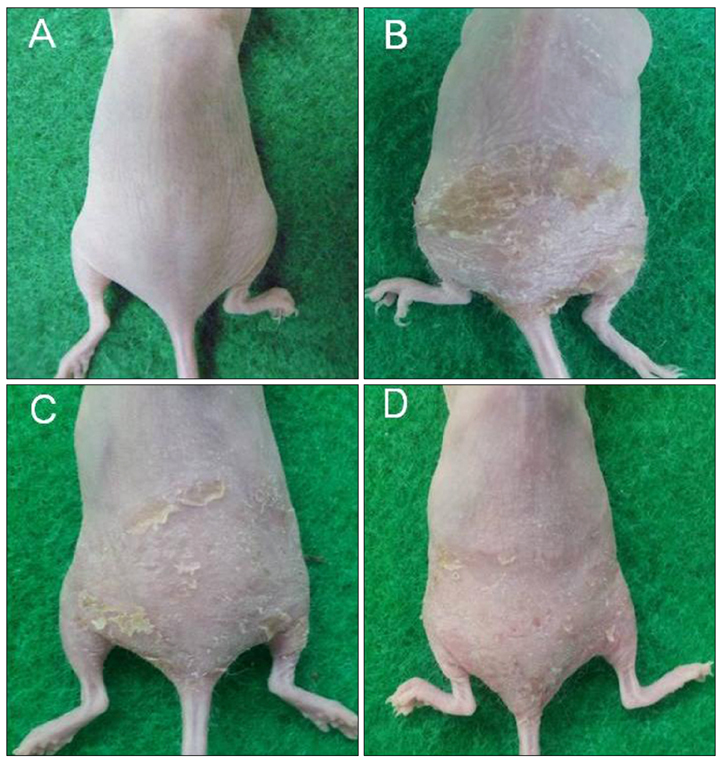
CSP0510 lotion applied twice daily for 4 weeks to eczematous lesions improved objective and subjective (itch) symptoms of AD. The physician's global assessment (PGA) score for objective symptoms decreased from 2.5±0.6 before application to 1.3±0.5 after application in the CSP0510-treated group (n=42, p<0.001). Also, the PGA score decreased from 2.3±0.6 to 1.9±0.5 by vehicle-treated (without CA and TSP) control group (p=0.001), but there was no statistical difference between CSP0510-treated and vehicle-treated groups (p=0.089). The visual analogue scale score for itch decreased from 4.8±1.3 to 2.0±0.9 in the CSP0510-treated group (p<0.001), and from 4.6±1.1 to 3.5±0.9 in the control group (p=0.075), showing a statistical significance between two groups (p=0.002). Our results in humans were further supported by in vitro and animal experiments. In HaCaT cells treated with compound 48/80 (7.5 µg/ml), CA:TSP (1:1, vol:vol) synergistically suppressed the compound 48/80-induced upregulation of thymic stromal lymphopoietin, nerve grow factor, and calcitonin gene-related peptide. Application of CSP0510 to the dorsal skin of hairless mice for 3 weeks suppressed the oxazolone-induced allergic skin inflammation.
CONCLUSION
In conclusion, CSP0510 lotion has anti-itch and anti-inflammatory activity in the skin, which improves both objective and subjective symptoms of AD.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Guttman-Yassky E, Nograles KE, Krueger JG. Contrasting pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis and psoriasis--part II: immune cell subsets and therapeutic concepts. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2011; 127:1420–1432.
Article2. Ostlere LS, Cowen T, Rustin MH. Neuropeptides in the skin of patients with atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Dermatol. 1995; 20:462–467.
Article3. Scholzen T, Armstrong CA, Bunnett NW, Luger TA, Olerud JE, Ansel JC. Neuropeptides in the skin: interactions between the neuroendocrine and the skin immune systems. Exp Dermatol. 1998; 7:81–96.
Article4. Wang IJ, Hsieh WS, Guo YL, Jee SH, Hsieh CJ, Hwang YH, et al. Neuro-mediators as predictors of paediatric atopic dermatitis. Clin Exp Allergy. 2008; 38:1302–1308.
Article5. Yamaguchi J, Aihara M, Kobayashi Y, Kambara T, Ikezawa Z. Quantitative analysis of nerve growth factor (NGF) in the atopic dermatitis and psoriasis horny layer and effect of treatment on NGF in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. 2009; 53:48–54.
Article6. Wang YH, Liu YJ. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin, OX40-ligand, and interleukin-25 in allergic responses. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009; 39:798–806.
Article7. Takai T. TSLP expression: cellular sources, triggers, and regulatory mechanisms. Allergol Int. 2012; 61:3–17.
Article8. Ikezawa Z, Komori J, Ikezawa Y, Inoue Y, Kirino M, Katsuyama M, et al. A role of staphyococcus aureus, Interleukin-18, nerve growth factor and semaphorin 3A, an Axon guidance molecule, in pathogenesis and treatment of atopic dermatitis. Allergy Asthma Immunol Res. 2010; 2:235–246.
Article9. Antúnez C, Torres MJ, López S, Rodriguez-Pena R, Blanca M, Mayorga C, et al. Calcitonin gene-related peptide modulates interleukin-13 in circulating cutaneous lymphocyte-associated antigen-positive T cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. Br J Dermatol. 2009; 161:547–553.
Article10. Park TJ, Comer C, Carol A, Lu Y, Hong HS, Rice FL. Somatosensory organization and behavior in naked mole-rats: II. Peripheral structures, innervation, and selective lack of neuropeptides associated with thermoregulation and pain. J Comp Neurol. 2003; 465:104–120.
Article11. Salomon J, Baran E. The role of selected neuropeptides in pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2008; 22:223–228.
Article12. Jung CH, Cho HH, Choi GJ, Kang SY, Yang NW. The anti-sticking effect of mixture of trisodium phosphate and citric acid on oral streptococcus species. Korean J Microbiol. 2008; 44:289–292.13. Man MQ, Hatano Y, Lee SH, Man M, Chang S, Feingold KR, et al. Characterization of a hapten-induced, murine model with multiple features of atopic dermatitis: structural, immunologic, and biochemical changes following single versus multiple oxazolone challenges. J Invest Dermatol. 2008; 128:79–86.
Article14. Choi DI, Choi JY, Kim YJ, Lee JB, Kim SO, Shin HT, et al. Ethanol extract of peanut sprout exhibits a potent anti-inflammatory activity in both an oxazolone-induced contact dermatitis mouse model and compound 48/80-Treated HaCaT Cells. Ann Dermatol. 2015; 27:142–151.
Article15. Hanifin JM, Rajka G. Diagnostic features of atopic dermatitis. Acta Derm Venereol. 1980; 92:Suppl. S44–S47.16. Penniston KL, Nakada SY, Holmes RP, Assimos DG. Quantitative assessment of citric acid in lemon juice, lime juice, and commercially-available fruit juice products. J Endourol. 2008; 22:567–570.
Article17. Xiong H, Li Y, Slavik MF, Walker JT. Spraying chicken skin with selected chemicals to reduce attached Salmonella typhimurium. J Food Prot. 1998; 61:272–275.
Article18. Lee HJ, Yoon NY, Lee NR, Jung M, Kim DH, Choi EH. Topical acidic cream prevents the development of atopic dermatitis- and asthma-like lesions in murine model. Exp Dermatol. 2014; 23:736–741.
Article19. Grove G, Zerweck C. An evaluation of the moisturizing and anti-itch effects of a lactic acid and pramoxine hydrochloride cream. Cutis. 2004; 73:135–139.20. Vilaplana J, Coll J, Trullás C, Azón A, Pelejero C. Clinical and non-invasive evaluation of 12% ammonium lactate emulsion for the treatment of dry skin in atopic and non-atopic subjects. Acta Derm Venereol. 1992; 72:28–33.21. Darlenski R, Kazandjieva J, Fluhr JW, Maurer M, Tsankov N. Lactic acid sting test does not differentiate between facial and generalized skin functional impairment in sensitive skin in atopic dermatitis and rosacea. J Dermatol Sci. 2014; 76:151–153.
Article22. Lodén M. The clinical benefit of moisturizers. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005; 19:672–688.
Article23. Babilas P, Knie U, Abels C. Cosmetic and dermatologic use of alpha hydroxy acids. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2012; 10:488–491.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Evaluation of the Anti-inflammatory Effect of a Moisturizer Containing Green-Tea Extracts
- The Growth Inhibition Effect on the Bacterial Vaginosis Causative Bacteria by Citric Acid and Trisodium Phosphate
- The Efficacy and Safety of Zinc-alpha-2 Glycoprotein (ZAG) Containing Moisturizer in Atopic Dermatitis
- Evaluation of Subjective Irritation Using the Lactic Acid Sting Test in Atopic Dermatitis
- Measurement of Atopic Dermatitis Disability