Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Jun;7(2):158-163. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.158.
Arthroscopic Treatment of Symptomatic Internal Snapping Hip with Combined Pathologies
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chungnam National University College of Medicine, Daejeon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Bumin Seoul Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Chung-Ang University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. hayongch@naver.com
- KMID: 2164539
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.2.158
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
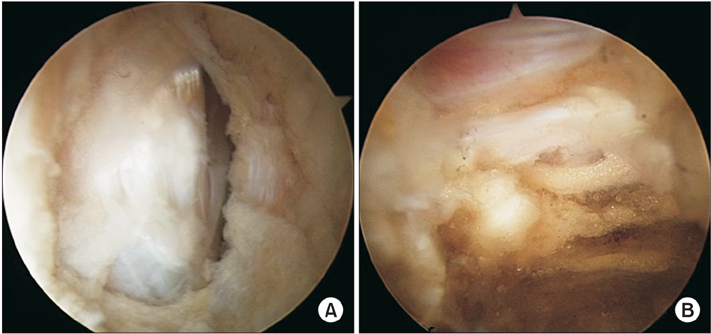
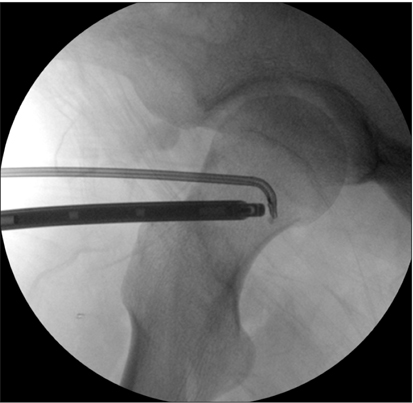
Arthroscopic iliopsoas tendon release was introduced in 2000. The purpose of this study was to evaluate clinical outcomes of arthroscopic iliopsoas tendon release for painful internal snapping hip with concomitant hip pathologies.
METHODS
Between January 2009 and December 2011, we performed arthroscopic iliopsoas tendon release and related surgeries in 25 patients (20 men and 5 women; mean age, 32 years; range, 17 to 53 years) with combined intraarticular hip pathologies. The patients were followed for a minimum of 2 years postoperatively. Clinical and radiological evaluations were performed.
RESULTS
Snapping sounds had disappeared by the 2-year follow-up in 24 of the 25 patients. All patients who had presented with loss of flexion strength postoperatively showed recovery at postoperative week 6 to 10. Harris hip score improved from 65 points (range, 46 to 86 points) preoperatively to 84 points (range, 67 to 98 points) postoperatively (p < 0.001). Seven hips (28%) had an excellent score, 15 hips (60%) a good score, 2 hips (8%) a fair score, and one hip (4%) a poor score (p < 0.001). The Tonnis grade of osteoarthritis did not change in any of the patients at the last follow-up.
CONCLUSIONS
Patients with painful internal snapping hip have combined hip pathologies. Therefore, the surgeon should keep in mind that painful internal snapping hips are frequently combined with concomitant intraarticular pathologies.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dobbs MB, Gordon JE, Luhmann SJ, Szymanski DA, Schoenecker PL. Surgical correction of the snapping iliopsoas tendon in adolescents. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84(3):420–424.2. Ward WT, Fleisch ID, Ganz R. Anatomy of the iliocapsularis muscle: relevance to surgery of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2000; (374):278–285.3. Taher RT, Power RA. Iliopsoas tendon dysfunction as a cause of pain after total hip arthroplasty relieved by surgical release. J Arthroplasty. 2003; 18(3):387–388.4. Tanzer M, Noiseux N. Osseous abnormalities and early osteoarthritis: the role of hip impingement. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004; (429):170–177.5. Byrd JW. Evaluation and management of the snapping iliopsoas tendon. Instr Course Lect. 2006; 55:347–355.6. Clarke NM, Taylor G. Differing approaches to the surgical correction of snapping hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003; 85(2):383–384.7. Jacobson T, Allen WC. Surgical correction of the snapping iliopsoas tendon. Am J Sports Med. 1990; 18(5):470–474.8. Hoskins JS, Burd TA, Allen WC. Surgical correction of internal coxa saltans: a 20-year consecutive study. Am J Sports Med. 2004; 32(4):998–1001.9. Contreras ME, Dani WS, Endges WK, De Araujo LC, Berral FJ. Arthroscopic treatment of the snapping iliopsoas tendon through the central compartment of the hip: a pilot study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2010; 92(6):777–780.10. Ilizaliturri VM Jr, Martinez-Escalante FA, Chaidez PA, Camacho-Galindo J. Endoscopic iliotibial band release for external snapping hip syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2006; 22(5):505–510.11. Ilizaliturri VM Jr, Chaidez C, Villegas P, Briseno A, Camacho-Galindo J. Prospective randomized study of 2 different techniques for endoscopic iliopsoas tendon release in the treatment of internal snapping hip syndrome. Arthroscopy. 2009; 25(2):159–163.12. Domb BG, Shindle MK, McArthur B, Voos JE, Magennis EM, Kelly BT. Iliopsoas impingement: a newly identified cause of labral pathology in the hip. HSS J. 2011; 7(2):145–150.13. Shu B, Safran MR. Case report: bifid iliopsoas tendon causing refractory internal snapping hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011; 469(1):289–293.14. Harris WH. Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty: an end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969; 51(4):737–755.15. Tonnis D. Normal values of the hip joint for the evaluation of X-rays in children and adults. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1976; (119):39–47.16. Outerbridge RE. The etiology of chondromalacia patellae. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1961; 43(4):752–757.17. Fabricant PD, Bedi A, De La Torre K, Kelly BT. Clinical outcomes after arthroscopic psoas lengthening: the effect of femoral version. Arthroscopy. 2012; 28(7):965–971.18. Flanum ME, Keene JS, Blankenbaker DG, Desmet AA. Arthroscopic treatment of the painful "internal" snapping hip: results of a new endoscopic technique and imaging protocol. Am J Sports Med. 2007; 35(5):770–779.19. Khan M, Adamich J, Simunovic N, Philippon MJ, Bhandari M, Ayeni OR. Surgical management of internal snapping hip syndrome: a systematic review evaluating open and arthroscopic approaches. Arthroscopy. 2013; 29(5):942–948.20. McCormick F, Kleweno CP, Kim YJ, Martin SD. Vascular safe zones in hip arthroscopy. Am J Sports Med. 2011; 39:Suppl. 64S–71S.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Arthroscopic Resection of Osteochondroma of Hip Joint Associated with Internal Snapping: A Case Report
- Arthroscopic Treatment for External Snapping Hip
- Snapping Knee caused by the Gracilis and Semitendinosus tendon
- Osteochondroma Arising from Anterior Inferior Iliac Spine as a Cause of Snapping Hip
- Treatment of the Snapping Discoid Lateral Meniscus without Tear in Pediatrics: Contouring Surgery and Posterolateral Repair