J Dent Rehabil Appl Sci.
2016 Mar;32(1):80-86. 10.14368/jdras.2016.32.1.80.
A clinical case of hybrid telescopic double crown using friction pin with an isolated few remaining teeth
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Prosthodontics, School of Dentistry, Kyoungpook National University, Daegu, Republic of Korea. sungamcho@gamil.com
- KMID: 2162382
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14368/jdras.2016.32.1.80
Abstract
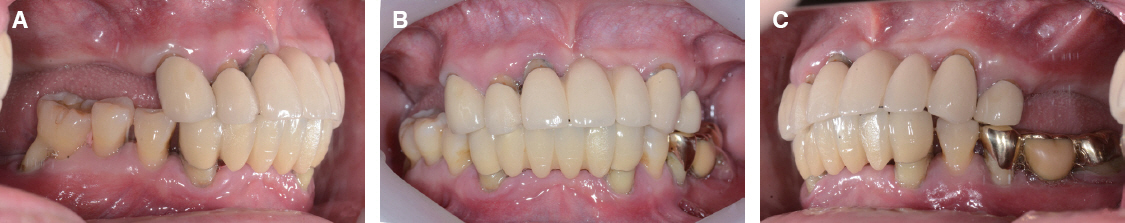
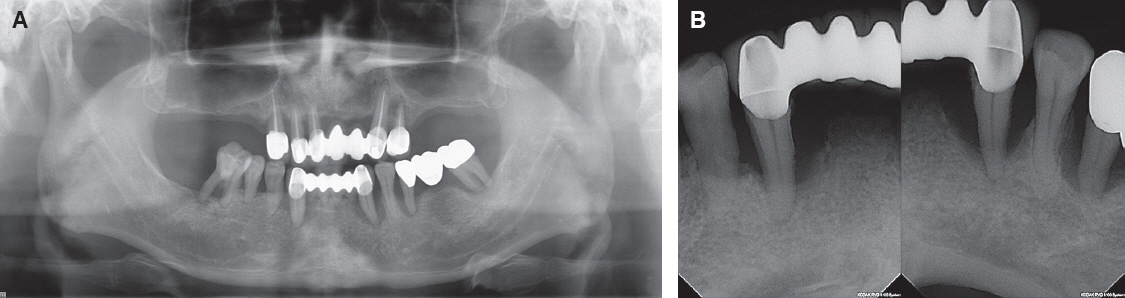
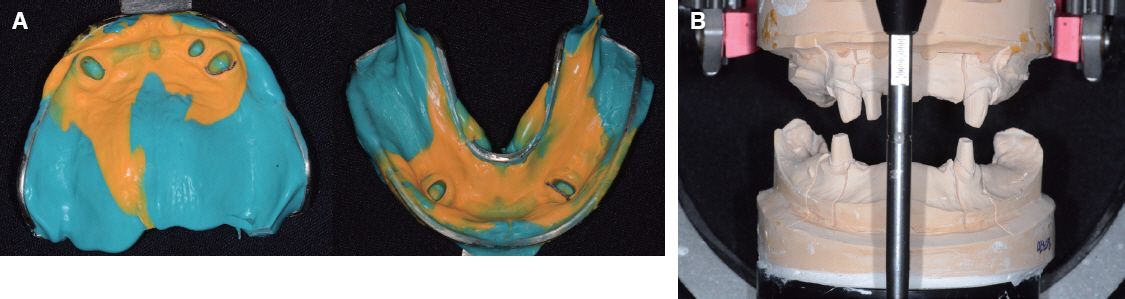
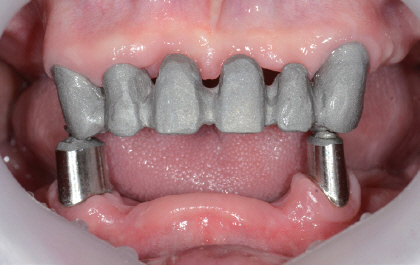
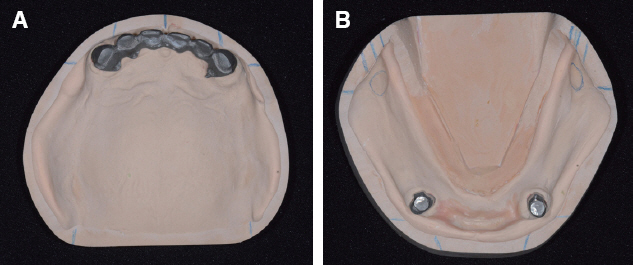
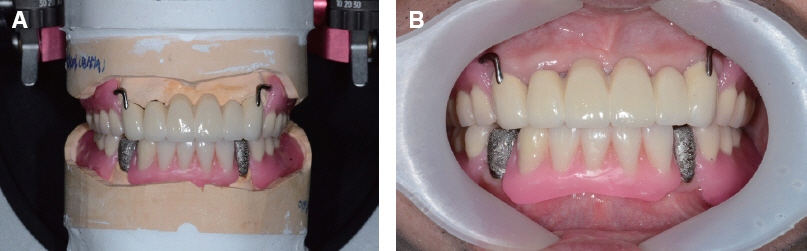
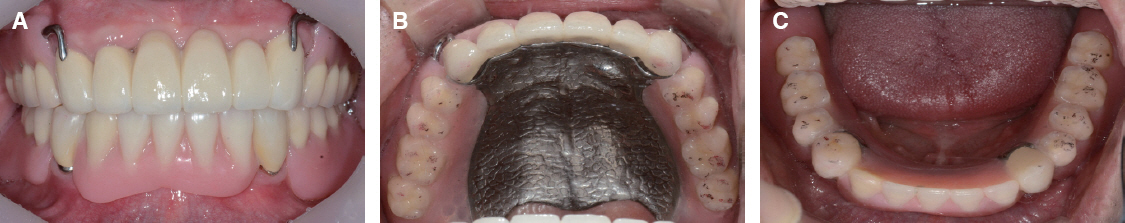
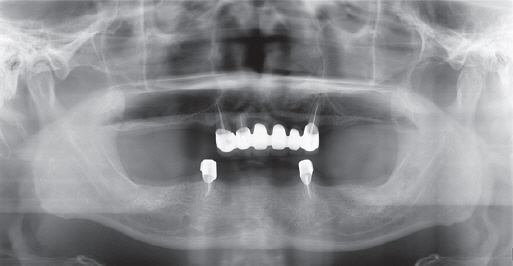
- A few authors have reported good clinical results using double crown removable partial denture (RPD) with a few remaining teeth. Hybrid telescopic double crown is a good indication for a patient with poor periodontal condition and/or few remaining teeth after extraction, especially located in cross-arch position. In this case, there was a poor periodontal condition with teeth mobility. Several teeth with poor prognosis were extracted. Remaining anterior teeth was restored with fixed prostheses and edentulism was restored with Kennedy class I removable partial denture in maxilla. In mandible, it was hard to restore with clasp removable partial prostheses because of bilaterally isolated remaining teeth so that hybrid double crown removable partial denture with friction pin was suitable for this case. The objective of this report is to discuss the characteristics and the utility of hybrid double crown prostheses using a few remaining teeth in mandible.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Wenz HJ, Lehmann KM. A telescopic crown concept for the restoration of the partially edentulous arch: the Marburg double crown system. Int J Prosthodont. 1998; 11:541–50. PMID: 10023261.2. Koller B, Att W, Strub JR. Survival rates of teeth, implants, and double crown-retained removable dental prostheses: a systematic literature review. Int J Prosthodont. 2011; 24:109–17. PMID: 21479275.3. Berman B, Ericson A, Molin M. Long-term clinical results after treatment with conical crown-retained dentures. Int J Prosthodont. 1996; 9:533–38.4. Isaacson GO. Telescope crown retainers for removable partial dentures. J Prosthet Dent. 1969; 22:436–48. DOI: 10.1016/0022-3913(69)90211-X.5. Wenz HJ, Hertrampf K, Lehmann KM. Clinical longevity of removable partial dentures retained by telescopic crowns: outcome of the double crown with clearance fit. Int J Prosthodont. 2001; 14:207–13. PMID: 11484566.6. Jo LJ. Spark erosion process: An overview. J Dent Implant. 2011; 1:2–6. DOI: 10.4103/0974-6781.76424.7. Ha SJ, Lee CH, Cho JH. Periodontal prosthesis on medically compromised patient with few remaining teeth: hybrid telescopic double crown with friction pin method. J Korean Acad Prosthodont. 2014; 52:359–65. DOI: 10.4047/jkap.2014.52.4.359.8. Widbon T, Lofquist L, Widbom C, Soberfeldt B, Kronstrom M. Tooth-supported telescopic crownretained dentures: an up to 9-year restrospective clinical follow-up study. Int J Prosthodont. 2004; 17:29–34.9. Verma R, Joda T, Bragger U, Wittneben JG. A systemic review of clinical performance of toothretained and implant-retained double crown prostheses with a follow-up of ≥3 years. J Prosthodont. 2013; 22:2–12. DOI: 10.1111/j.1532-849X.2012.00905.x. PMID: 22947104.10. Sigh K, Gupta N. Telescopic denture - A treatment modality for minimizing the conventional removable complete denture problems: A case report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2012; 6:1112–6.11. Saito M, Miura Y, Notani K, Kawasaki T. Stress distribution of abutments and base displacement with precision attachment- and telescopic crownretained removable partial dentures. J Oral Rehabil. 2003; 30:482–7. DOI: 10.1046/j.1365-2842.2003.01092.x. PMID: 12752927.12. Sahin V, Akaltan F, Parnas L. Effects of the type and rigidity of the retainer and the number of abutting teeth on stress distribution of telescopicretained removable partial dentures. J Dent Sci. 2012; 7:7–13. DOI: 10.1016/j.jds.2012.01.001.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Report by using hybrid telescopic double crown Removable Partial Denture on a few remaining teeth with severe periodontal disease
- Prosthetic treatment for patient with anterior overbite and partial edentulism using maxillary hybrid telescopic double crown RPD and mandibular fixed prostheses: A 11-yr follow-up
- A clinical report of hybrid telescopic double crown denture with friction pin in a failed double crown denture case
- Causes of failures of long-term used double crown denture and new rehabilitation with dental implant and tooth combined denture using remaining teeth and implants
- Treatment of the cleft lip and palate patient with few remaining posterior teeth using hybrid telescopic crown denture