J Korean Med Sci.
2005 Dec;20(6):1070-1072. 10.3346/jkms.2005.20.6.1070.
Infected Infradiaphragmatic Retroperitoneal Extralobar Pulmonary Sequestration: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery, Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. kughcs@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Pathology, Anam Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 3Department of Pathology, Guro Hospital, Korea University Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2157765
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2005.20.6.1070
Abstract
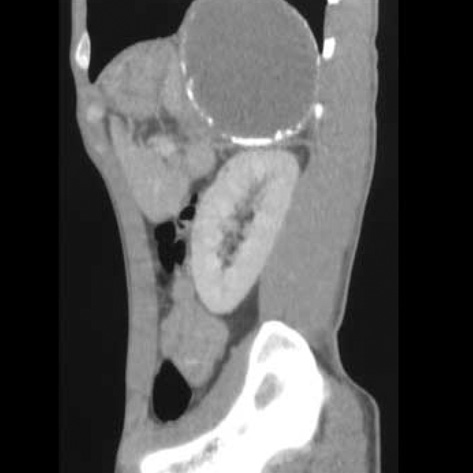
- Infradiaphragmatic extralobar pulmonary sequestration is an extremely rare congenital malformation. It is more frequently diagnosed in the antenatal period due to routine ultrasonic examination of the fetus or in the first 6 months of life, though on rare occasions it is discovered incidentally in adults. A 32-yr-old man presenting with epigastric discomfort and fever was referred. Computed tomographic scanning showed that a 16-cm, multiseptated, dumbbell-shaped, huge cystic tumor was located beneath the diaphragm. On the next day, 850 mL of thick yellowish pus was drained by sonography-guided fine needle aspiration for the purpose of infection control and diagnosis, but no microscopic organisms were found in repeated culture studies. Surgical removal of the cyst was performed through thoracoabdominal incision and most of these pathologic lesions were removed but we could not find the feeding arteries or any fistulous tract to surrounding structures. Histopathologic study revealed that it was extralobar pulmonary sequestration and culture study showed that many WBC and necrotic materials were found but there were no microorganisms in the cystic contents. We report the first case of an infected infradiaphragmatic retroperitoneal extralobar sequestration which was administered a staged management and achieved an excellent clinical course.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Huang CC, Ko SF, Chung MY, Shieh CS, Tiao MM, Lui CC, Ng SH. Infradiaphragmatic pulmonary sequestration combined with cystic adenomatoid malformation: unusual postnatal computed tomographic features. Abdom Imaging. 2004. 29:439–442.
Article2. Chan Y, Oldfield R, Vogel S, Ferguson S. Pulmonary sequestration presenting as a prenatally detected suprarenal lesion in a neonate. J Pediatr Surg. 2000. 35:1367–1369.
Article3. Rajendiran S, Kapoor V, Schoedel K. Fine-needle aspiration cytology of intraabdominal extralobar pulmonary sequestration: a case report. Diagn Cytopathol. 2003. 29:24–27.
Article4. Corbett HJ, Humphrey GM. Pulmonary sequestration. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2004. 5:59–68.
Article5. Carrasco R, Castanon M, San Vincente B, Tarrado X, Montaner A, Morales L. Extralobar infradiaphragmatic pulmonary sequestration with a digestive communication. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2002. 123:188–189.
Article6. Danielson PD, Sherman NJ. Laparoscopic removal of an abdominal extralobar pulmonary sequestration. J Pediatr Surg. 2001. 36:1653–1655.
Article7. Garcia-Pena P, Lucaya J, Hendry GM, McAndrew PT, Duran C. Spontaneous involution of pulmonary sequestration in children: a report of two cases and review of the literature. Pediatr Radiol. 1998. 28:266–270.8. Morad NA, al-Malki T, e-Tahir M. Intra-abdominal pulmonary sequestration: diagnostic difficulties. Pathology. 1997. 29:218–220.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Infradiaphragmatic Retroperitoneal Pulmonary Sequestration: A Case Report
- Congenital Cystic Adenomatoid Malformation Associated with Extralobar Pulmonary Sequestration: A case report
- Unusual Presentation of Extralobar Pulmonary Sequestration: A Case Report
- A case of pulmonary sequestration mimicking mediastinal mass detected by prenatal ultrasonography
- Extralobar Pulmonary Sequestration located in Right Oblique Fissure with Unusual Vascularture