Ann Dermatol.
2008 Dec;20(4):216-220. 10.5021/ad.2008.20.4.216.
Acrokeratosis Paraneoplastica with Adenocarcinoma of the Colon Treated with Topical Tretinoin
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dermatology, Gachon University of Medicine and Science, Incheon, Korea. jyroh1@gilhospital.com
- KMID: 2156398
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5021/ad.2008.20.4.216
Abstract
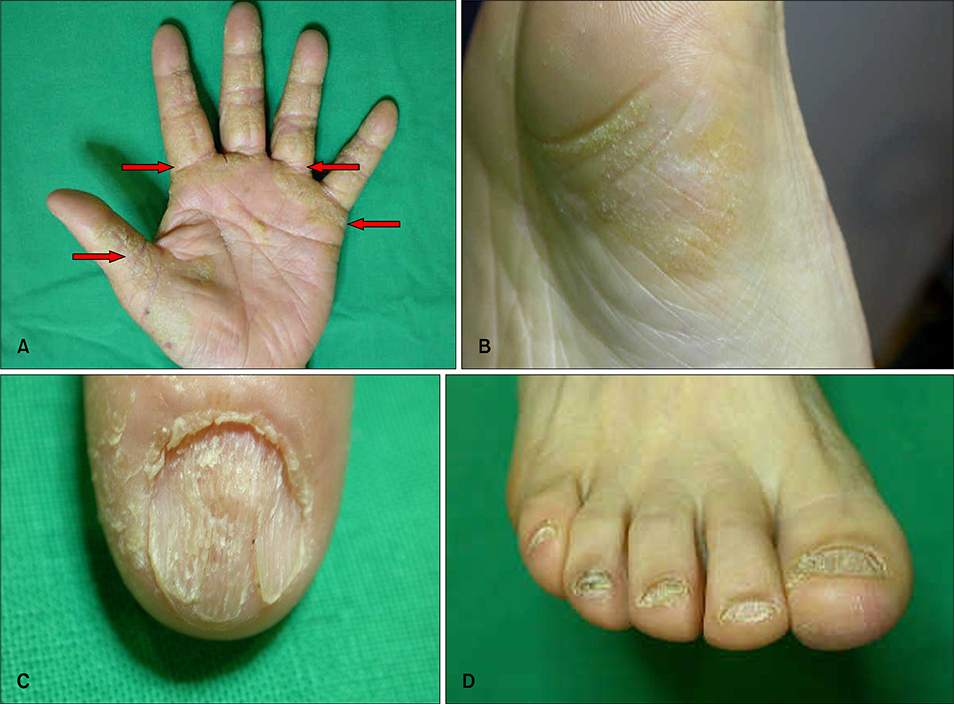
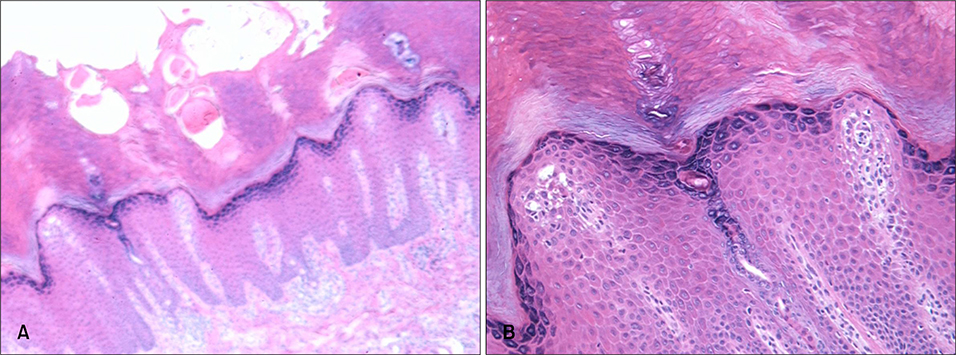
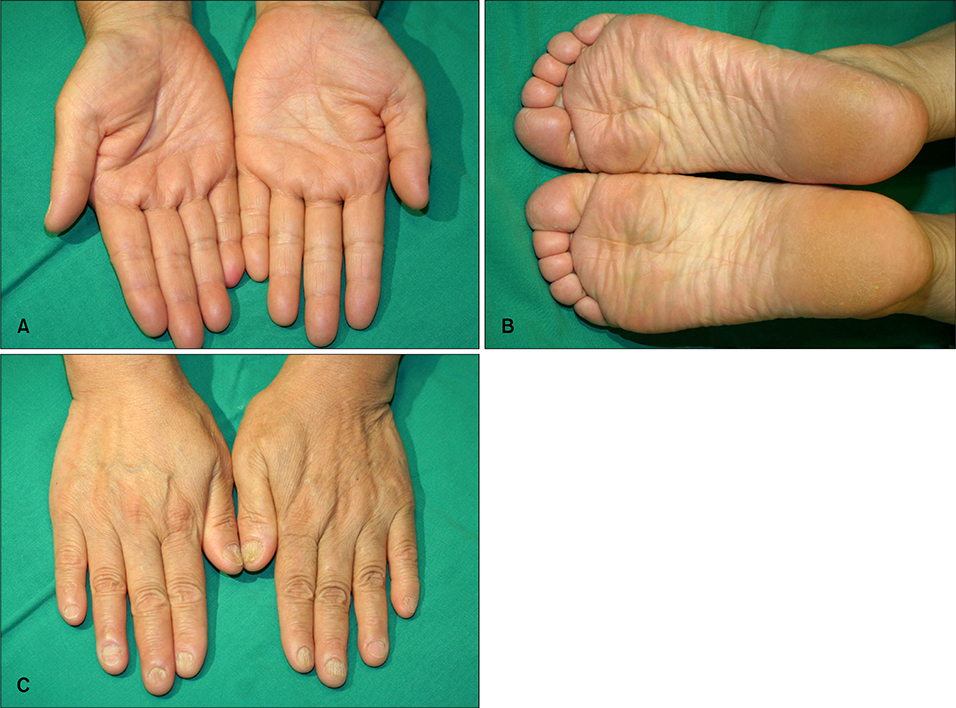
- Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica, or Bazex syndrome, is one of the paraneoplastic syndromes. The characteristic skin lesions include palmoplantar keratoderma, psoriasiform skin lesions, hyperpigmentation, and nail dystrophy. The most common associated neoplasms are squamous cell carcinoma of the upper respiratory tract and other kinds of tumors with cervical lymph node metastasis. A 63-year-old woman presented with an 11 month history of hyperkeratotic lesions on the palms and soles. Ten months before she had been diagnosed with adenocarcinoma of the colon and undergone a left hemicolectomy. We report a case of acrokeratosis paraneoplastica associated with colon cancer which persisted after removal of the primary cancer, but resolved with topical tretinoin treatment.
MeSH Terms
-
Adenocarcinoma
Carcinoma, Basal Cell
Carcinoma, Squamous Cell
Colon
Colonic Neoplasms
Female
Histiocytoma, Benign Fibrous
Humans
Hyperpigmentation
Hypotrichosis
Keratoderma, Palmoplantar
Lymph Nodes
Middle Aged
Nails
Neoplasm Metastasis
Paraneoplastic Syndromes
Respiratory System
Skin
Skin Neoplasms
Tretinoin
Carcinoma, Basal Cell
Histiocytoma, Benign Fibrous
Hypotrichosis
Skin Neoplasms
Tretinoin
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gougerot H, Grupper C. Dermatoses erythematosquameuse avec hyperkeratose palmo-plantaire, porectasies digitales et cancer de la langue latent. Paris Med. 1922; 43:234–237.2. Bazex A, Griffiths A. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica--a new cutaneous marker of malignancy. Br J Dermatol. 1980; 103:301–306.
Article3. Strobel ES, Bouveret C, Kohl PK. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica of Bazex as an indicator for underlying squamous cell carcinoma of the lung. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2006; 132:376–378.
Article4. Hara M, Hunayama M, Aiba S, Suetake T, Watanabe M, Tanaka M, et al. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome) associated with primary cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma of the lower leg, vitiligo and alopecia areata. Br J Dermatol. 1995; 133:121–124.
Article5. Akhyani M, Mansoori P, Taheri A, Asadi Kani Z. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome) associated with breast cancer. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2004; 29:429–430.
Article6. Hsu YS, Lien GS, Lai HH, Cheng YS, Hu CH, Hsieh MC, et al. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome) with adenocarcinoma of the colon: report of a case and review of the literature. J Gastroenterol. 2000; 35:460–464.
Article7. Bolognia JL. Bazex syndrome: acrokeratosis paraneoplastica. Semin Dermatol. 1995; 14:84–89.
Article8. Lucker GP, Steijlen PM. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex syndrome) occurring with acquired ichthyosis in Hodgkin's disease. Br J Dermatol. 1995; 133:322–325.
Article9. Valdivielso M, Longo I, Suarez R, Huerta M, Lazaro P. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica: Bazex syndrome. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2005; 19:340–344.
Article10. Pecora AL, Landsman L, Imgrund SP, Lambert WC. Acrokeratosis paraneoplastica (Bazex’ syndrome). Report of a case and review of the literature. Arch Dermatol. 1983; 119:820–826.
Article11. Bolognia JL, Brewer YP, Cooper DL. Bazex syndrome (acrokeratosis paraneoplastica). An analytic review. Medicine (Baltimore). 1991; 70:269–280.
Article12. Politi Y, Ophir J, Brenner S. Cutaneous paraneoplastic syndromes. Acta Derm Venereol. 1993; 73:161–170.13. Gill D, Fergin P, Kelly J. Bullous lesions in Bazex syndrome and successful treatment with oral psoralen phototherapy. Australas J Dermatol. 2001; 42:278–280.
Article14. Esteve E, Serpier H, Cambie MP, Armingaud P, Huet C, Penouil MH, et al. Bazex paraneoplastic acrokeratosis. Treatment with acitretin. Ann Dermatol Venereol. 1995; 122:26–29.15. Wishart JM. Bazex paraneoplastic acrokeratosis: a case report and response to Tigason. Br J Dermatol. 1986; 115:595–599.
Article16. Darmstadt GL, Yokel BK, Horn TD. Treatment of acanthosis nigricans with tretinoin. Arch Dermatol. 1991; 127:1139–1140.
Article17. Blobstein SH. Topical therapy with tretinoin and ammonium lactate for acanthosis nigricans associated with obesity. Cutis. 2003; 71:33–34.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Twenty Nail Dystrophy Treated with Topical Tretinoin Application
- A Case of Darier' s Disease Treated by the Combined Treatment with Oral Etretinate and Topical Tretinoin Cream
- Nevoid Acanthosis Nigricans Localized to the Umbilicus: Successful Treatment with Topical Tretinoin
- The Effect of Tretinoin Intradermal Injection on Dermal Thickening in Rabbit
- Topical Tretinoin Treatment for Confluent and Reticulated Papillomatosis