J Korean Med Sci.
2015 May;30(5):658-661. 10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.658.
Virtual Endoscopic and Laparoscopic Exploration of Stomach Wall Based on a Cadaver's Sectioned Images
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Computer Science and Information Technology, Inha University, Incheon, Korea.
- 2Department of Orthopaedic Biomaterial Science, Osaka University Graduate School of Medicine, Osaka, Japan.
- 3Korea Institute of Science and Technology Information, Daejeon, Korea.
- 4Graduate School of Information and Communication, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea.
- 5Department of Anatomy, Dongguk University College of Medicine, Gyeongju, Korea.
- 6Department of Anatomy, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. dissect@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2155482
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2015.30.5.658
Abstract
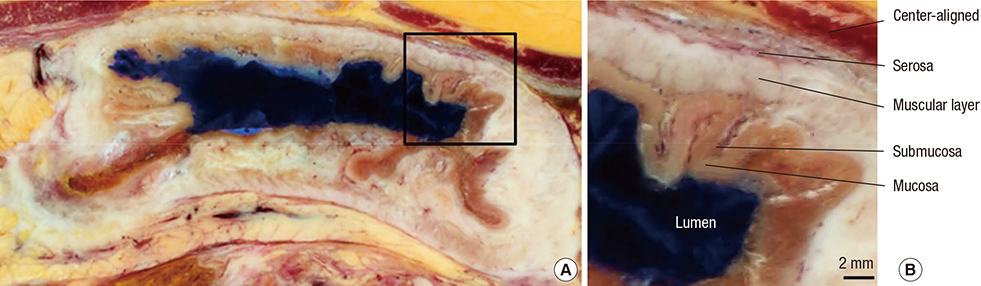
- We intended to determine that virtual endoscopy and laparoscopy of the stomach based on serially sectioned cadaver images is beneficial. Therefore, the outlines between the gastric wall and lumen were traced using the new female data of the Visible Korean to build a volume model. While the outlines were expanded at appropriate thicknesses, the stomach was observed endoscopically and laparoscopically in comparison with a chosen sectioned image. Four layers (mucosa, submucosa, muscular layer, and serosa) of the stomach were discernible by their proper colors in the sectioned images. All layers except the submucosa were identified in the endoscopic and laparoscopic views by using consistent colors. The stepwise expansion of the outlines revealed thickness of each layer as well as whether the thickness was uniform. Our ideas and the Visible Korean images could be a robust resource of virtual reality learning for medical students and clinicians.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Three Software Tools for Viewing Sectional Planes, Volume Models, and Surface Models of a Cadaver Hand
Beom Sun Chung, Min Suk Chung, Byeong-Seok Shin, Koojoo Kwon
J Korean Med Sci. 2018;33(8):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2018.33.e64.New Viewpoint of Surface Anatomy Using the Curved Sectional Planes of a Male Cadaver
Koojoo Kwon, Byeong-Seok Shin, Min Suk Chung, Beom Sun Chung
J Korean Med Sci. 2019;34(3):. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2019.34.e15.
Reference
-
1. Shin DS, Chung MS, Shin BS, Kwon K. Laparoscopic and endoscopic exploration of the ascending colon wall based on a cadaver sectioned images. Anat Sci Int. 2014; 89:21–27.2. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Lee YS, Har DH, Park HS. Visible Korean human: improved serially sectioned images of the entire body. IEEE Trans Med Imaging. 2005; 24:352–360.3. Borgefors G. On digital distance transforms in three dimensions. Comput Vis Image Und. 1996; 64:368–376.4. Pudney C. Distance-ordered homotopic thinning: a skeletonization algorithm for 3D digital images. Comput Vis Image Und. 1998; 72:404–413.5. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Lee YS, Har DH. Technical report on semiautomatic segmentation using the Adobe Photoshop. J Digit Imaging. 2005; 18:333–343.6. Shin DS, Park JS, Lee SB, Lee SH, Chung J, Chung MS. Surface model of the gastrointestinal tract constructed from the Visible Korean. Clin Anat. 2009; 22:601–609.7. Shin DS, Park JS, Park HS, Hwang SB, Chung MS. Outlining of the detailed structures in sectioned images from Visible Korean. Surg Radiol Anat. 2012; 34:235–247.8. Mescher AL, Junqueira LCU. Junqueira's basic histology : text and atlas. 13th ed. New York: McGraw-Hill;2013. p. 303.9. Krüger J, Westermann R. Acceleration techniques for GPU-based volume rendering. In : Proceedings of the IEEE Visualization, 2003; Seattle, Washington. IEEE;2003. p. 287–292.10. Hadwiger M, Kniss JM, Rezk-salama C, Weiskopf D, Engel K. Real-time volume graphics. A. K. Peters, Ltd.;2006. p. 163–185.11. Park JS, Chung MS, Hwang SB, Shin BS, Park HS. Visible Korean Human: its techniques and applications. Clin Anat. 2006; 19:216–224.12. Park JS, Jung YW, Lee JW, Shin DS, Chung MS, Riemer M, Handels H. Generating useful images for medical applications from the Visible Korean Human. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2008; 92:257–266.13. Shin DS, Chung MS, Park JS, Park HS, Lee S, Moon YL, Jang HG. Portable document format file showing the surface models of cadaver whole body. J Korean Med Sci. 2012; 27:849–856.14. Ackerman MJ. The Visible Human Project: a resource for education. Acad Med. 1999; 74:667–670.15. Jastrow H, Vollrath L. Teaching and learning gross anatomy using modern electronic media based on the Visible Human Project. Clin Anat. 2003; 16:44–54.16. Heng PA, Zhang SX, Xie YM, Wong TT, Chui YP, Cheng CY. Photorealistic virtual anatomy based on Chinese Visible Human data. Clin Anat. 2006; 19:232–239.17. Liu K, Fang B, Wu Y, Li Y, Jin J, Tan L, Zhang S. Anatomical education and surgical simulation based on the Chinese Visible Human: a three-dimensional virtual model of the larynx region. Anat Sci Int. 2013; 88:254–258.18. Shin DS, Chung MS, Park HS, Park JS, Hwang SB. Browsing software of the Visible Korean data used for teaching sectional anatomy. Anat Sci Educ. 2011; 4:327–332.19. Shin DS, Chung MS, Lee JW, Park JS, Chung J, Lee SB, Lee SH. Advanced surface reconstruction technique to build detailed surface models of the liver and neighboring structures from the Visible Korean Human. J Korean Med Sci. 2009; 24:375–383.20. Park JS, Chung MS, Chi JG, Park HS, Shin DS. Segmentation of cerebral gyri in the sectioned images by referring to volume model. J Korean Med Sci. 2010; 25:1710–1715.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Registration of Cadaver's Sectioned Images to Patient's Head MRIs
- Three-Dimensional Image and Virtual Dissection Program of the Lung Made of Korean Cadaver
- Manufacture of the Serially Sectioned Images of the Whole Body (Fifth Report: Methods for Manufacture of the Three Dimensional Images and Virtual Dissection Software)
- Manufacture of the Serially Sectioned Images of the Whole Body (First Report: Methods for Embedding and Serial Sectioning)
- Three-Dimensional Image and Virtual Dissection Program of the BronchopulmonarY Segments Made of Korean Cadaver: Three-dimensional image of bronchopulmonary segments