Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jan;48(1):415-421. 10.4143/crt.2014.160.
A Unique Case of Erdheim-Chester Disease with Axial Skeleton, Lymph Node, and Bone Marrow Involvement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Division of Hematology and Medical Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea. floresta405@gmail.com
- 3Division of Rheumatology, Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul, Korea.
- 4Department of Pathology, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- 5Department of Laboratory Medicine, SMG-SNU Boramae Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2152302
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2014.160
Abstract
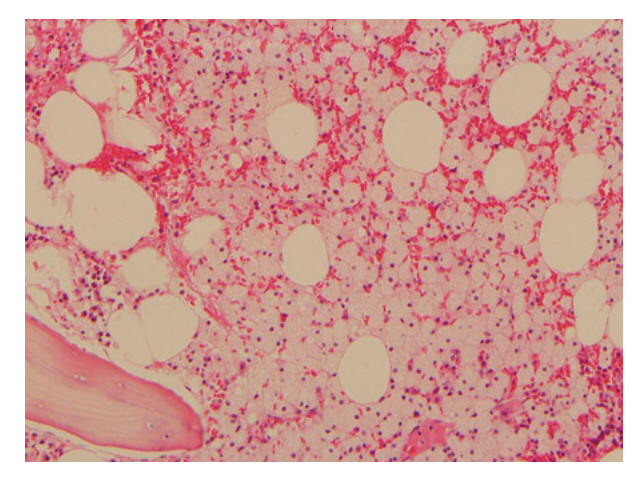
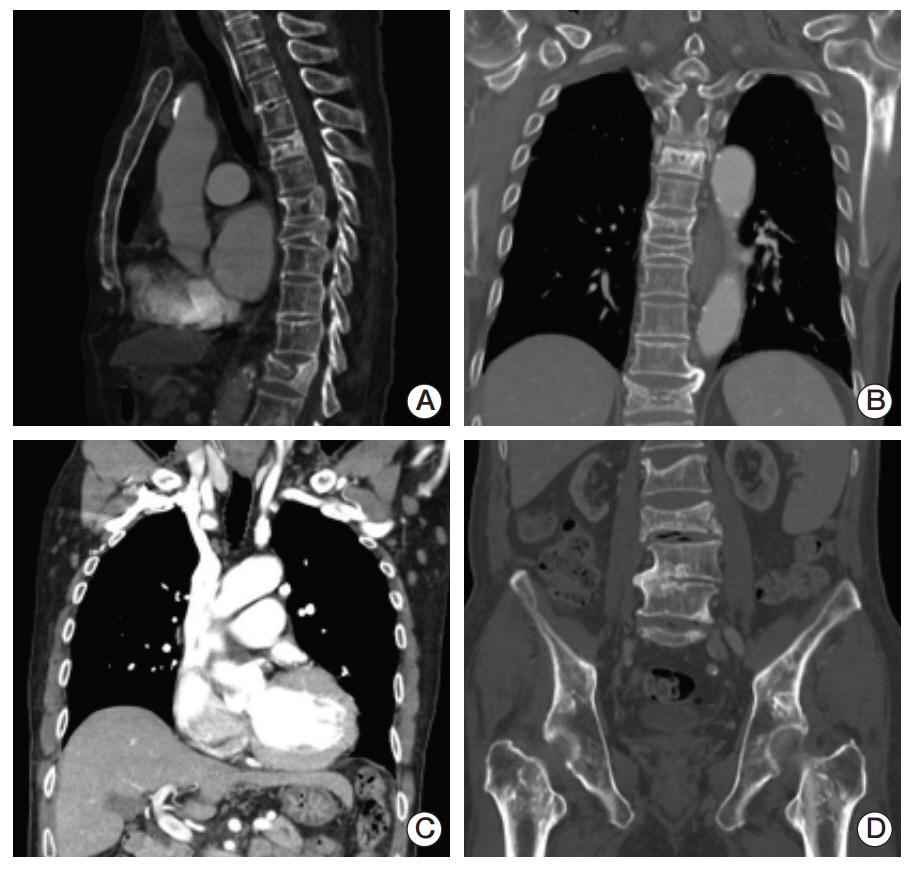
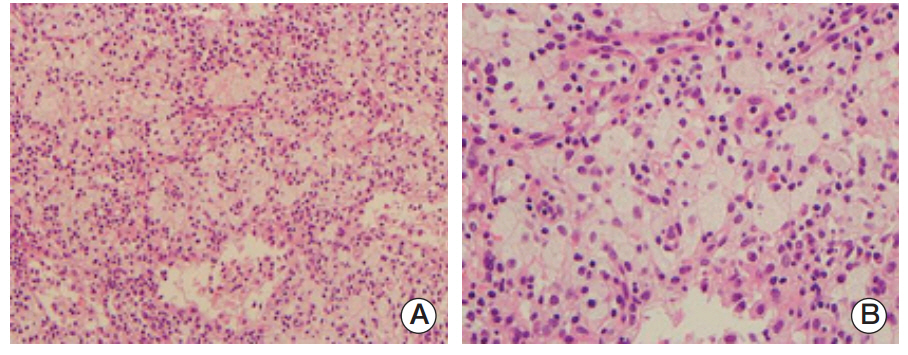
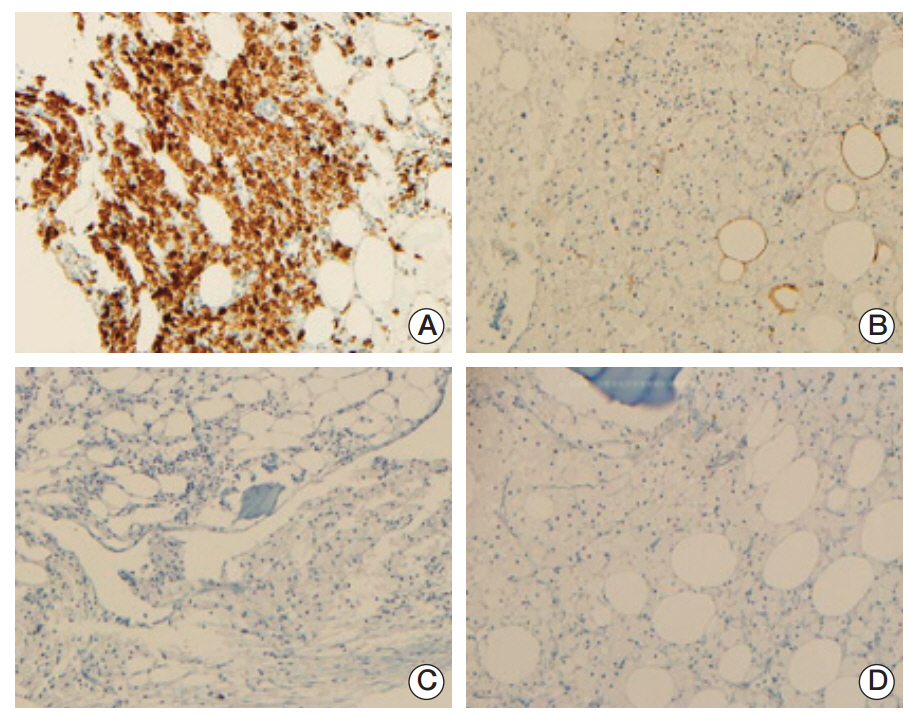
- Erdheim-Chester disease is a rare non-Langerhans-cell histiocytosis with bone and organ involvement. A 76-year-old man presented with low back pain and a history of visits for exertional dyspnea. We diagnosed him with anemia of chronic disease, cytopenia related to chronic illness, chronic renal failure due to hypertension, and hypothyroidism. However, we could not determine a definite cause or explanation for the cytopenia. Multiple osteosclerotic axial skeleton lesions and axillary lymph node enlargement were detected by computed tomography. Bone marrow biopsy revealed histiocytic infiltration, which was CD68-positive and CD1a-negative. This report describes an unusual presentation of Erdheim-Chester disease involving the bone marrow, axial skeleton, and lymph nodes.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Erdheim-Chester Disease Involving Lymph Nodes and Liver Clinically Mimicking Lymphoma: A Case Report
Yeoun Eun Sung, Yoon Seo Lee, Jieun Lee, Kyo Young Lee
J Pathol Transl Med. 2018;52(3):183-190. doi: 10.4132/jptm.2017.10.16.Erdheim-Chester Disease with Emperipolesis: A Unique Case Involving the Heart
Pengcheng Zhu, Naping Li, Lu Yu, Mariajose Navia Miranda, Guoping Wang, Yaqi Duan
Cancer Res Treat. 2017;49(2):553-558. doi: 10.4143/crt.2016.078.
Reference
-
References
1. Cavalli G, Guglielmi B, Berti A, Campochiaro C, Sabbadini MG, Dagna L. The multifaceted clinical presentations and manifestations of Erdheim-Chester disease: comprehensive review of the literature and of 10 new cases. Ann Rheum Dis. 2013; 72:1691–5.
Article2. Veyssier-Belot C, Cacoub P, Caparros-Lefebvre D, Wechsler J, Brun B, Remy M, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: clinical and radiologic characteristics of 59 cases. Medicine (Baltimore). 1996; 75:157–69.
Article3. Park YK, Ryu KN, Huh B, Kim JD. Erdheim-Chester disease: a case report. J Korean Med Sci. 1999; 14:323–6.
Article4. Arnaud L, Pierre I, Beigelman-Aubry C, Capron F, Brun AL, Rigolet A, et al. Pulmonary involvement in Erdheim-Chester disease: a single-center study of thirty-four patients and a review of the literature. Arthritis Rheum. 2010; 62:3504–12.
Article5. Haroche J, Amoura Z, Touraine P, Seilhean D, Graef C, Birmele B, et al. Bilateral adrenal infiltration in Erdheim-Chester disease: report of seven cases and literature review. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007; 92:2007–12.
Article6. Sheu SY, Wenzel RR, Kersting C, Merten R, Graef C, Otterbach F, Schmid KW. Erdheim-Chester disease: case report with multisystemic manifestations including testes, thyroid, and lymph nodes, and a review of literature. J Clin Patho. 2004; 57:1225–8.
Article7. Lachenal F, Cotton F, Desmurs-Clavel H, Haroche J, Taillia H, Magy N, et al. Neurological manifestations and neuroradiological presentation of Erdheim-Chester disease: report of 6 cases and systematic review of the literature. J Neurol. 2006; 253:1267–77.
Article8. Haroche J, Amoura Z, Dion E, Wechsler B, Costedoat-Chalumeau N, Cacoub P, et al. Cardiovascular involvement, an overlooked feature of Erdheim-Chester disease: report of 6 new cases and a literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2004; 83:371–92.9. Dagna L, Girlanda S, Langheim S, Rizzo N, Bozzolo EP, Sabbadini MG, et al. Erdheim-Chester disease: report on a case and new insights on its immunopathogenesis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:1203–6.
Article10. Weitzman S, Jaffe R. Uncommon histiocytic disorders: the non-Langerhans cell histiocytoses. Pediatr Blood Cancer. 2005; 45:256–64.
Article11. Boissel N, Wechsler B, Leblond V. Treatment of refractory Erdheim-Chester disease with double autologous hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation. Ann Intern Med. 2001; 135:844–5.
Article12. Haroche J, Amoura Z, Trad SG, Wechsler B, Cluzel P, Grenier PA, et al. Variability in the efficacy of interferon-alpha in Erdheim-Chester disease by patient and site of involvement: results in eight patients. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:3330–6.13. Haroche J, Amoura Z, Charlotte F, Salvatierra J, Wechsler B, Graux C, et al. Imatinib mesylate for platelet-derived growth factor receptor-beta-positive Erdheim-Chester histiocytosis. Blood. 2008; 111:5413–5.
Article14. Haroche J, Cohen-Aubart F, Emile JF, Arnaud L, Maksud P, Charlotte F, et al. Dramatic efficacy of vemurafenib in both multisystemic and refractory Erdheim-Chester disease and Langerhans cell histiocytosis harboring the BRAF V600E mutation. Blood. 2013; 121:1495–500.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Erdheim-Chester Disease with Perirenal Masses Containing Macroscopic Fat Tissue
- Commentary on "A Case of Erdheim-Chester Disease with Asymptomatic Renal Involvement"
- Reply to Commentary on "A Case of Erdheim-Chester Disease with Asymptomatic Renal Involvement"
- Erdheim-Chester Disease Involving Lymph Nodes and Liver Clinically Mimicking Lymphoma: A Case Report
- Intracranial Erdheim-Chester Disease