Cancer Res Treat.
2016 Jan;48(1):198-207. 10.4143/crt.2015.024.
Clinical Significance of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma and TRAP220 in Patients with Operable Colorectal Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Internal Medicine, Dongnam Institute of Radiological and Medical Sciences, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Biochemistry, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 3Department of Internal Medicine, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. kimhj@dau.ac.kr
- 4Department of Surgery, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea.
- 5Department of Pathology, Dong-A University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. msroh@dau.ac.kr
- KMID: 2152276
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4143/crt.2015.024
Abstract
- PURPOSE
The peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARgamma) is a nuclear receptor that regulates expression of mediators of lipid metabolism and the inflammatory response. Thyroid hormone receptor-associated proteins 220 (TRAP220) is an essential component of the TRAP/Mediator complex. The objective of this study was to clarify whether PPARgamma or TRAP220 are significant prognostic markers in resectable colorectal cancer (CRC).
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A total of 399 patients who underwent curative resection for CRC were enrolled. We investigated the presence of PPARgamma and TARP220 in CRC tissues and adjacent normal tissues by immunohistochemistry. Correlation between the expression of these factors and clinicopathologic features and survival was investigated.
RESULTS
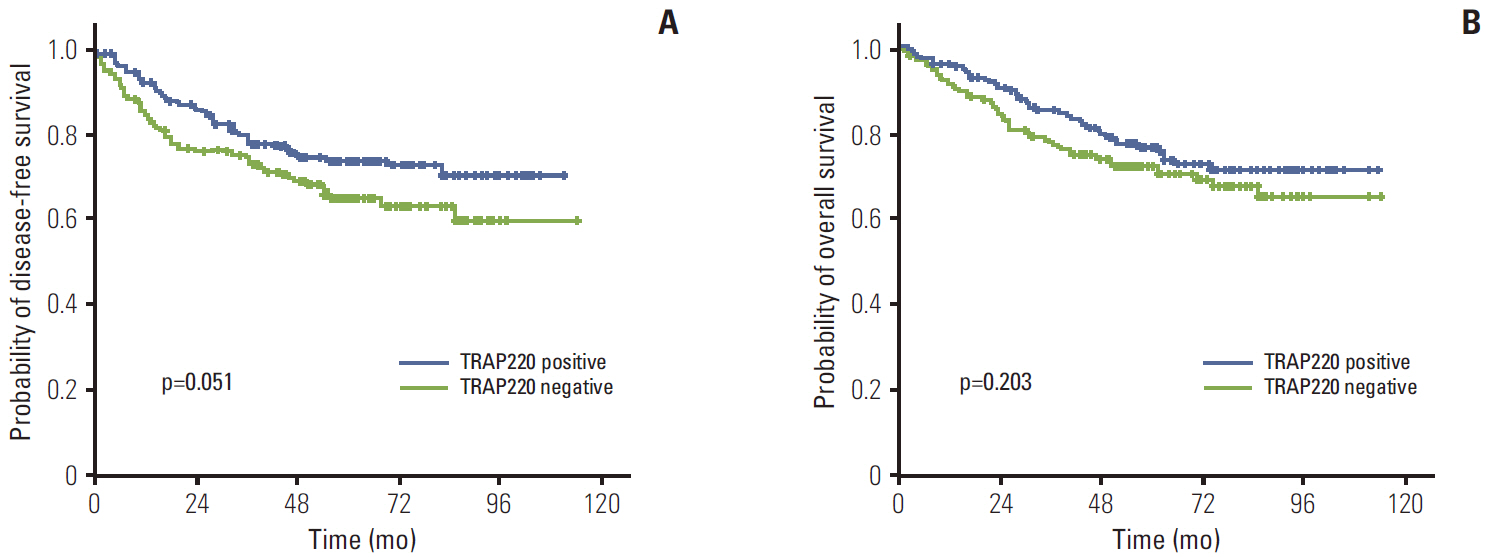
Median age of the patients was 63 years (range, 22 to 87 years), and median follow-up duration 61.1 months (range, 2 to 114 months). PPARgamma and TRAP220 expression showed significant correlation with depth of invasion (p=0.013 and p=0.001, respectively). Expression of TRAP220 also showed association with lymph node metastasis and TNM stage (p=0.001). Compared with patients with TRAP220 negative tumors, patients with TRAP220 positive tumors had longer 5-year disease-free survival (DFS) tendency (p=0.051). Patients who were PPARgamma positive combined with TRAP220 positive had a better 5-year DFS (64.8% vs. 79.3%, p=0.013). In multivariate analysis expression of both PPARgamma and TRAP220 significantly affected DFS (hazard ratio, 0.620; 95% confidence interval, 0.379 to 0.997; p=0.048).
CONCLUSION
TRAP220 may be a valuable marker for nodal metastasis and TNM stage. Tumor co-expression of PPARgamma and TRAP220 represents a biomarker for good prognosis in CRC patients.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward E, Forman D. Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 2011; 61:69–90.
Article2. Jung KW, Park S, Kong HJ, Won YJ, Lee JY, Seo HG, et al. Cancer statistics in Korea: incidence, mortality, survival, and prevalence in 2009. Cancer Res Treat. 2012; 44:11–24.
Article3. Pritchard CC, Grady WM. Colorectal cancer molecular biology moves into clinical practice. Gut. 2011; 60:116–29.
Article4. Malik S, Roeder RG. Dynamic regulation of pol II transcription by the mammalian Mediator complex. Trends Biochem Sci. 2005; 30:256–63.
Article5. Yuan CX, Ito M, Fondell JD, Fu ZY, Roeder RG. The TRAP220 component of a thyroid hormone receptor-associated protein (TRAP) coactivator complex interacts directly with nuclear receptors in a ligand-dependent fashion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998; 95:7939–44.6. Yun J, Son CH, Um SJ, Kwon HC, Lee KE, Choi PJ, et al. A different TRAP220 expression in distinct histologic subtypes of lung adenocarcinoma and the prognostic significance. Lung Cancer. 2011; 71:312–8.
Article7. Howard JH, Frolov A, Tzeng CW, Stewart A, Midzak A, Majmundar A, et al. Epigenetic downregulation of the DNA repair gene MED1/MBD4 in colorectal and ovarian cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 2009; 8:94–100.
Article8. Nolte RT, Wisely GB, Westin S, Cobb JE, Lambert MH, Kurokawa R, et al. Ligand binding and co-activator assembly of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma. Nature. 1998; 395:137–43.9. Willson TM, Brown PJ, Sternbach DD, Henke BR. The PPARs: from orphan receptors to drug discovery. J Med Chem. 2000; 43:527–50.
Article10. Michalik L, Desvergne B, Wahli W. Peroxisome-proliferator-activated receptors and cancers: complex stories. Nat Rev Cancer. 2004; 4:61–70.
Article11. Pancione M, Forte N, Sabatino L, Tomaselli E, Parente D, Febbraro A, et al. Reduced beta-catenin and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma expression levels are associated with colorectal cancer metastatic progression: correlation with tumor-associated macrophages, cyclooxygenase 2, and patient outcome. Hum Pathol. 2009; 40:714–25.12. Ogino S, Shima K, Baba Y, Nosho K, Irahara N, Kure S, et al. Colorectal cancer expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma (PPARG, PPARgamma) is associated with good prognosis. Gastroenterology. 2009; 136:1242–50.13. Theocharis S, Giaginis C, Parasi A, Margeli A, Kakisis J, Agapitos E, et al. Expression of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma in colon cancer: correlation with histopathological parameters, cell cycle-related molecules, and patients' survival. Dig Dis Sci. 2007; 52:2305–11.14. Gustafsson A, Hansson E, Kressner U, Nordgren S, Andersson M, Wang W, et al. EP1-4 subtype, COX and PPAR gamma receptor expression in colorectal cancer in prediction of disease-specific mortality. Int J Cancer. 2007; 121:232–40.15. Ge K, Guermah M, Yuan CX, Ito M, Wallberg AE, Spiegelman BM, et al. Transcription coactivator TRAP220 is required for PPAR gamma 2-stimulated adipogenesis. Nature. 2002; 417:563–7.16. Zhu Y, Qi C, Jain S, Rao MS, Reddy JK. Isolation and characterization of PBP, a protein that interacts with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor. J Biol Chem. 1997; 272:25500–6.
Article17. Hsu FD, Nielsen TO, Alkushi A, Dupuis B, Huntsman D, Liu CL, et al. Tissue microarrays are an effective quality assurance tool for diagnostic immunohistochemistry. Mod Pathol. 2002; 15:1374–80.
Article18. Calle EE, Rodriguez C, Walker-Thurmond K, Thun MJ. Overweight, obesity, and mortality from cancer in a prospectively studied cohort of U.S. adults. N Engl J Med. 2003; 348:1625–38.
Article19. Kliewer SA, Sundseth SS, Jones SA, Brown PJ, Wisely GB, Koble CS, et al. Fatty acids and eicosanoids regulate gene expression through direct interactions with peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors alpha and gamma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997; 94:4318–23.20. Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK, et al. Coregulator codes of transcriptional regulation by nuclear receptors. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:36865–8.
Article21. Qiao L, Li GH, Dai Y, Wang J, Li Z, Zou B, et al. Gene expression profile in colon cancer cells with respect to XIAP expression status. Int J Colorectal Dis. 2009; 24:245–60.
Article22. Gupta RA, Brockman JA, Sarraf P, Willson TMJ, DuBois RN, et al. Target genes of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma in colorectal cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 2001; 276:29681–7.23. Kim HJ, Roh MS, Son CH, Kim AJ, Jee HJ, Song N, et al. Loss of Med1/TRAP220 promotes the invasion and metastasis of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells by modulating the expression of metastasis-related genes. Cancer Lett. 2012; 321:195–202.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Colorectal Cancer Expression of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor gamma Is Associated with Good Prognosis
- Peroxisome Proliferator-activated Receptors (PPARs) in Diabetic Nephropathy
- Expression of the Peroxisome-proliferator-activated Receptor-gamma in Human Gastric Cancer
- Peroxisome Proliferator Activated Receptor-delta (PPAR-delta)
- Downregulation of Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor (PPAR)alpha, PPARgamma, and Phosphoglycerate Mutase 2 in Prostate Cancer