J Korean Med Sci.
2014 Nov;29(Suppl 3):S201-S209. 10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S3.S201.
A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Matched-Pairs, Active-Controlled Clinical Trial and Preclinical Animal Study to Compare the Durability, Efficacy and Safety between Polynucleotide Filler and Hyaluronic Acid Filler in the Correction of Crow's Feet: A New Concept of Regenerative Filler
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. lionheo@snu.ac.kr
- 2Kyung Hee University Skin Biotechnology Center, Gyeonggi Bio-Center, Suwon, Korea.
- 3Pharmaresearch Products R&D Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2151414
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3346/jkms.2014.29.S3.S201
Abstract
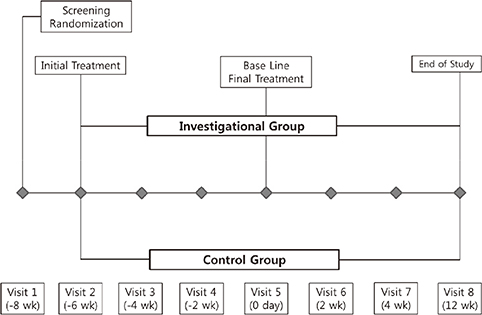
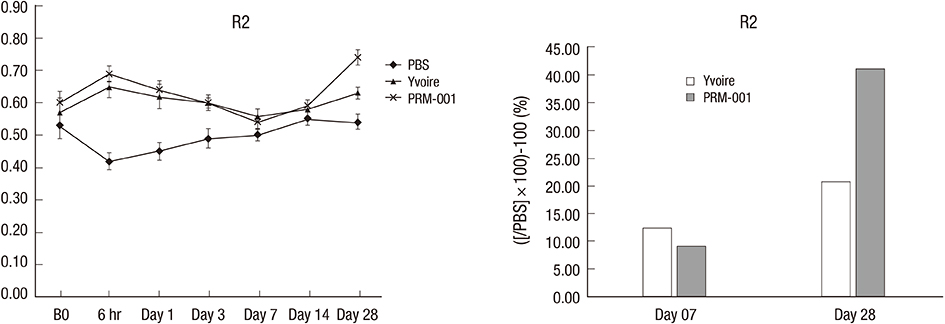
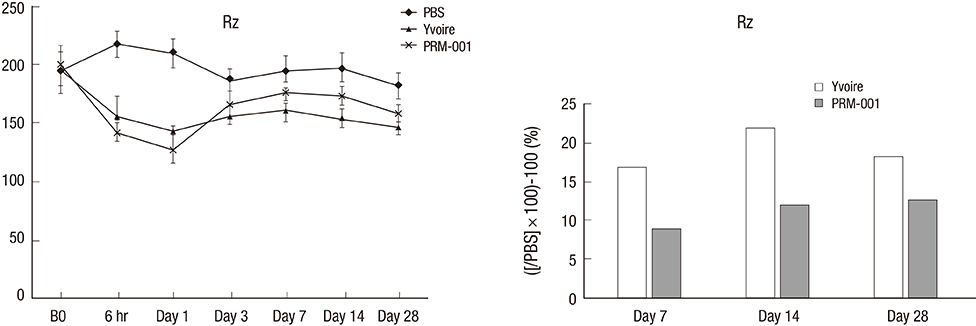
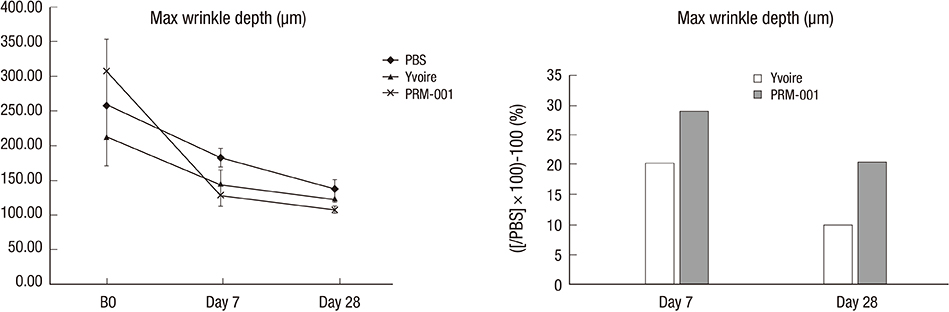
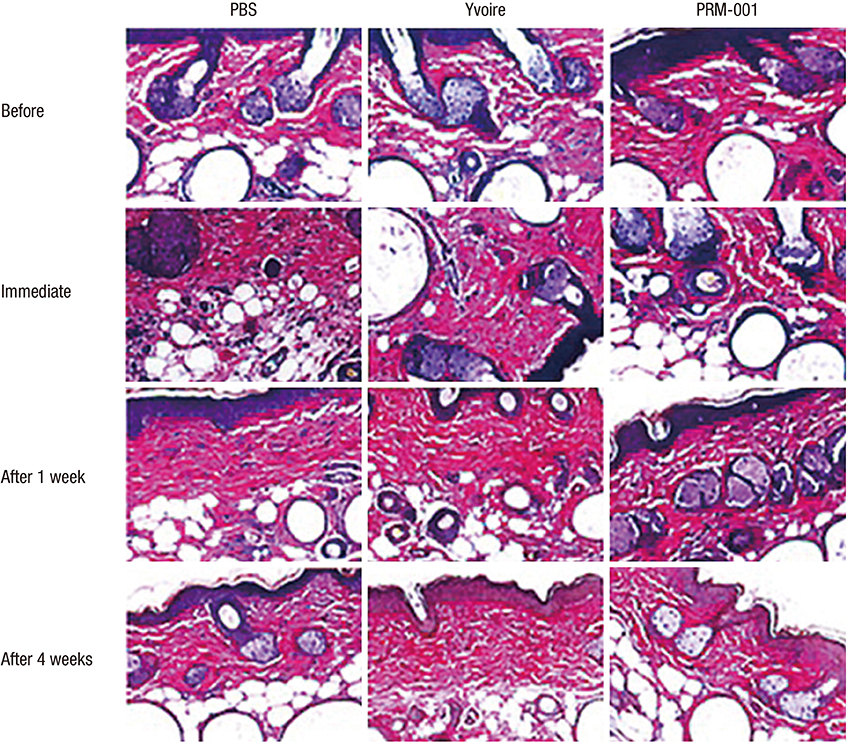
- The Rejuran(R) is a new filler product made from purified polynucleotides. Here we present data from an animal study and a clinical trial to examine the durability, efficacy and safety of the Rejuran(R) on crow's feet. For the animal study, 25 mice were divided into three groups: Group 1 received phosphate buffered saline (PBS); Group 2 were treated with Yvoire(R); and Group 3 were treated with Rejuran(R). The durability and efficacy of each treatment were assessed by microscopy and staining. In the clinical trial, 72 patients were randomized to receive Rejuran(R) treatment for crow's feet on one side and Yvoire-Hydro(R) on the contralateral side, at a ratio of 1:1. Repeated treatments were performed every two weeks for a total of three times, over a total of 12 weeks' observation. All injections and observations of efficacy and safety were performed by the same two investigators. In the animal study, the Rejuran(R) group showed similar durability and inflammatory response to the Yvoire(R) group. Upon efficacy assessment, the Rejuran(R) group showed the greatest elasticity and collagen composition, and a significant difference in skin surface roughness and wrinkle depth. In the clinical trial, the primary and secondary objective efficacy outcome measure showed no statistical significance between the two groups, and in safety outcomes there were no unexpected adverse effects. Our data suggest that the Rejuran(R), as a new regenerative filler, can be useful to reduce wrinkles, by showing evidence for its efficacy and safety.
MeSH Terms
-
Adult
Animals
Dermatologic Surgical Procedures/*methods
Double-Blind Method
Elasticity/drug effects
Female
Humans
Hyaluronic Acid/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Injections, Intradermal
Male
Mice
Middle Aged
Polynucleotides/adverse effects/*therapeutic use
Skin
Skin Aging
Surgery, Plastic/*methods
Treatment Outcome
Wound Healing
Hyaluronic Acid
Polynucleotides
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Treatments of Infra-Orbital Dark Circles by Various Etiologies
Kui Young Park, Hyun Jung Kwon, Choon Shik Youn, Seong Jun Seo, Myeong Nam Kim
Ann Dermatol. 2018;30(5):522-528. doi: 10.5021/ad.2018.30.5.522.
Reference
-
1. Sung HM, Suh IS, Lee HB, Tak KS, Moon KM, Jung MS. Case reports of adipose-derived stem cell therapy for nasal skin necrosis after filler injection. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:51–54.2. Do ER, Shim JS. Long-term complications from breast augmentation by injected polyacrylamide hydrogel. Arch Plast Surg. 2012; 39:267–269.3. Cavallini M, Papagni M. Long chain polynucleotides gel and skin biorevitalization. Int J Plast Dermatol. 2007; 3:27–32.4. Avantaggiato A, Palmieri A, Carinci F, Pasin M, Bertuzzi G. Biostimulation and biorevitalization: effects on human skin fibroblasts. Ann Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2013; 1:11.5. Cavallini M. Biorevitalization and cosmetic surgery of the face: synergies of action. J Appl Cosmetol. 2004; 22:125–132.6. De Aloe G, Rubegni P, Biagioli M, Taddeucci P, Fimiani M. Skin graft donor site and use of polydeoxyribonucleotide as a treatment for skin regeneration: a randomized, controlled, double-blind, clinical trial. Wounds. 2004; 16:258–263.7. Rathbone MP, Christjanson L, Deforge S, Deluca B, Gysbers JW, Hindley S, Jovetich M, Middlemiss P, Takhal S. Extracellular purine nucleosides stimulate cell division and morphogenesis: pathological and physiological implications. Med Hypotheses. 1992; 37:232–240.8. Rubegni P, De Aloe G, Mazzatenta C, Cattarini L, Fimiani M. Clinical evaluation of the trophic effect of polydeoxyribonucleotide (PDRN) in patients undergoing skin explants. A Pilot Study. Curr Med Res Opin. 2001; 17:128–131.9. Squadrito F, Bitto A, Altavilla D, Arcoraci V, De Caridi G, De Feo ME, Corrao S, Pallio G, Sterrantino C, Minutoli L, et al. The effect of PDRN, an adenosine receptor A2A agonist, on the healing of chronic diabetic foot ulcers: results of a clinical trial. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014; 99:E746–E753.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Notice of Retraction: Pak CS, et al. A Phase III, Randomized, Double-Blind, Matched-Pairs, Active-Controlled Clinical Trial and Preclinical Animal Study to Compare the Durability, Efficacy and Safety between Polynucleotide Filler and Hyaluronic Acid Filler in the Correction of Crow's Feet: A New Concept of Regenerative Filler. J Korean Med Sci 2014; 29(Suppl 3): S201-S209
- Hyaluronidase: An overview of its properties, applications, and side effects
- The Stability of the ALSA Plasma Gel Filler and the Hyaluronic Acid Filler in Rabbits
- Comparison of the efficacy and safety between a new monophasic hyaluronic acid filler and a biphasic hyaluronic acid filler in correcting facial wrinkles
- Overview of Filler: Compositions, Effects, Rheological Consideration