J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2015 Dec;17(4):301-312. 10.7461/jcen.2015.17.4.301.
Outcomes of Stent-assisted Coil Embolization of Wide-necked Intracranial Aneurysms Using the Solitaire(TM) AB Neurovascular Remodeling Device
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Busan Baik Hospital, Inje University, Busan, Korea.
- 2Department of Neurosurgery, Kosin University Gospel Hospital, Kosin University College of Medicine, Busan, Korea. peiothmd@daum.net
- KMID: 2150968
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.4.301
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
This retrospective study presents our experience with respect to the clinical and angiographic outcomes of patients treated with stent-assisted coil embolization using Solitaire(TM) AB stents.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
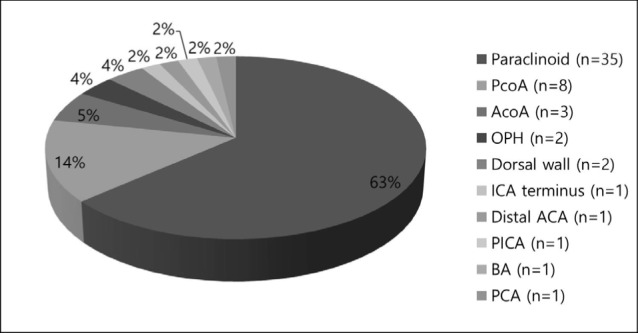
From March 2011 to December 2014, 50 patients with 55 wide-necked and/or complex intracranial aneurysms were evaluated. Four patients presented with an acute subarachnoid hemorrhage. Stent deployment was performed with a standard coiling procedure in 49 aneurysms. Three patients underwent bailout stenting, 2 patients were treated by temporary stenting and one patient was treated only by stenting without coiling for dissecting aneurysm.
RESULTS
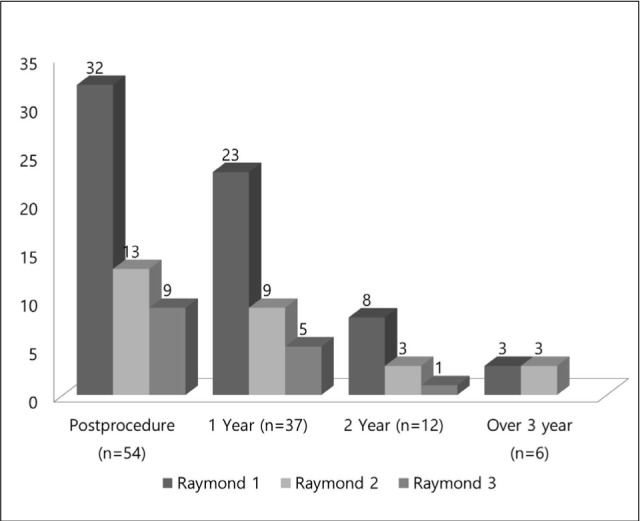
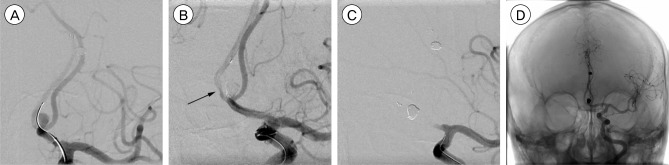
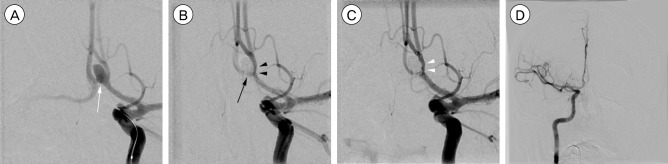
Successful placement of the Solitaire AB stent was achieved in all the cases. Based on the postprocedural angiographic results, a Raymond 1 was obtained in 32 (59%) of 54 aneurysms, excluded by one case of dissecting aneurysm, and a Raymond 2 in 13 (24%), and a Raymond 3 in 9 (17%). There was one thromboembolic (2%) and three hemorrhagic complications (6%). However, procedure-related morbidity or mortality was not found. Annual follow-up angiographic results from the embolization were obtained in 40 (74.1%) of 54 cases. These results were represented as Raymond 1 in 27 (67.5%), class 2 in 9 (22.5%), and class 3 in 4 (10%) cases. Angiographic improvement associated with progressive thrombosis of the aneurysm was obtained in 10 aneurysms. Four aneurysms were recanalized without requiring additional treatment. In-stent stenosis was found in one aneurysm, but stent migration was not seen on follow-up angiography.
CONCLUSION
Stent-assisted coil embolization using the Solitaire AB stent for treating wide-necked and/or complex intracranial aneurysms was found to be safe and effective immediately post-embolization and after follow-up. Long-term follow-up will be required to identify the effect of the Solitaire AB stent on recanalization rates.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Selective Temporary Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization for Intracranial Wide-Necked Small Aneurysms Using Solitaire AB Retrievable Stent
Han Yong Heo, Jae Guen Ahn, Cheol Ji, Won Ki Yoon
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2019;62(1):27-34. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2018.0064.
Reference
-
1. Akpek S, Arat A, Morsi H, Klucznick RP, Strother CM, Mawad ME. Self-expandable stent-assisted coiling of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms: a single-center experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 5. 26(5):1223–1231. PMID: 15891189.2. Almekhlafi MA, Hockley A, Wong JH, Goyal M. Temporary Solitaire stent neck remodeling in the coiling of ruptured aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2013; 11. 5(Suppl 3):iii76–iii78. PMID: 23749789.
Article3. Benitez RP, Silva MT, Klem J, Veznedaroglu E, Rosenwasser RH. Endovascular occlusion of wide-necked aneurysms with a new intracranial microstent (Neuroform) and detachable coils. Neurosurgery. 2004; 6. 54(6):1359–1367. discussion 1368PMID: 15157292.
Article4. Biondi A, Janardhan V, Katz JM, Salvaggio K, Riina HA, Gobin YP. Neurofrom stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms: strategies in stent deployment and midterm follow-up. Neurosurgery. 2007; 9. 61(3):460–468. discussion 468-9PMID: 17881956.5. Byrne JV, Sohn MJ, Molyneux AJ, Chir B. Five-year experience in using coil embolization for ruptured intracranial aneurysms: outcomes and incidence of late rebleeding. J Neurosurg. 1999; 4. 90(4):656–663. PMID: 10193610.
Article6. Canton G, Levy DI, Lasheras JC. Hemodynamic changes due to stent placement in bifurcating intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2005; 7. 103(1):146–155. PMID: 16121985.7. Clajus C, Sychra V, Strasilla C, Klisch J. Stent-assisted coil embolization of intracranial aneurysms using the Solitaire™ AB neurovascular remodeling device: initial and midterm follow-up results. Neuroradiology. 2013; 5. 55(5):629–638. PMID: 23386222.
Article8. Cloft HJ, Joseph GJ, Tong FC, Goldstein JH, Dion JE. Use of three-dimensional Guglielmi detachable coils in the treatment of wide-necked cerebral aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2000; 8. 21(7):1312–1314. PMID: 10954285.9. Cognard C, Weill A, Spelle L, Piotin M, Castaings L, Rey A, et al. Long-term angiographic follow-up of 169 intracranial berry aneurysms occluded with detachable coils. Radiology. 1999; 8. 212(2):348–356. PMID: 10429689.
Article10. Cui YF, Xu H, Liu HT, Wang Y. Clinical application of solitaire AB stents in the embolization of intracranial aneurysms. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2015; 4. 19(7):1227–1233. PMID: 25912582.11. Debrun GM, Aletich VA, Kehrli P, Misra M, Ausman JI, Charbel F. Selection of cerebral aneurysms for treatment using Guglielmi detachable coils: the preliminary University of Illinois at Chicago experience. Neurosurgery. 1998; 12. 43(6):1281–1295. discussion 1296-7PMID: 9848841.
Article12. de Paula Lucas C, Piotin M, Spelle L, Moret J. Stent-jack technique in stent-assisted coiling of wide-neck aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2008; 5. 62(5 Suppl 2):ONS414–ONS416. discussion ONS416-7PMID: 18596523.13. Fessler RD, Ringer AJ, Qureshi AI, Guterman LR, Hopkins LN. Intracranial stent placement to trap an extruded coil during endovascular aneurysm treatment: technical note. Neurosurgery. 2000; 1. 46(1):248–251. discussion 251-3PMID: 10626961.
Article14. Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Han P, MacDougrall C. Preliminary experience using the Neuroform stent for the treatment of cerebral aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2004; 1. 54(1):6–16. discussion 16-7PMID: 14683536.
Article15. Fiorella D, Albuquerque FC, Woo H, Rasmussen PA, Masaryk TJ, McDougall CG. Neuroform in-stent stenosis: incidence, natural history, and treatment strategies. Neurosurgery. 2006; 7. 59(1):34–42. discussion 34-42PMID: 16823298.
Article16. Gory B, Klisch J, Bonafé A, Mounayer C, Beaujeux R, Moret J, et al. Solitaire AB stent-assisted coiling of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms: mid-term results from the SOLARE study. Neurosurgery. 2014; 9. 75(3):215–219. discussion 219PMID: 24818784.17. Gu DQ, Zhang X, Luo B, Long XA, Duan CZ. The effect of Neuroform stent-assisted coil embolization of wide-necked intracranial aneurysms and clinical factors on progressive aneurysm occlusion on angiographic follow-up. J Clin Neurosci. 2013; 2. 20(2):244–247. PMID: 23201094.
Article18. Hong B, Patel NV, Gounis MJ, DeLeo MJ 3rd, Linfante I, Wojak JC, et al. Semi-jailing technique for coil embolization of complex, wide-necked intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 2009; 12. 65(6):1131–1138. discussion 1138-9PMID: 19934972.
Article19. Huang QH, Liu JM, Yang PF, Hong B, Xu Y. Endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysm using stenting after coiling technique. Chin J Cerebrovasc Disc (Electronic Edition). 2009; 3:208–213.20. Kim YW, Park IS, Baik MW, Jo KW. Endovascular treatment of blood blister-like aneurysms using multiple self-expanding stents. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2011; 2. 49(2):116–119. PMID: 21519501.
Article21. King B, Vaziri S, Singla A, Fargen KM, Mocco J. Clinical and angiographic outcomes after stent-assisted coiling of cerebral aneurysms with Enterprise and Neuroform stents: a comparative analysis of the literature. J Neurointerv Surg. 2015; 12. 7(12):905–909. PMID: 25352581.
Article22. Klisch J, Clajus C, Synchra V, Eger C, Strasilla C, Rosahl S, et al. Coil embolization of anterior circulation aneurysms supported by the Solitaire AB neurovascular remodeling device. Neuroradiology. 2010; 5. 52(5):349–359. PMID: 19644683.
Article23. Klisch J, Eger C, Sychra V, Strasilla C, Basche S, Weber J. Stent-assisted coil embolization of posterior circulation aneurysms using Solitaire AB: preliminary experience. Neurosurgery. 2009; 8. 65(2):258–266. discussion 266PMID: 19625903.24. Lee JI, Ko JK, Lee TH, Choi CH, Lee SW, Cho WH. Sole stenting technique for the treatment of uncoilable very small aneurysms in the intracranial internal carotid artery. Neurol Med Chir (Tokyo). 2013; 53(5):310–317. PMID: 23708222.
Article25. Lee SY, Chae KS, Rho SJ, Choi HK, Park HS, Ghang CG. Clinical and angiographic outcomes of wide-necked aneurysms treated with the Solitaire AB stent. J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg. 2013; 9. 15(3):158–163. PMID: 24167794.
Article26. Li CH, Su XH, Zhang B, Han YF, Zhang EW, Yang L, et al. The stent-assisted coil-jailing technique facilitates efficient embolization of tiny cerebral aneurysms. Korean J Radiol. 2014; Nov-Dec. 15(6):850–857. PMID: 25469099.
Article27. Lieber BB, Gounis MJ. The physics of endoluminal stenting in the treatment of cerebrovascular aneurysms. Neurol Res. 2002; 24(Suppl 1):S33–S42. PMID: 12074435.
Article28. Lubicz B, Fran . 231;ois O, Levivier M, Brotchi J, Balériaux D. Preliminary experience with the Enterprise stent for endovascular treatment of complex intracranial aneurysms: Potential advantages and limiting characteristics. Neurosurgery. 2008; 5. 62(5):1063–1069. discussion 1069-70PMID: 18580804.29. Luo CB, Chang FC, Teng MM, Guo WY, Chang CY. Stent management of coil herniation in embolization of internal carotid aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 11. 29(10):1951–1955. PMID: 18719031.
Article30. Lv X, Li Y, Xinjian Y, Jiang C, Wu Z. Results of endovascular treatment for intracranial wide-necked saccular and dissecting aneurysms using the enterprise stent: A single center experience. Eur J Radiol. 2012; 6. 81(6):1179–1183. PMID: 21546179.
Article31. Lylyk P, Ferrario A, Pasbon B, Miranda C, Doroszuk G. Buenos Aires experience with the Neuroform self-expanding stent for the treatment of intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2005; 2. 102(2):235–241. PMID: 15739550.
Article32. Malek AM, Higashida RT, Phatouros CC, Dowd CF, Halbach VV. Treatment of an intracranial aneurysm using a new three-dimensional-shape Guglielmi detachable coil: technical case report. Neurosurgery. 1999; 5. 44(5):1142–1144. discussion 1144-5PMID: 10232552.
Article33. Mangiafico S, Guarnieri G, Consoli A, Ambrosanio G, Muto M. Endovascular strategy for unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Eur J Radiol. 2013; 10. 82(10):1638–1645. PMID: 23238358.
Article34. Martínez-Gáldamez M, Saura P, Aaura J, Martínez A, De Campos JM, Pérez A. Y-stent-assisted coil embolization of anterior circulation aneurysms using two Solitaire AB devices: a single center experience. Interv Neuroradiol. 2012; 6. 18(2):158–163. PMID: 22681730.
Article35. Mocco J, Snyder KV, Albuquerque FC, Bendok BR, Alan SB, Carpenter JS, et al. Treatment of intracranial aneurysms with the Enterprise stent: A multicenter registry. J Neurosurg. 2009; 1. 110(1):35–39. PMID: 18976057.
Article36. Moret J, Cognard C, Weill A, Castaings L, Rey A. Reconstruction technique in the treatment of wide-neck intracranial aneurysms. Long-term angiographic and clinical results. Apropos of 56 cases. J Neuroradiol. 1997; 6. 24(1):30–44. PMID: 9303942.37. Pandey AS, Koebbe C, Rosenwasser RH, Veznedaroglu E. Endovascular coil embolization of ruptured and unruptured posterior circulation aneurysms: Review of a 10-year experience. Neurosurgery. 2007; 4. 60(4):626–636. discussion 636-7PMID: 17415199.38. Park HK, Horowitz M, Jungreis C, Genevro J, Koebbe C, Levy E, et al. Periprocedural morbidity and mortality associated with endovascular treatment of intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2005; 3. 26(3):506–514. PMID: 15760857.39. Pelz DM, Lownie SP, Fox AJ. Thromboembolic events associated with the treatment of cerebral aneurysms with Guglielmi detachable coils. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1998; 9. 19(8):1541–1547. PMID: 9763391.40. Phatouros CC, McConachie NS, Jaspan T. Post-procedure migration of Guglielmi detachable coils and mechanical detachable spirals. Neuroradiology. 1999; 5. 41(5):324–327. PMID: 10379587.
Article41. Raymond J, Roy D. Safety and efficacy of endovascular treatment of acutely ruptured aneurysms. Neurosurgery. 1997; 12. 41(6):1235–1245. discussion 1245-6PMID: 9402574.
Article42. Schutz A, Solymosi L, Vince GH, Bendszus M. Proximal stent fixation of fractured coils: technical note. Neuroradiology. 2005; 11. 47(11):874–878. PMID: 16142481.
Article43. Signorelli F, Gory B, Turjman F. Temporary Solitaire stent-assisted coiling: a technique for the treatment of acutely ruptured wide-neck intracranial aneurysms. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2014; 5. 35(5):984–988. PMID: 24335544.
Article44. Spiotta AM, Wheeler AM, Smithason S, Hui F, Moskowitz S. Comparison of techniques for stent assisted coil embolization of aneurysms. J Neurointerv Surg. 2012; 9. 4(5):339–344. PMID: 21990514.
Article45. Sychra V, Klisch J, Werner M, Dettenborn C, Petrovitch A, Strasilla C, et al. Waffle-cone technique with Solitaire™ AB remodeling device: endovascular treatment of highly selected complex cerebral aneurysms. Neuroradiology. 2011; 12. 53(12):961–972. PMID: 20821314.
Article46. Vinuela F, Duckwiler G, Maward M. Guglielmi detachable coil embolization of acute intracranial aneurysm: perioperative anatomical and clinical outcome in 403 patients. J Neurosurg. 1997; 3. 86(3):475–482. PMID: 9046305.47. Wu Z, Lu X, Yang X, He H. Ruptured vertebra-inferioposterior cerebellar artery dissecting aneurysm treated with the Neuroform stent deployment and vertebral artery occlusion. Eur J Radiol Extra. 2009; 70:e100–e103.48. Yavuz K, Geyik S, Pamuk AG, Koc O, Saatci I, Cekirqe HS. Immediate and midterm follow-up results of using an electrodetachable, fully retrievable SOLO stent system in the endovascular coil occlusion of wide-necked cerebral aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2007; 7. 107(1):49–55. PMID: 17639873.
Article49. Ye HW, Liu YQ, Wang QJ, Zheng T, Cui XB, Gao YY, et al. Comparison between Solitaire™ AB and Enterprise stent-assisted coiling for intracranial aneurysms. Exp Ther Med. 2015; 7. 10(1):145–153. PMID: 26170926.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes of Wide-necked Aneurysms Treated with the Solitaire AB Stent
- Selective Temporary Stent-Assisted Coil Embolization for Intracranial Wide-Necked Small Aneurysms Using Solitaire AB Retrievable Stent
- Solitaire AB Stent-Assisted Coiling of Wide-Neck Micro Aneurysms
- A Complicated Case of Endovascular Stent Assisted Coil Embolization of an Aneurysm
- Endovascular Treatment of Wide-Necked Intracranial Aneurysms : Techniques and Outcomes in 15 Patients