Hanyang Med Rev.
2015 Feb;35(1):18-22. 10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.18.
Searching Medical Literature Effectively
- Affiliations
-
- 1Institute for Evidence-based Medicine, Department of Preventive Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. moole@korea.ac.kr
- 2Department of Preventive Medicine, Korea University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2149100
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.18
Abstract
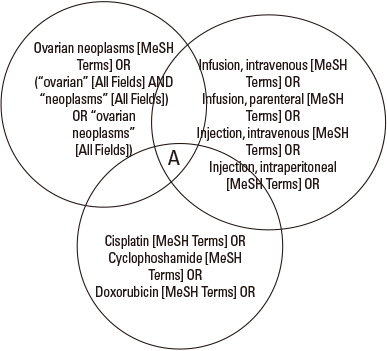
- To make updated and unbiased answers to a clinical question, it is essential to effectively and efficiently search the medical literature. The goal of medical literature searching is comprehensive and transparent and is a replicable procedure to get correct conclusions to the question. To do this, each user should make well formulated clinical questions, and have knowledge on what specific characteristics each database has. There are several readily accessible English databases that provide literature information including PubMed, EMBASE, and CINAHL. The Korean medical literature database including Koreamed and KMBase are also available. Users can search information through formulated search terms such as in MeSH in Pubmed. Skills in finding and using search terms are essential in effective searching. Also knowledge on using filters is frequently needed to search database quickly for articles on several study designs. After running a search in the database, one needs to retrieve search results effectively. In comprehensive literature search, especially for writing a systematic review, one needs to include literature to overcome and minimize publication bias. This process often requires searching in gray literature, and the common types and sources of publication bias are described. Finally, we need to constantly validate search results, and revise the search through a continuous process. In this article, the basic concepts and procedures of searching medical literature are described.
Keyword
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Why Perform Meta-Analysis?
Woo Jong Shin
Hanyang Med Rev. 2015;35(1):1-2. doi: 10.7599/hmr.2015.35.1.1.
Reference
-
1. U.S National Library of Medicine. [Internet]. (USA): NLM, Fact Sheets, MEDLINE® (May 7, 2014). c2014. cited 2014 December 8. Available from: http://www.nlm.nih.gov/pubs/factsheets/medline.html/.2. ELSEVIER. [Internet]. (USA): Embase Biomedical Database. c2014. cited 2014 December 8. Available from: http://www.elsevier.com/online-tools/embase/training-and-support#faqs/.3. The Cochrane Library. [Internet]. About the Cochrane Library. c2014. cited 2014 December 8. Available from: http://www.cochranelibrary.com/about/about-the-cochrane-library.html/.4. Higgins JP, Green S. Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of interventions version 5.1.0. The Cochrane Collaboration;2011. updated March 2011.5. Hopewell S, McDonald S, Clarke M, Egger M. Grey literature in meta-analyses of randomized trials of health care interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; Mr000010.
Article6. Hopewell S, Clarke M, Lefebvre C, Scherer R. Handsearching versus electronic searching to identify reports of randomized trials. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007; Mr000001.
Article7. Glanville JM, Lefebvre C, Miles JN, Camosso-Stefinovic J. How to identify randomized controlled trials in MEDLINE: ten years on. J Med Libr Assoc. 2006; 94:130–136.8. Dickersin K. The existence of publication bias and risk factors for its occurrence. JAMA. 1990; 263:1385–1389.
Article9. Ioannidis JP. Effect of the statistical significance of results on the time to completion and publication of randomized efficacy trials. JAMA. 1998; 279:281–286.
Article10. Manzoli L, Flacco ME, D'Addario M, Capasso L, De Vito C, Marzuillo C, et al. Non-publication and delayed publication of randomized trials on vaccines: survey. BMJ. 2014; 348.
Article11. Ross JS, Mulvey GK, Hines EM, Nissen SE, Krumholz HM. Trial Publication after Registration in ClinicalTrials.gov: a cross-sectional analysis. PLoS Med. 2009; 6:e1000144.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Computer Program for Searching the Korean Journal of Urology
- The Effect and Applicability of Anatographic for Anatomy Education
- DNA Database Searching Using Genetic Relationship
- Retrieval of Articles in Personal Computer
- Comparison of the Utility of Korean Bibliographic Databases for Searching Domestic Literature Related to Microbiology and Infectious Diseases