Korean J Lab Med.
2006 Feb;26(1):27-31. 10.3343/kjlm.2006.26.1.27.
Characterization of a Toxin A-Negative, Toxin B-Positive Variant Strain of Clostridium difficile
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Sanggye Paik Hospital, Inje University, Seoul, Korea. bmshin@unitel.co.kr
- KMID: 2143193
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/kjlm.2006.26.1.27
Abstract
-
BACKGROUND: Clostridium difficile is one of the most important pathogens responsible for nosocomial diarrhea. Recently, we have frequently experienced culture positive, toxin A enzyme immunoassay negative strains. Therefore, we evaluated the strains with several PCR primer sets to characterize them.
METHODS
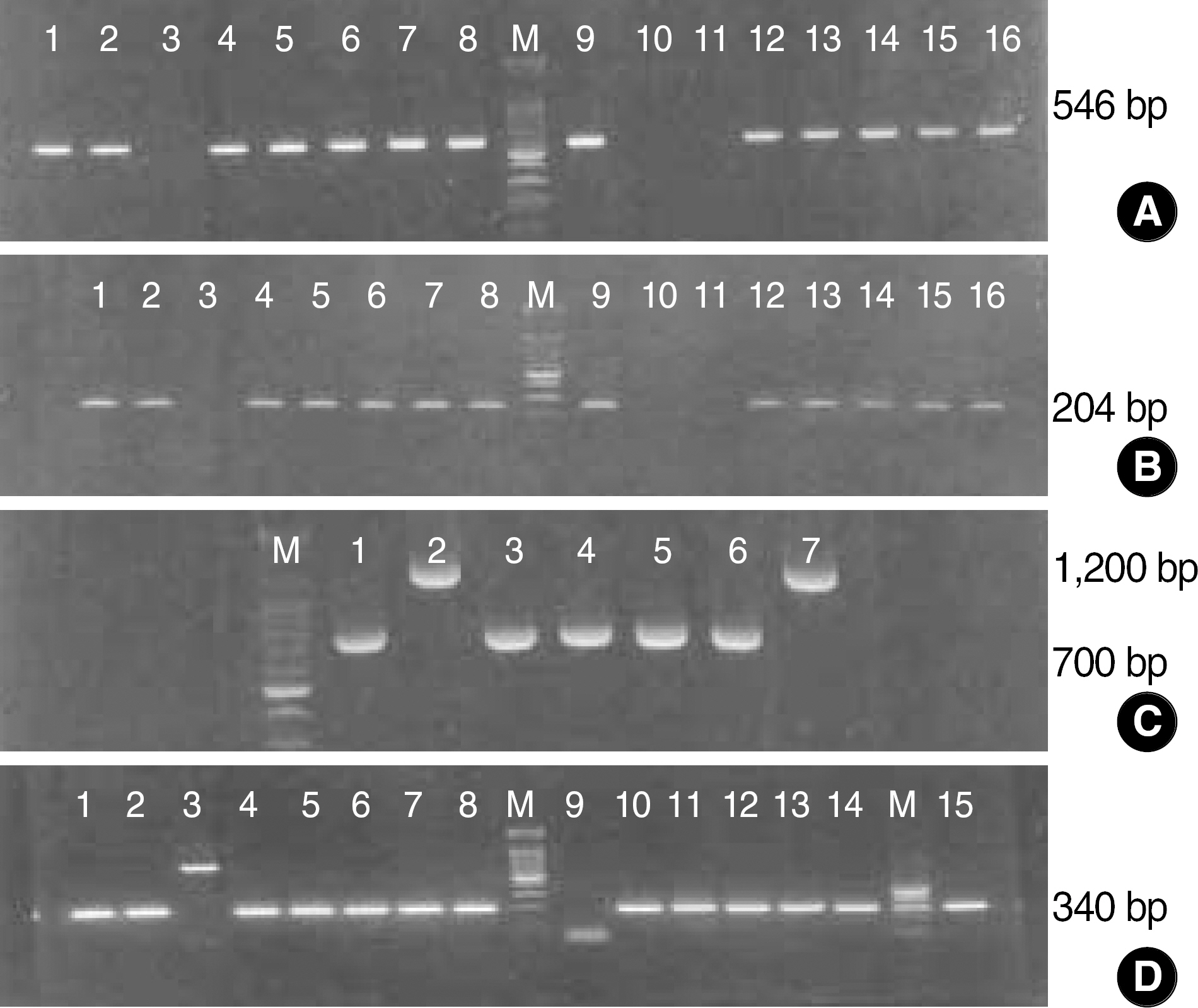
A total of 351 stool specimens were examined for toxin A using enzyme linked fluorescent immunoassay (ELFA) and also cultured for C. difficile using cycloserine cefoxitine fructose agar incubated under anaerobic conditions. Spore stain and Vitek ANA identification card (BioMerieux, France) were used for identification of C. difficile. We amplified toxin A and toxin B genes in 81 isolates using primers NK1- NK2, NK3-NK2, NK9- NK11, and NK104-NK105.
RESULTS
The concordance rate between ELFA and culture was 65.2% (229/351). PCR for the toxin A gene using NK1-NK2, NK3-NK2 and for the toxin B gene using NK104-NK105 showed almost the same results. However, toxin A gene PCR using NK9-NK11 showed that 45.7% (37/81) of the evaluated strains were toxin A (-)/ toxin B(+) variant strains; thus, the corrected sensitivity and specificity of the ELFA based on the PCR results for toxin A and B genes were 65.6% and 100%, respectively.
CONCLUSIONS
The low sensitivity of the ELFA results for toxin A was due to the toxin A(-)/toxin B(+) variants of C. difficile, suggesting that the prevalence of the variant strains could be higher in Korea than was expected.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
References
1. Bartlett JG. Antibiotic-associated diarrhea. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:334–9.
Article2. Wilkins TD, Lyerly DM. Clostirdium difficile testing: after 20 years, still challenging. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:531–4.3. Shanholtzer CJ, Willard KE, Holter JJ, Olson MM, Gerding DN, Peterson LR. Comparison of the Vidas Clostridium difficile toxin A immunoassay with C. difficile culture and cytotoxin and latex tests. J Clin Microbiol. 1992; 30:1837–40.4. Staneck JL, Weckbach LS, Allen SD, Siders JA, Gilligan PH, Coppitt G, et al. Multicenter evaluation of four methods for Clostridium difficile detection: Immunocard C. difficile, cytotoxin assay, culture and latex agglutination. Clin Microbiol. 1996; 34:2718–21.5. Fedorko D, Engler HD, O'Shaughnessy EM, Williams EC, Reicheldereer CJ, Smith WI. Evaluation of two rapid assays for detection of Clostridium difficile toxin A in stool specimens. J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 37:3044–7.6. Peterson LR, Olson MM, Shanholtzer CJ, Gerding DN. Results of a prospective, 18-month clinical evaluation of culture, cytotoxin testing, and culturerette brand (CDT) latex testing in the diagnosis of Clostridium diffcile-associted diarrhea. Diag Microbiol Infect Dis. 1988; 10:85–91.7. Kelly MT, Champagne SG, Sherlock CH, Noble MA, Freeman HJ, Smith JA. Commercial latex agglutination test for detection of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 1987; 25:1244–7.8. Lyerly DM, Neville LM, Evans DT, Fill J, Allen S, Greene W, et al. Multicenter evaluation of the Clostidium difficile TOX A/B test. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:184–90.9. Shin BM, Kim EC. SDS-PAGE profiles of Clostridium difficile isolated from patients and hospital environments. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1992; 12:223–32.10. Lee HJ, Chung Y. Toxin test and quantitative culture of stool for the diagnosis of Clostridium difficile associated diseases. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1993; 13:461–6.11. Kang JO, Chae JD, Eom JI, Han D, Park PW, Park IK, et al. Comparison of Clostridium difficile toxin A immunoassay with cytotoxicity assay. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 3:43–7.12. Lee SH, Pai CH. Clinical significance of VIDAS Clostridium difficile toxin A immunoassay. Korean J Clin Pathol. 1996; 16:563–9.13. Yong D, Lee HM, Ryu JH, Roh KH, Kim WH, Lee K, et al. Evaluation of quantitative culture of Clostridium difficile from fecal specimens for the diagnosis of C. difficile-associated disease. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2002; 5:124–8.14. Kato H, Kato N, Watanabe K, Iwai N, Nakamura H, Yamamoto T, et al. Identification of toxin A negative, toxin B positive Clostridium difficile by PCR. J Clin Microbiol. 1998; 36:2178–82.15. Harris AD, Samore MH, Lipsitch M, Kaye KS, Perencevich E, Carmeli Y. Control-group selection importance in studies of antimicrobial resistance: examples applied to Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Enterococci, and Escherichia coli. Clin Infect Dis. 2002; 15:1558–63.16. Shin BM, Lee EJ. Comparison of toxin A enzyme linked fluorescence assay and latex agglutination based on Clostridium difficile culture and toxin A and B PCR assay. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 2005; 8:130–5.17. Barbut F, Lalande V, Burghoffer B, Thien HV, Grimprel E, Petit JC. Prevalence and genetic characterization of toxin A variant strains of Clostridium difficile among adults and children with diarrhea in France. J Clin Microbiol. 2002; 40:2079–83.18. Frey SM, Wilkins TD. Localization of two epitopes recognized by monoclonal antibody PCG-4 on Clostridium difficile toxin A. Infect. Immun. 1992; 60:2488–92.19. Braun V, Hundsberger T, Leukel P, Sauerborn M, von Eichel-Streiber C. Definition of the single integration site of the pathogenicity locus in Clostridium difficile. Gene. 1996; 181:29–38.20. Brazier JS, Stubbs SLJ, Duerden BI. Prevalence of toxin A-negative/toxin B-positive Clostridium difficile strains. J Hospital Infect. 1992; 42:248–9.21. Alfa MJ, Kabani A, Lyerly D, Moncrief S, Neville LM, Al-Barrack A, et al. Characterization of a toxin A-negative, toxin B-positive strain of Clostridium difficile responsible for a nosocomial outbreak of Clostridium difficile-associated diarrhea. J Clin Microbiol. 2000; 38:2706–14.22. Rupnik M, Kato N, Grabnar M, Kato H. New types of toxin A-negative, toxin B-Positive strains among Clostridium difficile isolates from Asia. J Clin Microbiol. 2003; 41:1118–25.23. Lee HM, Kim YA, Park KI, Lee KW, Chung Y. Detection of toxin B gene of Clostridium difficile by polymerase chain reaction from clinical isolates. Korean J Clin Microbiol. 1999; 2:77–81.24. Chung Y, Chung GT, Seong WK, Oh HB. Molecular analysis of Clostridium difficile isolates by arbitrarily primed-polymerase chain reaction and polymerase chain reaction-ribotyping. Korean J Infect Dis. 2002; 34:167–75.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Two Enzyme Immunoassays for Clostridium difficile Toxin A
- Comparison of Two Enzyme Immunoassay for Detection of Clostridium difficile Toxin A and Toxin B
- Comparison of Simultaneous Use of C. DIFF QUIK CHEK and VIDAS C. difficile Toxin A&B to detect C. difficile in Fecal Specimen
- Clinical and Microbiologic Characteristics of Clostridium difficile Infection Caused by Binary Toxin Producing Strain in Korea
- A Case of Clostridium difficile Pseudomembranous Colitis