J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2013 Nov;54(5):399-404. 10.3340/jkns.2013.54.5.399.
Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases from Breast Cancer
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jilee@skku.edu
- 2Division of Hematology-Oncology, Department of Medicine, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2138355
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2013.54.5.399
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
The authors conducted a retrospective cohort study to determine prognostic factors and treatment outcomes of brain metastases (BM) from breast cancer (BC) after Gamma Knife radiosurgery (GKS).
METHODS
Pathologic and clinical features, and outcomes were analyzed in a cohort of 62 patients with BM from BC treated by GKS. The Kaplan-Meier method, the log-rank test, and Cox's proportional hazards model were used to assess prognostic factors.
RESULTS
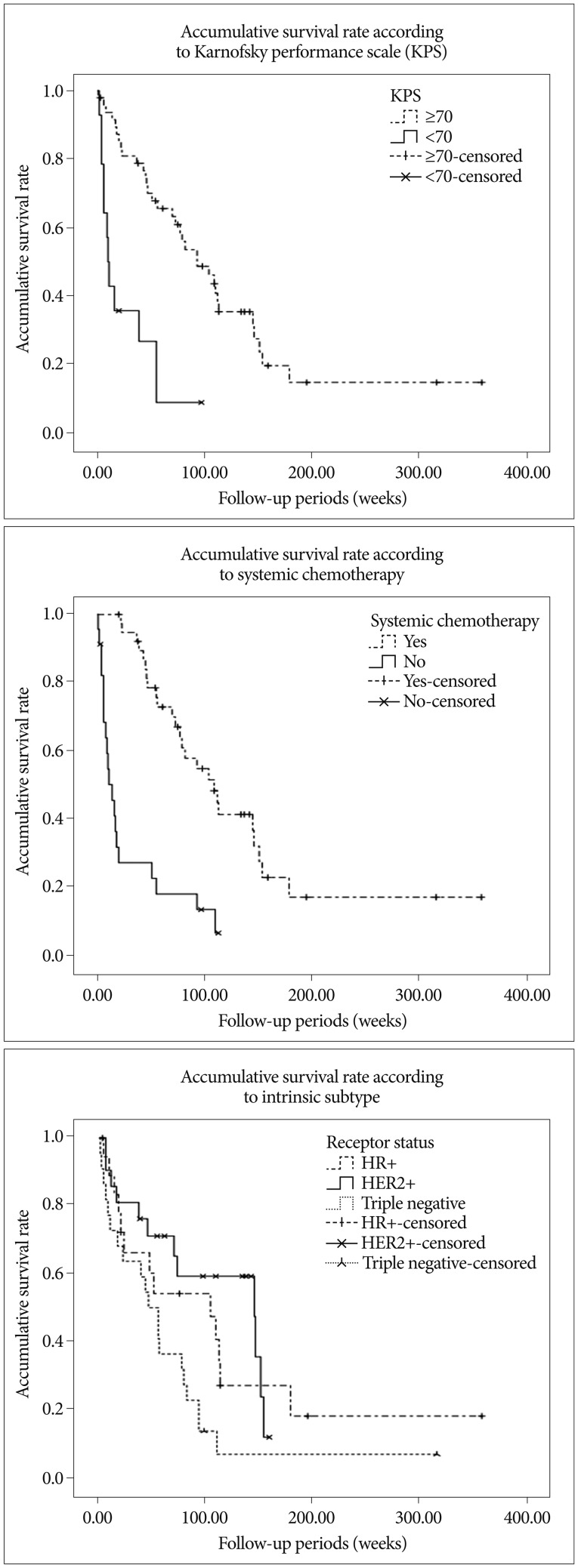
Median survival after GKS was 73.0 weeks (95% confidence interval, 46.0-100.1). HER2+ [hazard ratio (HR) 0.441; p=0.045], Karnofsky performance scale (KPS) > or =70 (RR 0.416; p=0.050) and systemic chemotherapy after GKS (RR 0.282; p=0.001) were found to be a favorable prognostic factor of overall survival. Actuarial local control (LC) rate were 89.5+/-4.5% and 70.5+/-6.9% at 6 and 12 months after GKS, respectively. No prognostic factors were found to affect LC rate. Uni- and multivariate analysis revealed that the distant control (DC) rate was higher in patients with; a small number (< or =3) of metastasis (HR 0.300; p=0.045), no known extracranial metastasis (p=0.013, log-rank test), or the HER2+ subtype (HR 0.267; p=0.027). Additional whole brain radiation therapy and metastasis volume were not found to be significantly associated with LC, DC, or overall survival.
CONCLUSION
The treatment outcomes of patients with newly diagnosed BM from BC treated with GKS could be affected primarily by intrinsic subtype, KPS, and systemic chemotherapy. Therapeutic strategy and prognosis scoring system should be individualized based on considerations of intrinsic subtype in addition to traditionally known parameters related to stereotactic radiosurgery.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Efficacy and Safety of Fractionated Stereotactic Radiosurgery for Large Brain Metastases
Won Joo Jeong, Jae Hong Park, Eun Jung Lee, Jeong Hoon Kim, Chang Jin Kim, Young Hyun Cho
J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2015;58(3):217-224. doi: 10.3340/jkns.2015.58.3.217.
Reference
-
1. Aoyama H. Radiation therapy for brain metastases in breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer. 2011; 18:244–251. PMID: 20458564.
Article2. Chang EL, Wefel JS, Hess KR, Allen PK, Lang FF, Kornguth DG, et al. Neurocognition in patients with brain metastases treated with radiosurgery or radiosurgery plus whole-brain irradiation : a randomised controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 2009; 10:1037–1044. PMID: 19801201.
Article3. Duchnowska R, Dziadziuszko R, Czartoryska-Arłukowicz B, Radecka B, Szostakiewicz B, Sosińska-Mielcarek K, et al. Risk factors for brain relapse in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer patients. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2009; 117:297–303. PMID: 19130219.
Article4. Eichler AF, Kuter I, Ryan P, Schapira L, Younger J, Henson JW. Survival in patients with brain metastases from breast cancer : the importance of HER-2 status. Cancer. 2008; 112:2359–2367. PMID: 18361426.
Article5. Gabos Z, Sinha R, Hanson J, Chauhan N, Hugh J, Mackey JR, et al. Prognostic significance of human epidermal growth factor receptor positivity for the development of brain metastasis after newly diagnosed breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2006; 24:5658–5663. PMID: 17102066.
Article6. Golden DW, Lamborn KR, McDermott MW, Kunwar S, Wara WM, Nakamura JL, et al. Prognostic factors and grading systems for overall survival in patients treated with radiosurgery for brain metastases : variation by primary site. J Neurosurg. 2008; 109(Suppl):77–86. PMID: 19123892.
Article7. Goyal S, Prasad D, Harrell F Jr, Matsumoto J, Rich T, Steiner L. Gamma knife surgery for the treatment of intracranial metastases from breast cancer. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103:218–223. PMID: 16175849.
Article8. Gu HW, Sohn MJ, Lee DJ, Lee HR, Lee CH, Whang CJ. Clinical analysis of novalis stereotactic radiosurgery for brain metastases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2009; 46:245–251. PMID: 19844626.
Article9. Le Scodan R, Massard C, Mouret-Fourme E, Guinebretierre JM, Cohen-Solal C, De Lalande B, et al. Brain metastases from breast carcinoma : validation of the radiation therapy oncology group recursive partitioning analysis classification and proposition of a new prognostic score. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 2007; 69:839–845. PMID: 17544592.
Article10. Lee S, Ahn HK, Park YH, Nam DH, Lee JI, Park W, et al. Leptomeningeal metastases from breast cancer : intrinsic subtypes may affect unique clinical manifestations. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011; 129:809–817. PMID: 21785952.
Article11. Liu MT, Hsieh CY, Wang AY, Chang TH, Pi CP, Huang CC, et al. Prognostic factors affecting the outcome of brain metastases from breast cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2006; 14:936–942. PMID: 16575571.
Article12. Matsumoto K, Ando M, Yamauchi C, Egawa C, Hamamoto Y, Kataoka M, et al. Questionnaire survey of treatment choice for breast cancer patients with brain metastasis in Japan : results of a nationwide survey by the task force of the Japanese Breast Cancer Society. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2009; 39:22–26. PMID: 19008214.
Article13. Monje ML, Palmer T. Radiation injury and neurogenesis. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003; 16:129–134. PMID: 12644738.
Article14. Nieder C, Marienhagen K, Astner ST, Molls M. Prognostic scores in brain metastases from breast cancer. BMC Cancer. 2009; 9:105. PMID: 19351389.
Article15. Ono M, Ando M, Yunokawa M, Nakano E, Yonemori K, Matsumoto K, et al. Brain metastases in patients who receive trastuzumab-containing chemotherapy for HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Int J Clin Oncol. 2009; 14:48–52. PMID: 19225924.
Article16. Park IH, Ro J, Lee KS, Nam BH, Kwon Y, Shin KH. Trastuzumab treatment beyond brain progression in HER2-positive metastatic breast cancer. Ann Oncol. 2009; 20:56–62. PMID: 18664558.
Article17. Park YH, Park MJ, Ji SH, Yi SY, Lim DH, Nam DH, et al. Trastuzumab treatment improves brain metastasis outcomes through control and durable prolongation of systemic extracranial disease in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer patients. Br J Cancer. 2009; 100:894–900. PMID: 19240719.
Article18. Siu TL, Jeffree RL, Fuller JW. Current strategies in the surgical management of cerebral metastases : an evidence-based review. J Clin Neurosci. 2011; 18:1429–1434. PMID: 21868230.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Clinical Analysis of Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases
- Gamma Knife Surgery for Brain Metastases from Breast Carcinoma
- How to use Leksell GammaPlan
- A Case of Brain Metastases from Advanced Ovarian Cancer
- Letters to the Editor: Gamma Knife Radiosurgery for Brain Metastases in Patients Harboring Four or More Lesions : Survival and Prognostic Factors