Clin Endosc.
2012 Nov;45(4):435-439.
One Case of Common Bile Duct Cancer Mimicking Cystic Neoplasm of the Pancreas, Arising 9 Years after Excision of a Choledochal Cyst
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seongnam, Korea. gidoctor@snubh.org
- 2Department of Internal Medicine and Liver Research Institute, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
Abstract
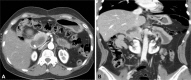
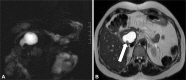
- A 42-years-old woman had undergone operation for cholecochal cyst with gallbladder cancer 9 years ago. Pathology revealed a polypoid mass in the gallbladder with liver infiltration as poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. Computed tomography, magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography, and endoscopic ultrasound showed a newly developed suspected solid nodule in the peripheral portion of cystic lesion in the pancreas head. She underwent a pylorus preserving pancreaticoduodenectomy for the suspected mucinous cystic neoplasm of the pancreas. Pathology revealed poorly differentiated adenocarcinoma. The remnant choledochal cyst had developed to cholangiocarcinoma, which mimicked cystic neoplasm of the pancreas.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. De Wilde VG, Elewaut AG, De Vos MM, Hendrix RF, Barbier FE. Choledochal cysts in the adult. Endoscopy. 1991; 23:4–7. PMID: 2009837.
Article2. Tsuchiya R, Harada N, Ito T, Furukawa M, Yoshihiro I. Malignant tumors in choledochal cysts. Ann Surg. 1977; 186:22–28. PMID: 879871.
Article3. Todani T, Watanabe Y, Fujii T, et al. Carcinoma arising from the bile duct in choledochal cyst and anomalous arrangement of the pancreaticobiliary ductal union. Tan Sui. 1985; 6:525–535.4. Imazu M, Iwai N, Tokiwa K, Shimotake T, Kimura O, Ono S. Factors of biliary carcinogenesis in choledochal cysts. Eur J Pediatr Surg. 2001; 11:24–27. PMID: 11370978.
Article5. Okada A, Hasegawa T, Oguchi Y, Nakamura T. Recent advances in pathophysiology and surgical treatment of congenital dilatation of the bile duct. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 2002; 9:342–351. PMID: 12353145.
Article6. Aggarwal S, Kumar S, Kumar A, Bhasin R, Garg PK, Bandhu S. Extra-hepatic bile duct adenoma in a patient with a choledochal cyst. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2003; 18:351–352. PMID: 12603542.
Article7. Singham J, Yoshida EM, Scudamore CH. Choledochal cysts. Part 3 of 3: management. Can J Surg. 2010; 53:51–56. PMID: 20100414.8. Watanabe Y, Toki A, Todani T. Bile duct cancer developed after cyst excision for choledochal cyst. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1999; 6:207–212. PMID: 10526053.
Article9. Kelly TR, Schlueter TM. Choledochal cyst with coexistent carcinoma of the pancreas. Am Surg. 1964; 30:209–212. PMID: 14128682.10. Gallagher PJ, Millis RR, Mitchinson MJ. Congenital dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts with cholangiocarcinoma. J Clin Pathol. 1972; 25:804–808. PMID: 4343747.
Article11. Nagorney DM, McIlrath DC, Adson MA. Choledochal cysts in adults: clinical management. Surgery. 1984; 96:656–663. PMID: 6091285.12. Rossi RL, Silverman ML, Braasch JW, Munson JL, ReMine SG. Carcinomas arising in cystic conditions of the bile ducts. A clinical and pathologic study. Ann Surg. 1987; 205:377–384. PMID: 3566373.13. Joseph VT, Prema Raj J. A review of choledochal cyst in pediatric and adult patients. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 1996; 3:396–404.
Article14. Song HJ, Seog W, Woo GH, et al. Squamous cell carcinoma of the liver after choledochal cystectomy. Korean J Gastroenterol. 1999; 34:704–708.15. Eriguchi N, Aoyagi S, Okuda K, et al. Carcinoma arising in the pancreas 17 years after primary excision of a choledochal cysts: report of a case. Surg Today. 2001; 31:534–537. PMID: 11428609.16. Ono S, Sakai K, Kimura O, Iwai N. Development of bile duct cancer in a 26-year-old man after resection of infantile choledochal cyst. J Pediatr Surg. 2008; 43:E17–E19. PMID: 18558159.
Article17. Cho MJ, Hwang S, Lee YJ, et al. Surgical experience of 204 cases of adult choledochal cyst disease over 14 years. World J Surg. 2011; 35:1094–1102. PMID: 21360306.
Article18. Lee SE, Jang JY, Lee YJ, et al. Choledochal cyst and associated malignant tumors in adults: a multicenter survey in South Korea. Arch Surg. 2011; 146:1178–1184. PMID: 22006877.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Type IVB Choledochal Cyst : A case report
- Type IV-A Choledochal Cyst with Intrahepatic Bile Duct Stricture
- Choledochal Cyst Associated with Cystic Duct Dilatation: Report of Three Cases
- A Case of Bile Duct Cancer Arising in Choledochal Cyst in a 13-Year-Old Girl
- Unilocular Extrahepatic Biliary Cystadenoma Mimicking Choledochal Cyst: A Case Report