Clin Endosc.
2012 Nov;45(4):350-357.
Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection Training
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Gastroenterology, Pontificia Universidad Catolica de Chile, Santiago, Chile. aparrab@med.puc.cl
- 2Department of Gastroenterology, (Prof. Henry Cohen), Hospital de Clinicas, Montevideo, Uruguay.
- 3Research Animal Laboratory, University of La Laguna, Tenerife, Spain.
Abstract
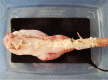
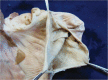
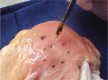
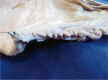
- Endoscopic submucosal dissection is a technically challenging but highly effective technique for the treatment of well selected early neoplasms in the digestive tract. Although it is frequently performed in East Asian countries, the Western world has not adopted this technique yet, probably due in part to the difficulty to learn it. Ex vivo and in vivo animal models are invaluable tools to overcome at least the beginning of the learning curve, although the initial step is the acquisition of basic knowledge about early diagnosis of neoplasias, and observing real procedures in expert centers. The practical issues, advantages, and disadvantages of the ex vivo and in vivo models are discussed.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gotoda T, Yamamoto H, Soetikno RM. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early gastric cancer. J Gastroenterol. 2006; 41:929–942. PMID: 17096062.
Article2. Oyama T, Tomori A, Hotta K, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection of early esophageal cancer. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2005; 3(7 Suppl 1):S67–S70. PMID: 16013002.
Article3. Saito Y, Uraoka T, Yamaguchi Y, et al. A prospective, multicenter study of 1111 colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissections (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:1217–1225. PMID: 21030017.
Article4. Uraoka T, Kawahara Y, Kato J, Saito Y, Yamamoto K. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in the colorectum: present status and future prospects. Dig Endosc. 2009; 21(Suppl 1):S13–S16. PMID: 19691725.
Article5. Chung IK, Lee JH, Lee SH, et al. Therapeutic outcomes in 1,000 cases of endoscopic submucosal dissection for early gastric neoplasms: Korean ESD Study Group multicenter study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 69:1228–1235. PMID: 19249769.
Article6. Lee EJ, Lee JB, Lee SH, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for colorectal tumors-1,000 colorectal ESD cases: one specialized institute's experiences. Surg Endosc. Epub 2012 Jun 23. DOI: 10.1007/s00464-012-2403-4.
Article7. Bergman JJ. How to justify endoscopic submucosal dissection in the Western world. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:988–990. PMID: 19866397.
Article8. Gotoda T, Friedland S, Hamanaka H, Soetikno R. A learning curve for advanced endoscopic resection. Gastrointest Endosc. 2005; 62:866–867. PMID: 16301027.
Article9. Kaltenbach T, Soetikno R, Kusano C, Gotoda T. Development of expertise in endoscopic mucosal resection and endoscopic submucosal dissection. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 13:100–104.
Article10. Ortiz-Fernández-Sordo J, Madrigal-Hoyos E, Waxman I. The role of live animal models for teaching endoscopy. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 13:113–118.11. Parra-Blanco A, Arnau MR, Nicolás-Pérez D, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection training with pig models in a Western country. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:2895–2900. PMID: 20556835.
Article12. Vázquez-Sequeiros E, de Miquel DB, Olcina JR, et al. Training model for teaching endoscopic submucosal dissection of gastric tumors. Rev Esp Enferm Dig. 2009; 101:546–552. PMID: 19785494.
Article13. Tanaka S, Morita Y, Fujita T, et al. Ex vivo pig training model for esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) for endoscopists with experience in gastric ESD. Surg Endosc. 2012; 26:1579–1586. PMID: 22223113.14. Hon SS, Ng SS, Lee JF, Li JC, Lo AW. In vitro porcine training model for colonic endoscopic submucosal dissection: an inexpensive and safe way to acquire a complex endoscopic technique. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:2439–2443. PMID: 20333407.
Article15. Parra-Blanco A, Saito Y, Yahagi N, et al. Recommendations about training for colorectal endoscopic submucosal dissection in the Western world: results of a survey to experts. Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 73(Suppl):AB419–AB420.16. Deprez PH, Bergman JJ, Meisner S, et al. Current practice with endoscopic submucosal dissection in Europe: position statement from a panel of experts. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:853–858. PMID: 20623442.
Article17. Moss A, Bourke MJ, Tran K, et al. Lesion isolation by circumferential submucosal incision prior to endoscopic mucosal resection (CSI-EMR) substantially improves en bloc resection rates for 40-mm colonic lesions. Endoscopy. 2010; 42:400–404. PMID: 20213591.
Article18. Freys SM, Heimbucher J, Fuchs KH. Teaching upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: the pig stomach. Endoscopy. 1995; 27:73–76. PMID: 7601041.
Article19. Yahagi N, Neuhaus H, Schumacher B, et al. Comparison of standard endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) versus an optimized ESD technique for the colon: an animal study. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:340–345. PMID: 19340739.
Article20. Teoh AY, Chiu PW, Wong SK, Sung JJ, Lau JY, Ng EK. Difficulties and outcomes in starting endoscopic submucosal dissection. Surg Endosc. 2010; 24:1049–1054. PMID: 19911227.
Article21. Berr F, Ponchon T, Neureiter D, et al. Experimental endoscopic submucosal dissection training in a porcine model: learning experience of skilled Western endoscopists. Dig Endosc. 2011; 23:281–289. PMID: 21951087.
Article22. Tanimoto MA, Torres-Villalobos G, Fujita R, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection in dogs in a World Gastroenterology Organisation training center. World J Gastroenterol. 2010; 16:1759–1764. PMID: 20380009.
Article23. Tanimoto MA, Torres-Villalobos G, Fujita R, et al. Learning curve in a Western training center of the circumferential en bloc esophageal endoscopic submucosal dissection in an in vivo animal model. Diagn Ther Endosc. 2011; 2011:847831. PMID: 21976950.
Article24. Neuhaus H, Wirths K, Schenk M, Enderle MD, Schumacher B. Randomized controlled study of EMR versus endoscopic submucosal dissection with a water-jet hybrid-knife of esophageal lesions in a porcine model. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009; 70:112–120. PMID: 19286176.
Article25. Kumano I, Ishihara M, Nakamura S, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection for pig esophagus by using photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel as submucosal fluid cushion. Gastrointest Endosc. 2012; 75:841–848. PMID: 22301341.
Article26. Neuhaus H, Costamagna G, Devière J, et al. Endoscopic submucosal dissection (ESD) of early neoplastic gastric lesions using a new double-channel endoscope (the "R-scope"). Endoscopy. 2006; 38:1016–1023. PMID: 17058167.
Article27. Yamasaki M, Kume K, Yoshikawa I, Otsuki M. A novel method of endoscopic submucosal dissection with blunt abrasion by submucosal injection of sodium carboxymethylcellulose: an animal preliminary study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2006; 64:958–965. PMID: 17140905.
Article28. Akahoshi K, Akahane H, Murata A, Akiba H, Oya M. Endoscopic submucosal dissection using a novel grasping type scissors forceps. Endoscopy. 2007; 39:1103–1105. PMID: 18072064.
Article29. von Delius S, Karagianni A, von Weyhern CH, et al. Percutaneously assistennd endoscopic surgery using a new PEG-minitrocar for advanced endoscopic submucosal dissection (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2008; 68:365–369. PMID: 18561928.30. Ishizuka T, Ishihara M, Aiko S, et al. Experimental evaluation of photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel as injection solution for endoscopic resection. Endoscopy. 2009; 41:25–28. PMID: 19160155.
Article31. Lee SH, Gromski MA, Derevianko A, et al. Efficacy of a prototype endoscope with two deflecting working channels for endoscopic submucosal dissection: a prospective, comparative, ex vivo study. Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 72:155–160. PMID: 20493486.
Article32. von Renteln D, Pohl H, Vassiliou MC, Walton MM, Rothstein RI. Endoscopic submucosal dissection by using a flexible Maryland dissector: a randomized, controlled, porcine study (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc. 2010; 71:1056–1062. PMID: 20438893.
Article33. Parra-Blanco A, Nicolas D, Arnau MR, Gimeno-Garcia AZ, Rodrigo L, Quintero E. Gastric endoscopic submucosal dissection assisted by a new traction method: the clip-band technique. A feasibility study in a porcine model (with video). Gastrointest Endosc. 2011; 74:1137–1141. PMID: 22032320.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ESD Hands-on Course Using Ex Vivo and In Vivo Models in South Korea
- Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection (ESD) Training and Performing ESD with Accurate and Safe Techniques
- Is Ex Vivo Training before In Vivo Training Effective in Learning Gastric Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection?
- History and Development of Accessories for Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection
- Debates on Colorectal Endoscopic Submucosal Dissection - Traction for Effective Dissection: Gravity Is Enough