Allergy Asthma Immunol Res.
2009 Oct;1(1):45-47. 10.4168/aair.2009.1.1.45.
Occupational asthma caused by inhalation of bovine serum albumin powder
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Allergy and Rheumatology, Ajou University School of Medicine, Suwon, Korea. hspark@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2133799
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4168/aair.2009.1.1.45
Abstract
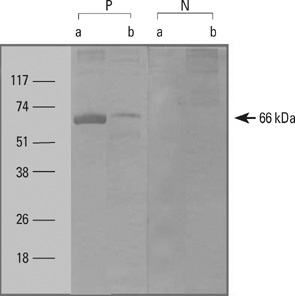
- Bovine serum albumin (BSA), which is present in bovine plasma, is one of the major allergens affecting patients with food allergies induced by milk and meat. It is also commonly used in research laboratories. Although some reports have documented food allergies associated with BSA, BSA-induced occupational asthma has not been reported. We report a case of occupational asthma and rhinitis in a laboratory worker caused by the inhalation of BSA powder, in which an IgE-mediated response was suggested as the pathogenic mechanism.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Dykewicz MS. Occupational asthma: current concepts in pathogenesis, diagnosis, and management. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2009. 123:519–528.2. Restani P, Ballabio C, Cattaneo A, Isoardi P, Terracciano L, Fiocchi A. Characterization of bovine serum albumin epitopes and their role in allergic reactions. Allergy. 2004. 59:21–24.3. Vicente-Serrano J, Caballero ML, Rodriguez-Perez R, Carretero P, Perez R, Blanco JG. Sensitization to serum albumins in children allergic to cow's milk and epithelia. Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 2007. 18:503–507.4. Choi SJ, Hur GY, Shin SY, Park HS. A case of adult onset cow's milk allergy presenting beef and pork meat allergy. Korean J Asthma Allergy Clin Immunol. 2007. 27:200–203.5. Wal JM. Cow's milk proteins/allergens. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002. 89:3–10.6. Martelli A, De Chiara A, Corvo M, Restani P, Fiocchi A. Beef allergy in children with cow's milk allergy; cow's milk allergy in children with beef allergy. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002. 89:38–43.7. Goldman AS, Anderson DW Jr, Sellers WA, Saperstein S, Kniker WT, Halpern SR. Milk allergy. I. Oral challenge with milk and isolated milk proteins in allergic children. Pediatrics. 1963. 32:425–443.8. Goldman AS, Sellars WA, Halpern SR, Anderson DW Jr, Furlow TE, Johnson CH Jr. Milk allergy. II. Skin testing of allergic and normal children with purified mild proteins. Pediatrics. 1963. 32:572–579.9. Han GD, Matsuno M, Ito G, Ikeucht Y, Suzuki A. Meat allergy: investigation of potential allergenic proteins in beef. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2000. 64:1887–1895.10. Restani P, Beretta B, Fiocchi A, Ballabio C, Galli CL. Cross-reactivity between mammalian proteins. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2002. 89:11–15.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Occupational Asthma Induced by the Reactive Dye Synozol Red-K 3BS
- A Case of Occupational Rhinitis Caused by Rice Powder in the Grain Industry
- New Sensitization to House Dust Mites in Cefteram-Induced Occupational Asthma: A Case Report
- Occupational asthma and IgE sensitization induced by inhalation of cefteram pivoxil powder
- A Case of Occupational Asthma and Allergic Rhinitis Due to Pronase