J Vet Sci.
2015 Dec;16(4):459-466. 10.4142/jvs.2015.16.4.459.
Phylogeography of the current rabies viruses in Indonesia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Animal Disease Investigation Centre, Denpasar 80226, Indonesia.
- 2Veterinary Science Post Graduate Program, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Gajah Mada University, Yogyakarta 55281, Indonesia.
- 3Veterinary Public Health Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Gajah Mada University, Yogyakarta 55281, Indonesia.
- 4Faculty of Veterinary Science, University of Sydney, Camden 2570, Australia.
- 5The Animal Biomedical and Molecular Biology Laboratory, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Udayana University, Denpasar 80226, Indonesia. gnmahardika@indosat.net.id
- KMID: 2133628
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4142/jvs.2015.16.4.459
Abstract
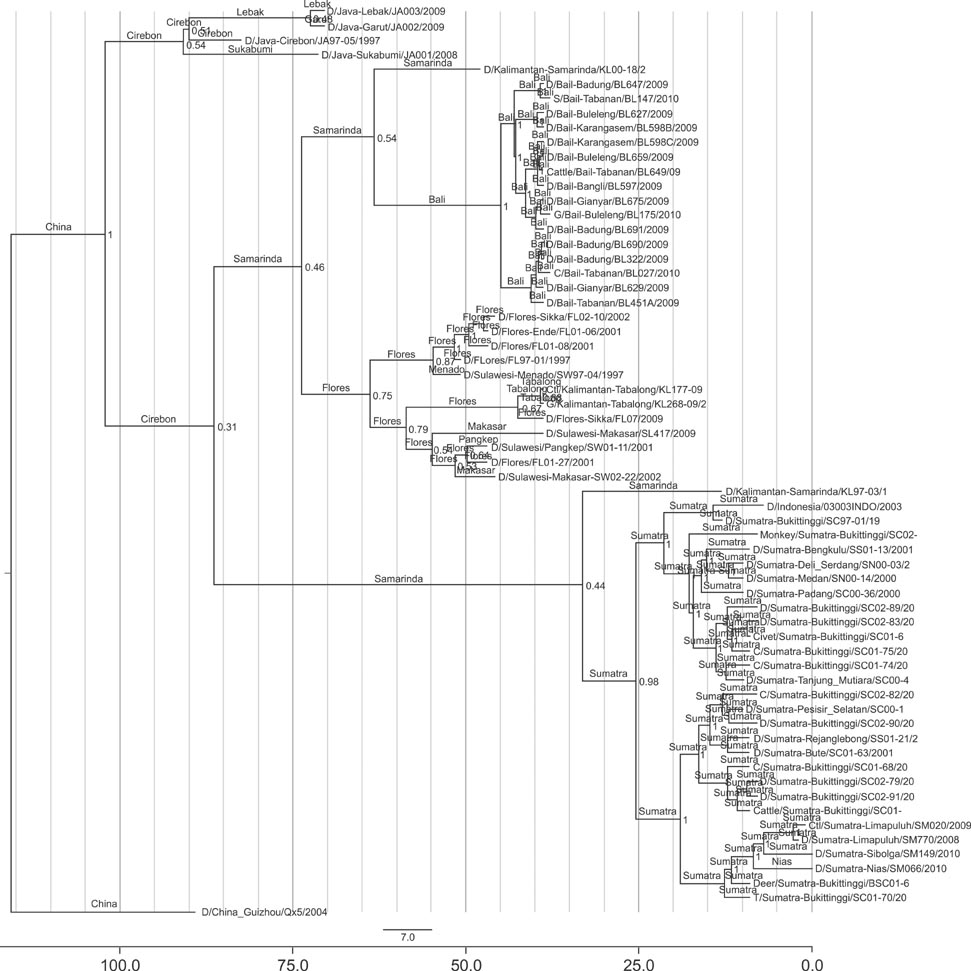
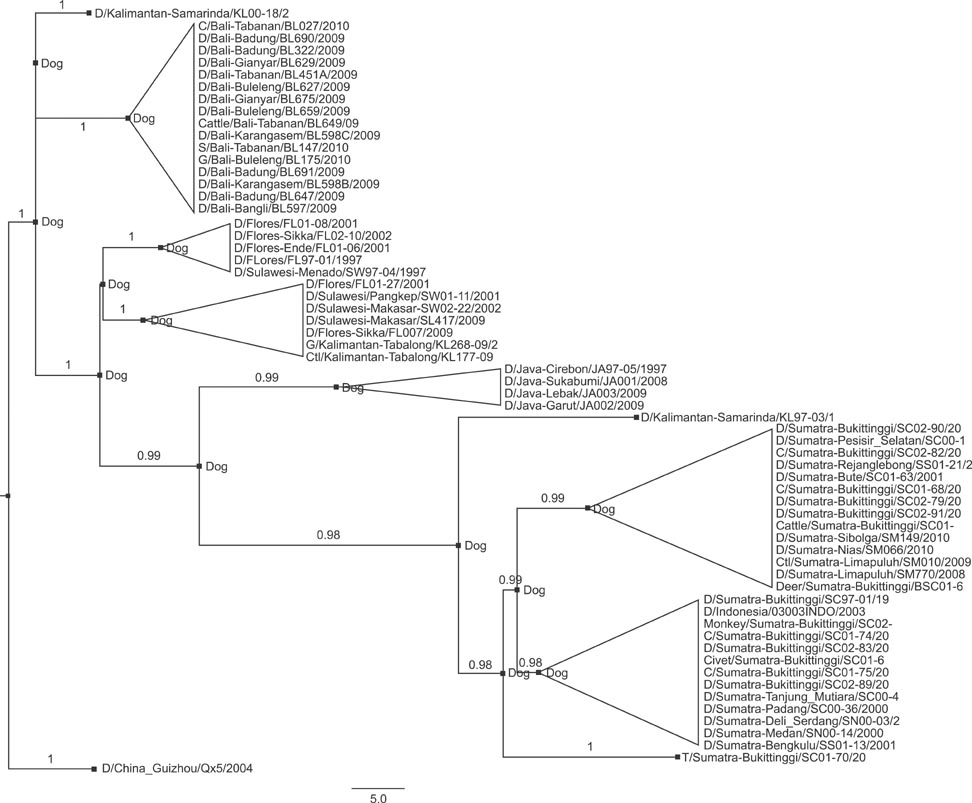
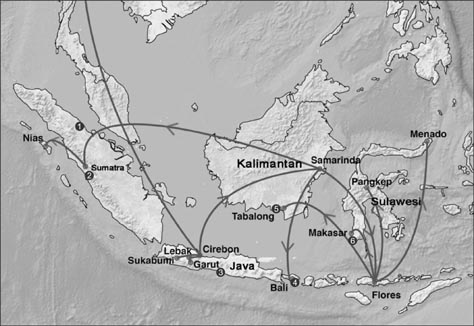
- Rabies is a major fatal zoonotic disease in Indonesia. This study was conducted to determine the recent dynamics of rabies virus (RABV) in various areas and animal species throughout Indonesia. A total of 27 brain samples collected from rabid animals of various species in Bali, Sumatra, Kalimantan, Sulawesi, Java, and Flores in 2008 to 2010 were investigated. The cDNA of the nucleoprotein gene from each sample was generated and amplified by one-step reverse transcription-PCR, after which the products were sequenced and analyzed. The symmetric substitution model of a Bayesian stochastic search variable selection extension of the discrete phylogeographic model of the social network was applied in BEAST ver. 1.7.5 software. The spatial dispersal was visualized in Cartographica using Spatial Phylogenetic Reconstruction of Evolutionary Dynamics. We demonstrated inter-island introduction and reintroduction, and dog was found to be the only source of infection of other animals. Ancestors of Indonesian RABVs originated in Java and its descendants were transmitted to Kalimantan, then further to Sumatra, Flores, and Bali. The Flores descendent was subsequently transmitted to Sulawesi and back to Kalimantan. The viruses found in various animal species were transmitted by the dog.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Altschul SF, Gish W, Miller W, Myers EW, Lipman DJ. Basic local alignment search tool. J Mol Biol. 1990; 215:403–410.
Article2. Avidor B, Turner D, Mor Z, Chalom S, Riesenberg K, Shahar E, Pollack S, Elbirt D, Sthoeger Z, Maayan S, Olshtain-Pops K, Averbuch D, Chowers M, Istomin V, Anis E, Mendelson E, Ram D, Levy I, Grossman Z. Transmission patterns of HIV-subtypes A/AE versus B: inferring risk-behavior trends and treatment-efficacy limitations from viral genotypic data obtained prior to and during antiretroviral therapy. PLoS One. 2013; 8:e57789.
Article3. Ayres DL, Darling A, Zwickl DJ, Beerli P, Holder MT, Lewis PO, Huelsenbeck JP, Ronquist F, Swofford DL, Cummings MP, Rambaut A, Suchard MA. BEAGLE: an application programming interface and high-performance computing library for statistical phylogenetics. Syst Biol. 2012; 61:170–173.
Article4. Bielejec F, Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Lemey P. SPREAD: spatial phylogenetic reconstruction of evolutionary dynamics. Bioinformatics. 2011; 27:2910–2912.
Article5. Bourhy H, Dacheux L, Strady C, Mailles A. Rabies in Europe in 2005. Euro Surveill. 2005; 10:213–216.
Article6. Bourhy H, Reynes JM, Dunham EJ, Dacheux L, Larrous F, Huong VT, Xu G, Yan J, Miranda ME, Holmes EC. The origin and phylogeography of dog rabies virus. J Gen Virol. 2008; 89:2673–2681.
Article7. Carnieli P Jr, de Novaes Oliveira R, Macedo CI, Castilho JG. Phylogeography of rabies virus isolated from dogs in Brazil between 1985 and 2006. Arch Virol. 2011; 156:1007–1012.
Article8. Crawford-Miksza LK, Wadford DA, Schnurr DP. Molecular epidemiology of enzootic rabies in California. J Clin Virol. 1999; 14:207–219.
Article9. David D, Hughes GJ, Yakobson BA, Davidson I, Un H, Aylan O, Kuzmin IV, Rupprecht CE. Identification of novel canine rabies virus clades in the Middle East and North Africa. J Gen Virol. 2007; 88:967–980.
Article10. de Carvalho LM, Santos LB, Faria NR, de Castro Silveira W. Phylogeography of foot-and-mouth disease virus serotype O in Ecuador. Infect Genet Evol. 2013; 13:76–88.
Article11. de Mattos CA, de Mattos CC, Rupprecht CE. Rhabdoviruses. In : Fields BN, Knipe DM, Howley PM, Griffin DE, editors. Fields Virology. 5th ed. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins: Philadelphia;2001.12. Dean S. Rabies and quarantine. Vet Rec. 1996; 139:551.13. Drummond AJ, Suchard MA, Xie D, Rambaut A. Bayesian phylogenetics with BEAUti and the BEAST 1.7. Mol Biol Evol. 2012; 29:1969–1973.
Article14. Faria NR, Suchard MA, Rambaut A, Lemey P. Toward a quantitative understanding of viral phylogeography. Curr Opin Virol. 2011; 1:423–429.
Article15. Fèvre EM, Kaboyo RW, Persson V, Edelsten M, Coleman PG, Cleaveland S. The epidemiology of animal bite injuries in Uganda and projections of the burden of rabies. Trop Med Int Health. 2005; 10:790–798.
Article16. Hardjosworo S. Rabies epidemiology in Indonesia. In : National Symphosium on Rabies: Indonesian Veterinary Medical Association-Bali Branch; 10-11 September 1984; Denpasar, Indonesia.17. Ito M, Itou T, Sakai T, Santos MF, Arai YT, Takasaki T, Kurane I, Ito FH. Detection of rabies virus RNA isolated from several species of animals in Brazil by RT-PCR. J Vet Med Sci. 2001; 63:1309–1313.
Article18. Ito M, Itou T, Shoji Y, Sakai T, Ito FH, Arai YT, Takasaki T, Kurane I. Discrimination between dog-related and vampire bat-related rabies viruses in Brazil by strain-specific reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction and restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis. J Clin Virol. 2003; 26:317–330.
Article19. Knobel DL, Cleaveland S, Coleman PG, Fèvre EM, Meltzer MI, Miranda ME, Shaw A, Zinsstag J, Meslin FX. Reevaluating the burden of rabies in Africa and Asia. Bull World Health Organ. 2005; 83:360–368.20. Lemey P, Rambaut A, Drummond AJ, Suchard MA. Bayesian phylogeography finds its roots. PLoS Comput Biol. 2009; 5:e1000520.
Article21. Loke YK, Murugesan E, Suryati A, Tan MH. An outbreak of rabies in dogs in the state of Terengganu 1995-1996. Med J Malaysia. 1998; 53:97–100.22. MacLachlan NJ, Dubovi EJ. Rhabdoviridae. In : MacLachlan NJ, Dubovi EJ, editors. Fenner's Veterinary Virology. 4th ed. Academic Press: San Diego;2011. p. 327–341.23. Mahardika GN, Dibia N, Budayanti NS, Susilawathi NM, Subrata K, Darwinata AE, Wignall FS, Richt JA, Valdivia-Granda WA, Sudewi AA. Phylogenetic analysis and victim contact tracing of rabies virus from humans and dogs in Bali, Indonesia. Epidemiol Infect. 2014; 142:1146–1156.
Article24. Putra AA, Hampson K, Girardi J, Hiby E, Knobel D, Mardiana IW, Townsend S, Scott-Orr H. Response to a rabies epidemic, Bali, Indonesia, 2008-2011. Emerg Infect Dis. 2013; 19:648–651.
Article25. Rambaut A, Suchard MA, Xie D, Drummond AJ. Tracer v1.6. 2014.26. Romijn PC, van der Heide R, Cattaneo CA, Silva Rde C, van der Poel WH. Study of lyssaviruses of bat origin as a source of rabies for other animal species in the State of Rio De Janeiro, Brazil. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2003; 69:81–86.
Article27. Schnell MJ, McGettigan JP, Wirblich C, Papaneri A. The cell biology of rabies virus: using stealth to reach the brain. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2010; 8:51–61.
Article28. Sinsheimer JS, Lake JA, Little RJ. Bayesian hypothesis testing of four-taxon topologies using molecular sequence data. Biometrics. 1996; 52:193–210.
Article29. Smith JS, Orciari LA, Yager PA, Seidel HD, Warner CK. Epidemiologic and historical relationships among 87 rabies virus isolates as determined by limited sequence analysis. J Infect Dis. 1992; 166:296–307.
Article30. Suchard MA, Weiss RE, Sinsheimer JS. Bayesian selection of continuous-time Markov chain evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol. 2001; 18:1001–1013.
Article31. Suchard MA, Weiss RE, Sinsheimer JS. Models for estimating Bayes factors with applications to phylogeny and tests of monophyly. Biometrics. 2005; 61:665–673.
Article32. Sugiyama M, Ito N. Control of rabies: epidemiology of rabies in Asia and development of new-generation vaccines for rabies. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2007; 30:273–286.
Article33. Susetya H, Sugiyama M, Inagaki A, Ito N, Mudiarto G, Minamoto N. Molecular epidemiology of rabies in Indonesia. Virus Res. 2008; 135:144–149.
Article34. Susilawathi NM, Darwinata AE, Dwija IB, Budayanti NS, Wirasandhi GA, Subrata K, Susilarini NK, Sudewi RA, Wignall FS, Mahardika GN. Epidemiological and clinical features of human rabies cases in Bali 2008-2010. BMC Infect Dis. 2012; 12:81.
Article35. Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007; 24:1596–1599.
Article36. Townsend SE, Lembo T, Cleaveland S, Meslin FX, Miranda ME, Putra AAG, Haydon DT, Hampson K. Surveillance guidelines for disease elimination: a case study of canine rabies. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis. 2013; 36:249–261.
Article37. Vieira LF, Pereira SR, Carnieli P Jr, Tavares LC, Kotait I. Phylogeography of rabies virus isolated from herbivores and bats in the Espírito Santo State, Brazil. Virus Genes. 2013; 46:330–336.
Article38. Windiyaningsih C, Wilde H, Meslin FX, Suroso T, Widarso HS. The rabies epidemic on Flores Island, Indonesia (1998-2003). J Med Assoc Thai. 2004; 87:1389–1393.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Molecular evolutionary analysis reveals Arctic-like rabies viruses evolved and dispersed independently in North and South Asia
- The present and future of rabies vaccine in animals
- Strategies to maintain Korea's animal rabies non-occurrence status
- General Features and Post-Exposure Prophylaxis of Rabies
- Three Cases Report of Suggestive Rabies