Ann Lab Med.
2014 Nov;34(6):478-480. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.6.478.
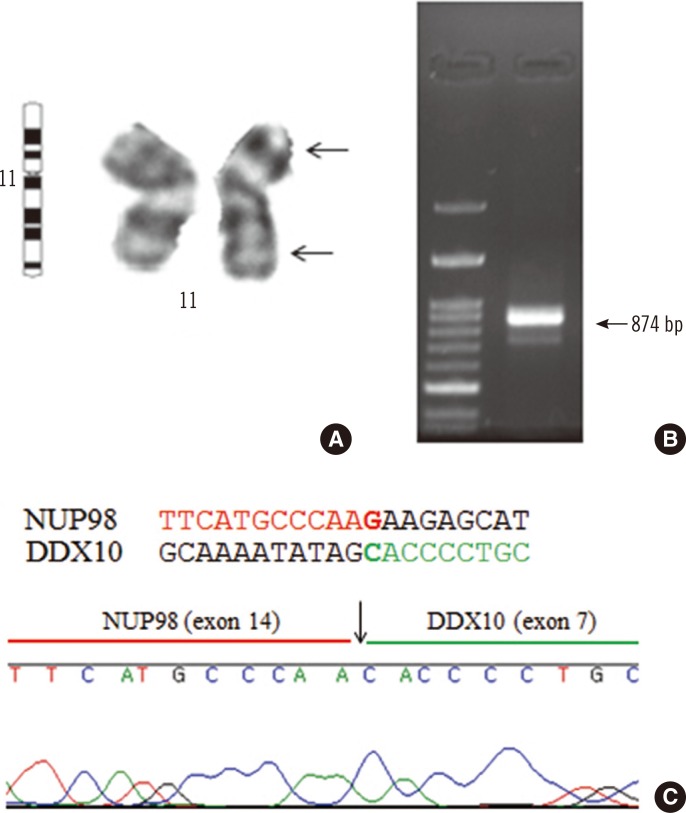
The First Korean Case of Childhood Acute Myeloid Leukemia with Inv(11)(p15q22)/NUP98-DDX10 Rearrangement: A Rare but Recurrent Genetic Abnormality
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine & Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunnyhk@skku.edu
- 2Department of Pediatrics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2129577
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.6.478
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
-
Asian Continental Ancestry Group/*genetics
Base Sequence
Bone Marrow Cells/metabolism/pathology
Child, Preschool
Chromosome Inversion/*genetics
*Chromosomes, Human, Pair 11
DEAD-box RNA Helicases/*genetics
Humans
Karyotyping
Leukemia, Myeloid, Acute/*diagnosis/genetics
Male
Nuclear Pore Complex Proteins/*genetics
Republic of Korea
DEAD-box RNA Helicases
Nuclear Pore Complex Proteins
Figure
Reference
-
1. Arai Y, Hosoda F, Kobayashi H, Arai K, Hayashi Y, Kamada N, et al. The inv(11)(p15q22) chromosome translocation of de novo and therapy-related myeloid malignancies results in fusion of the nucleoporin gene, NUP98, with the putative RNA helicase gene, DDX10. Blood. 1997; 89:3936–3944. PMID: 9166830.2. Ikeda T, Ikeda K, Sasaki K, Kawakami K, Takahara J. The inv(11)(p15q22) chromosome translocation of therapy-related myelodysplasia with NUP98-DDX10 and DDX10-NUP98 fusion transcripts. Int J Hematol. 1999; 69:160–164. PMID: 10222653.3. Nebral K, König M, Schmidt HH, Lutz D, Sperr WR, Kalwak K, et al. Screening for NUP98 rearrangements in hematopoietic malignancies by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Haematologica. 2005; 90:746–752. PMID: 15951287.4. Yamamoto M, Kakihana K, Kurosu T, Murakami N, Miura O. Clonal evolution with inv(11)(p15q22) and NUP98/DDX10 fusion gene in imatinib-resistant chronic myelogenous leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2005; 157:104–108. PMID: 15721630.5. Morerio C, Acquila M, Rapella A, Tassano E, Rosanda C, Panarello C. Inversion (11)(p15q22) with NUP98-DDX10 fusion gene in pediatric acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006; 171:122–125. PMID: 17116492.6. Romana SP, Radford-Weiss I, Ben Abdelali R, Schluth C, Petit A, Dastugue N, et al. NUP98 rearrangements in hematopoietic malignancies: a study of the Groupe Francophone de Cytogénétique Hématologique. Leukemia. 2006; 20:696–706. PMID: 16467868.7. Gorello P, Nofrini V, Brandimarte L, Pierini V, Crescenzi B, Nozza F, et al. Inv(11)(p15q22)/NUP98-DDX10 fusion and isoforms in a new case of de novo acute myeloid leukemia. Cancer Genet. 2013; 206:92–96. PMID: 23522748.8. Hollink IH, van den Heuvel-Eibrink MM, Arentsen-Peters ST, Pratcorona M, Abbas S, Kuipers JE, et al. NUP98/NSD1 characterizes a novel poor prognostic group in acute myeloid leukemia with a distinct HOX gene expression pattern. Blood. 2011; 118:3645–3656. PMID: 21813447.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Myeloid Sarcoma of Peritoneum in Acute Myeloid Leukemia Patient with Inversion of Chromosome 16
- Simultaneous Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction for Detection of 7 Gene Rearrangements in Acute Leukemia
- Sole Trisomy 22 Not Associated with inv(16) in Myelodysplastic Syndrome
- A case of biphenotypic acute leukemia with expression of the AML1-ETO gene rearrangement
- First Case Report of Acute Myeloid Leukemia with MN1-ETV6 Rearrangement at Relapse