Ann Lab Med.
2014 Nov;34(6):456-462. 10.3343/alm.2014.34.6.456.
Standardization of ABO Antibody Titer Measurement at Laboratories in Korea
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, School of Medicine, Ajou University, Suwon, Korea. limyoung@ajou.ac.kr
- KMID: 2129571
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2014.34.6.456
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Measurement of the ABO antibody (Ab) titer is important in ABO-incompatible transplantation. However, to the best of our knowledge, no standard protocol or external survey program to measure the ABO Ab titer has been established in Korea. We investigated the current status of ABO Ab titer measurements at various laboratories in Korea and the impact of the protocol provided to reduce interlaboratory variations in the methods and results of ABO Ab titers.
METHODS
The Korean external quality assessment of blood bank laboratories sent external survey samples with a questionnaire to 68 laboratories across Korea for the measurement of ABO Ab titers in May 2012. After 6 months, a second set of survey samples were sent with a standard protocol to 53 of the previously surveyed laboratories. The protocol recommended incubation at room temperature only and use of the indirect antihuman globulin method for the tube test as well as and the column agglutination test (CAT).
RESULTS
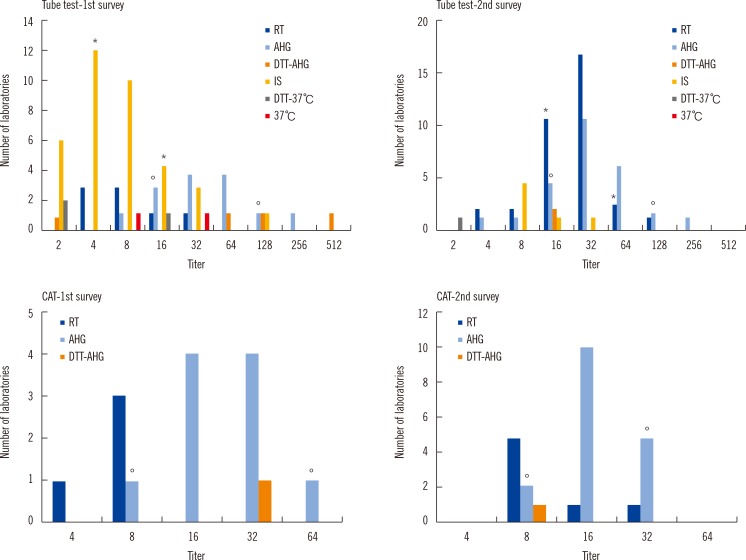
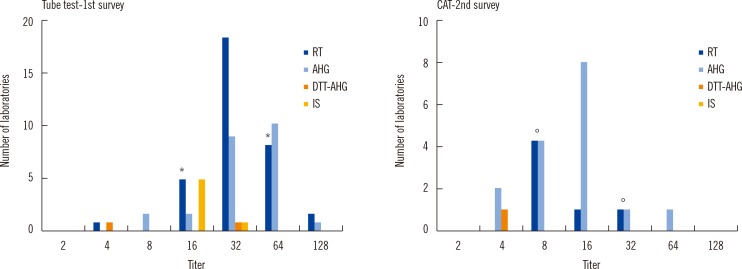
Several interlaboratory variations were observed in the results, technical procedures, and methods selected for measurement. We found that 80.4% laboratories hoped to change their protocol to the provisional one. Additionally, CAT showed significantly lower variation among laboratories (P=0.006) than the tube test.
CONCLUSIONS
Our study provides baseline data regarding the current status of ABO Ab titer measurement in Korea. The standard protocol and external survey were helpful to standardize the technical procedures and select methods for ABO Ab titer measurement.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alexandre GP, Squifflet JP, de Bruyere M, Latinne D, Moriau M, Ikabu N, et al. Splenectomy as a prerequisite for successful human ABO-incompatible renal-transplantation. Transplant Proc. 1985; 17:138–143.2. Chang CL, Jeong JH, Kim JP, Lee DR, Kong JM, Kim BC. A single center experience of ABO incompatible kidney transplantation. J Korean Soc Transplant. 2012; 26:261–268.
Article3. Tobian AA, Shirey RS, King KE. ABO antibody titer monitoring for incompatible renal transplantation. Transfusion. 2011; 51:454–457. PMID: 21388388.
Article4. Kobayashi T, Saito K. A series of surveys on assay for anti-A/B antibody by Japanese ABO-incompatible Transplantation Committee. Xenotransplantation. 2006; 13:136–140. PMID: 16623808.
Article5. AuBuchon JP, de Wildt-Eggen J, Dumont LJ. Reducing the variation in performance of antibody titrations. Vox Sang. 2008; 95:57–65. PMID: 18479347.
Article6. Lee EY, Kim S, Kim HO, Kwon SW, Kim DW, Han KS. Survey analysis of ABO antibody titration at four university hospitals in Korea. Korean J Blood Transfus. 2011; 22:24–30.7. Roback JD, Grossman BJ, Harris T, Hillyer CD, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 369.8. Roback JD, Grossman BJ, Harris T, Hillyer CD, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 907–910.9. Roback JD, Grossman BJ, Harris T, Hillyer CD, editors. Technical manual. 17th ed. Bethesda: American Association of Blood Banks;2011. p. 935–937.10. Kang MG, Lee SJ, Oh JS, Lim YA. Comparison of ABO isoagglutinin titers by different tube hemagglutination techniques. Korean J Blood Transfus. 2009; 20:227–234.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Laboratory support of ABO antibody monitoring for ABO-incompatible solid organ transplantation
- Comparison of ABO Antibody Titers on the Basis of the Antibody Detection Method Used
- Survey Analysis of ABO Antibody Titration at Four University Hospitals in Korea
- Comparison of Column Agglutination Technique and Tube Test for ABO Antibody Titration and Crossmatching
- Impact of baseline anti-ABO antibody titer on biliary complications following ABO-incompatible living donor liver transplantation