Clin Exp Otorhinolaryngol.
2015 Dec;8(4):396-401. 10.3342/ceo.2015.8.4.396.
Usefulness of Rigid Bronchoscopic Intervention Using Argon Plasma Coagulation for Central Airway Tumors
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Chonnam National University Hospital, Gwangju, Korea. yskwon@jnu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2128917
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3342/ceo.2015.8.4.396
Abstract
OBJECTIVES
Argon plasma coagulation (APC) is a noncontact form of electrocautery that utilizes ionized argon as the electrical current. A rigid bronchoscopic use of APC for the management of central airway obstruction could be safe and rapidly effective. This study evaluated the usefulness of rigid bronchoscopy with APC for the management of central airway obstructions due to benign or malignant tumors.
METHODS
Twenty patients with obstructing central airway tumors were retrospectively reviewed from February 2008 to February 2013 at Chonnam National University Hospital. All patients received rigid bronchoscopic tumor removal under general anesthesia. APC was applied before and after tumor removal.
RESULTS
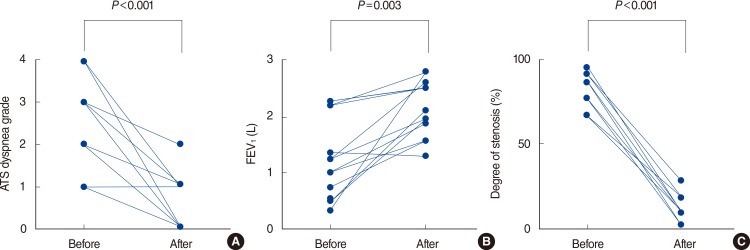
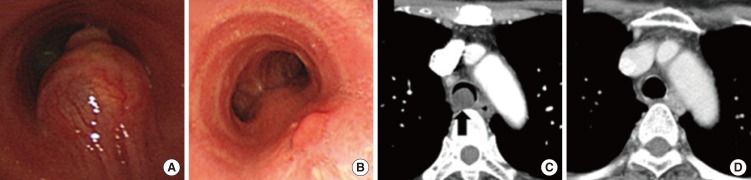
The median age of patients was 59 years (interquartile range [IQR], 51 to 67 years) and 70% were female. The causes of airway obstruction included malignancy (n=8) and benign tumor (n=12). Airway tumors comprised intraluminal lesions (n=11, 55%) and mixed intraluminal/extraluminal lesions (n=9, 45%). The median tumor size was 15 mm (IQR, 10 to 18 mm). The median degree of airway obstruction was significantly reduced after intervention (90% [IQR, 88% to 96%] vs. 10% [IQR, 0% to 20%], P<0.001). The median American Thoracic Society dyspnea grade (3 [IQR, 1 to 4] vs. 1 [IQR, 0 to 1], P<0.001) and forced expiratory volume in one second (1.03 L [IQR, 0.52 to 1.36 L] vs. 1.98 L [IQR, 1.57 to 2.64 L], P=0.004) were significantly improved after intervention. There were no procedure-related acute complications and deaths.
CONCLUSION
Rigid bronchoscopy with APC is an effective and safe procedure to alleviate central airway obstruction caused by tumors.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Ernst A, Feller-Kopman D, Becker HD, Mehta AC. Central airway obstruction. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2004; 6. 169(12):1278–1297. PMID: 15187010.
Article2. Amjadi K, Voduc N, Cruysberghs Y, Lemmens R, Fergusson DA, Doucette S, et al. Impact of interventional bronchoscopy on quality of life in malignant airway obstruction. Respiration. 2008; 76:421–428. PMID: 18758153.
Article3. Bolliger CT, Mathur PN, Beamis JF, Becker HD, Cavaliere S, Colt H, et al. European Respiratory Society/American Thoracic Society. ERS/ATS statement on interventional pulmonology. Eur Respir J. 2002; 19:356–373. PMID: 11866017.
Article4. Bolliger CT, Sutedja TG, Strausz J, Freitag L. Therapeutic bronchoscopy with immediate effect: laser, electrocautery, argon plasma coagulation and stents. Eur Respir J. 2006; 6. 27(6):1258–1271. PMID: 16772389.
Article5. Folch E, Mehta AC. Airway interventions in the tracheobronchial tree. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2008; 8. 29(4):441–452. PMID: 18651361.
Article6. Wahidi MM, Herth FJ, Ernst A. State of the art: interventional pulmonology. Chest. 2007; 1. 131(1):261–274. PMID: 17218585.7. Du Rand IA, Barber PV, Goldring J, Lewis RA, Mandal S, Munavvar M, et al. British Thoracic Society guideline for advanced diagnostic and therapeutic flexible bronchoscopy in adults. Thorax. 2011; 11. 66(Suppl 3):iii1–iii21. PMID: 21987439.
Article8. Dutau H, Vandemoortele T, Breen DP. Rigid bronchoscopy. Clin Chest Med. 2013; 9. 34(3):427–435. PMID: 23993814.
Article9. Sheski FD, Mathur PN. Endobronchial electrosurgery: argon plasma coagulation and electrocautery. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2004; 8. 25(4):367–374. PMID: 16088479.
Article10. Crosta C, Spaggiari L, De Stefano A, Fiori G, Ravizza D, Pastorino U. Endoscopic argon plasma coagulation for palliative treatment of malignant airway obstructions: early results in 47 cases. Lung Cancer. 2001; 7. 33(1):75–80. PMID: 11429198.
Article11. Keller CA, Hinerman R, Singh A, Alvarez F. The use of endoscopic argon plasma coagulation in airway complications after solid organ transplantation. Chest. 2001; 6. 119(6):1968–1975. PMID: 11399738.
Article12. Morice RC, Ece T, Ece F, Keus L. Endobronchial argon plasma coagulation for treatment of hemoptysis and neoplastic airway obstruction. Chest. 2001; 3. 119(3):781–787. PMID: 11243957.
Article13. Yasuo M, Tanabe T, Tsushima K, Nakamura M, Kanda S, Komatsu Y, et al. Endobronchial argon plasma coagulation for the management of post-intubation tracheal stenosis. Respirology. 2006; 9. 11(5):659–662. PMID: 16916344.
Article14. Reichle G, Freitag L, Kullmann HJ, Prenzel R, Macha HN, Farin G. Argon plasma coagulation in bronchology: a new method--alternative or complementary? Pneumologie. 2000; 11. 54(11):508–516. PMID: 11132548.
Article15. Cavaliere S, Foccoli P, Farina PL. Nd:YAG laser bronchoscopy: a five-year experience with 1,396 applications in 1,000 patients. Chest. 1988; 7. 94(1):15–21. PMID: 3383627.16. Han CC, Prasetyo D, Wright GM. Endobronchial palliation using Nd:YAG laser is associated with improved survival when combined with multimodal adjuvant treatments. J Thorac Oncol. 2007; 1. 2(1):59–64. PMID: 17410011.
Article17. Hermes A, Heigener D, Gatzemeier U, Schatz J, Reck M. Efficacy and safety of bronchoscopic laser therapy in patients with tracheal and bronchial obstruction: a retrospective single institution report. Clin Respir J. 2012; 4. 6(2):67–71. PMID: 21801329.
Article18. Hetzel MR, Nixon C, Edmondstone WM, Mitchell DM, Millard FJ, Nanson EM, et al. Laser therapy in 100 tracheobronchial tumours. Thorax. 1985; 5. 40(5):341–345. PMID: 4023988.
Article19. Choi JC, Yu CM, Ryu YJ, Jeon K, Choi KA, Kwon OJ, et al. The role of endoscopic surgery for completely obstructive endobronchial benign tumor. Korean J Intern Med. 2006; 3. 21(1):15–19. PMID: 16646559.
Article20. Shah H, Garbe L, Nussbaum E, Dumon JF, Chiodera PL, Cavaliere S. Benign tumors of the tracheobronchial tree. Endoscopic characteristics and role of laser resection. Chest. 1995; 6. 107(6):1744–1751. PMID: 7781378.21. Ernst A, Simoff M, Ost D, Goldman Y, Herth FJ. Prospective risk-adjusted morbidity and mortality outcome analysis after therapeutic bronchoscopic procedures: results of a multi-institutional outcomes database. Chest. 2008; 9. 134(3):514–519. PMID: 18641088.22. Reddy C, Majid A, Michaud G, Feller-Kopman D, Eberhardt R, Herth F, et al. Gas embolism following bronchoscopic argon plasma coagulation: a case series. Chest. 2008; 11. 134:1066–1069. PMID: 18988782.23. Shaw Y, Yoneda KY, Chan AL. Cerebral gas embolism from bronchoscopic argon plasma coagulation: a case report. Respiration. 2012; 83(3):267–270. PMID: 21821997.
Article24. Okada S, Yamauchi H, Ishimori S, Satoh S, Sugawara H, Tanaba Y. Endoscopic surgery with a flexible bronchoscope and argon plasma coagulation for tracheobronchial tumors. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2001; 1. 121(1):180–182. PMID: 11135176.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Two Cases of Central Airway Obstruction Treated with an Insulation-Tipped Diathermic Knife-2
- Endobronchial Schwannoma Treated by Rigid Bronchoscopy with Argon Plasma Coagulation
- Rigid bronchoscopic intervention for malignant central airway obstruction: A narrative review
- Successful Treatment of Tracheal Invasion Caused by Thyroid Cancer Using Endotracheal Tube Balloon Inflation under Flexible Bronchoscopic Guidance
- Direct cholangioscopy with argon plasma coagulation of an intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm of the bile duct