Imaging Sci Dent.
2015 Mar;45(1):61-65. 10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.61.
Accessory mental foramen: A rare anatomical variation detected by cone-beam computed tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Oral Radiology, School of Dentistry, Federal University of Bahia, Salvador, BA, Brazil. torresmarianna@hotmail.com
- KMID: 2116793
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5624/isd.2015.45.1.61
Abstract
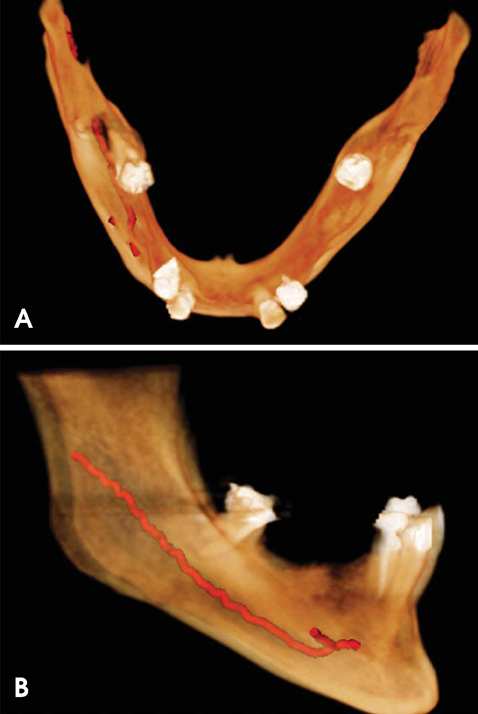
- The mental foramen is a bilateral opening in the vestibular portion of the mandible through which nerve endings, such as the mental nerve, emerge. In general, the mental foramen is located between the lower premolars. This region is a common area for the placement of dental implants. It is very important to identify anatomical variations in presurgical imaging exams since damage to neurovascular bundles may have a direct influence on treatment success. In the hemimandible, the mental foramen normally appears as a single structure, but there are some rare reports on the presence and number of anatomical variations; these variations may include accessory foramina. The present report describes the presence of accessory mental foramina in the right mandible, as detected by cone-beam computed tomography before dental implant placement.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Sawyer DR, Kiely ML, Pyle MA. The frequency of accessory mental foramina in four ethnic groups. Arch Oral Biol. 1998; 43:417–420.
Article2. Vayvada H, Demirdover C, Yilmaz M, Barutcu A. An anatomic variation of the mental nerve and foramina: a case report. Clin Anat. 2006; 19:700–701.
Article3. Neves FS, Oliveira LS, Torres MG, Crusoé-Souza M, Oliveira C, Campos PS, et al. Accessory mental foramen: case report. RPG Rev Pós-Gra. 2010; 17:173–176.4. Neves FS, Torres MG, Oliveira C, Campos PS, Crusoé-Rebello I. Lingual accessory mental foramen: a report of an extremely rare anatomical variation. J Oral Sci. 2010; 52:501–503.
Article5. Imada TS, Fernandes LM, Centurion BS, de Oliveira-Santos C, Honório HM, Rubira-Bullen IR. Accessory mental foramina: prevalence, position and diameter assessed by cone-beam computed tomography and digital panoramic radiographs. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2014; 25:e94–e99.
Article6. Pancer B, Garaicoa-Pazmiño C, Bashutski JD. Accessory mandibular foramen during dental implant placement: case report and review of literature. Implant Dent. 2014; 23:116–124.7. da Silva Ramos Fernandes LM, Capelozza AL, Rubira-Bullen IR. Absence and hypoplasia of the mental foramen detected in CBCT images: a case report. Surg Radiol Anat. 2011; 33:731–734.
Article8. Matsumoto K, Araki M, Honda K. Bilateral absence of the mental foramen detected by cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Radiol. 2013; 29:198–201.
Article9. Balcioglu HA, Kocaelli H. Accessory mental foramen. N Am J Med Sci. 2009; 1:314–315.10. Caǧirankaya LB, Kansu H. An accessory mental foramen: a case report. J Contemp Dent Pract. 2008; 9:98–104.11. Thakur G, Thomas S, Thayil SC, Nair PP. Accessory mental foramen: a rare anatomical finding. BMJ Case Rep. 2011; 2011:bcr0920103326.
Article12. Katakami K, Mishima A, Shiozaki K, Shimoda S, Hamada Y, Kobayashi K. Characteristics of accessory mental foramina observed on limited cone-beam computed tomography images. J Endod. 2008; 34:1441–1445.
Article13. Naitoh M, Hiraiwa Y, Aimiya H, Gotoh K, Ariji E. Accessory mental foramen assessment using cone-beam computed tomography. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 2009; 107:289–294.
Article14. von Arx T, Friedli M, Sendi P, Lozanoff S, Bornstein MM. Location and dimensions of the mental foramen: a radiographic analysis by using cone-beam computed tomography. J Endod. 2013; 39:1522–1528.15. Udhaya K, Saraladevi KV, Sridhar J. The morphometric analysis of the mental foramen in adult dry human mandibles: a study on the South Indian population. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013; 7:1547–1551.16. Igarashi C, Kobayashi K, Yamamoto A, Morita Y, Tanaka M. Double mental foramina of the mandible on computed tomography images: a case report. Oral Radiol. 2004; 20:68–71.
Article17. Naitoh M, Yoshida K, Nakahara K, Gotoh K, Ariji E. Demonstration of the accessory mental foramen using rotational panoramic radiography compared with cone-beam computed tomography. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2011; 22:1415–1419.
Article18. Kulkarni S, Kumar S, Kamath S, Thakur S. Accidental identification of accessory mental nerve and foramen during implant surgery. J Indian Soc Periodontol. 2011; 15:70–73.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- ANATOMICAL ASSESSMENT OF ACCESSORY MENTAL FORAMEN USING 3D CONE BEAM COMPUTED TOMOGRAPHY IN KOREAN
- Anatomical structure of lingual foramen in cone beam computed tomography
- Observation of the anterior loop and mental foramen of the mandibular canal using cone beam computed tomography
- Cone beam CT findings of retromolar canals: Report of cases and literature review
- Foramen transversarium enlargement caused by vertebral artery tortuosity: Diagnosis with cone-beam computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography