Brain Tumor Res Treat.
2015 Oct;3(2):132-137. 10.14791/btrt.2015.3.2.132.
Remote Postoperative Epidural Hematoma after Brain Tumor Surgery
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Seoul St. Mary's Hospital, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jhyun@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2114661
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.14791/btrt.2015.3.2.132
Abstract
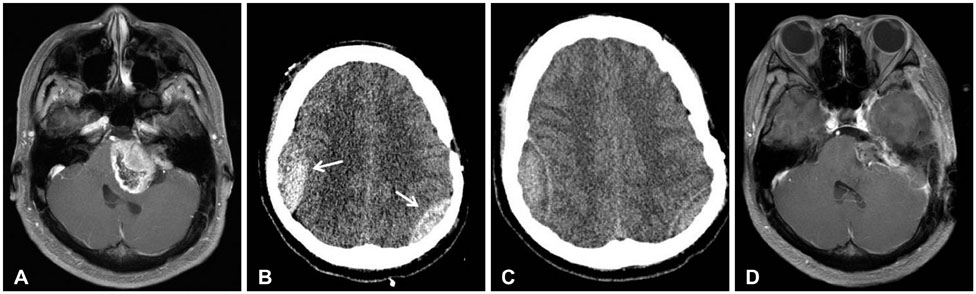
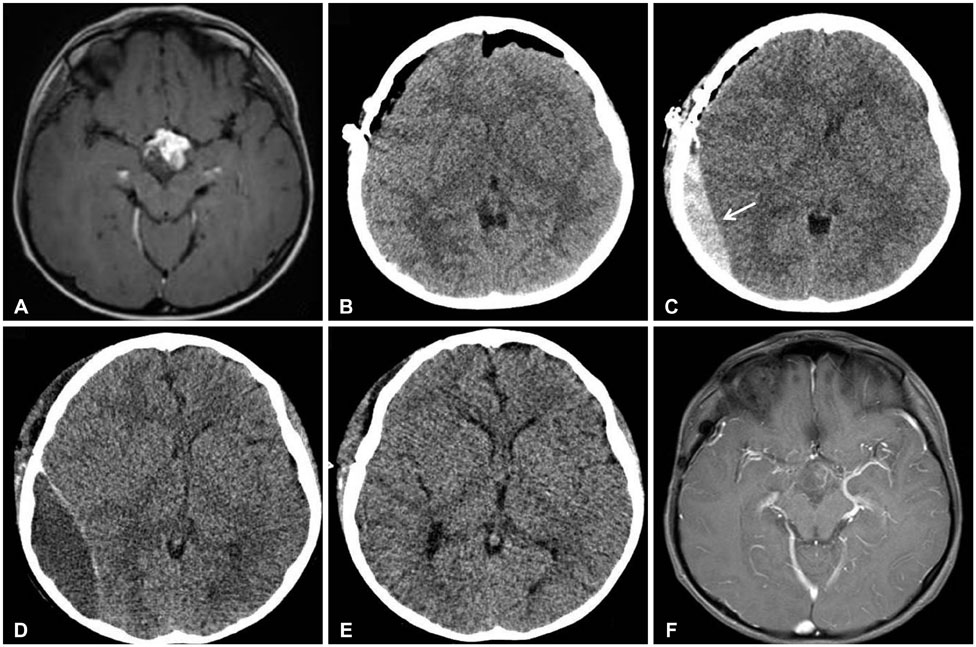
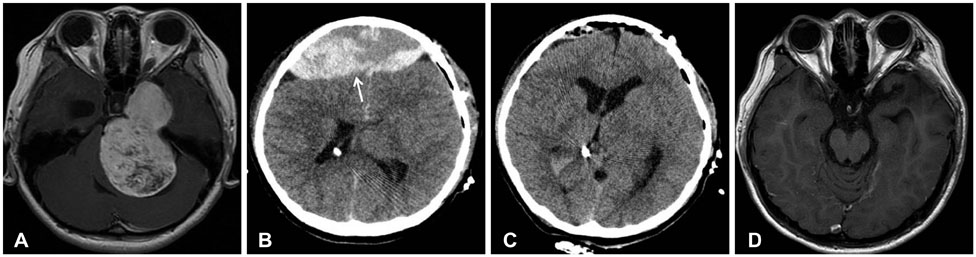
- A postoperative epidural hematoma (EDH) is a serious and embarrassing complication, which usually occurs at the site of operation after intracranial surgery. However, remote EDH is relatively rare. We report three cases of remote EDH after brain tumor surgery. All three cases seemed to have different causes of remote postoperative EDH; however, all patients were managed promptly and showed excellent outcomes. Although the exact mechanism of remote postoperative EDH is unknown, surgeons should be cautious of the speed of lowering intracranial pressure and implement basic procedures to prevent this hazardous complication of brain tumor surgery.
Keyword
Figure
Reference
-
1. Fukamachi A, Koizumi H, Nagaseki Y, Nukui H. Postoperative extradural hematomas: computed tomographic survey of 1105 intracranial operations. Neurosurgery. 1986; 19:589–593.
Article2. Kalfas IH, Little JR. Postoperative hemorrhage: a survey of 4992 intracranial procedures. Neurosurgery. 1988; 23:343–347.
Article3. Byrappa V, Redhu S, Varadarajan B. Delayed incidental diagnosis of postoperative extradural hematoma following ventriculoperitoneal shunt. J Neurosci Rural Pract. 2015; 6:94–96.
Article4. Noleto G, Neville IS, Tavares WM, et al. Giant acute epidural hematoma after ventriculoperitoneal shunt: a case report and literature review. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2014; 7:2355–2359.5. Louzada PR, Requejo PR, Barroso MV, et al. Bilateral extradural haematoma after acute ventricular over-drainage. Brain Inj. 2012; 26:95–100.
Article6. Chauvet D, Sichez JP, Boch AL. [Early epidural hematoma after CSF shunt for obstructive hydrocephalus]. Neurochirurgie. 2009; 55:350–353.7. Lee SC, Lee ST, Lui TN. Epidural hematoma of the cervical spine after cervical laminectomy in a patient with ventriculo-peritoneal shunt. J Clin Neurosci. 2004; 11:302–304.
Article8. Hamlat A, Heckly A, Doumbouya N, Seigneuret E, Brassier G. Epidural hematoma as a complication of endoscopic biopsy and shunt placement in a patient harboring a third ventricle tumor. Pediatr Neurosurg. 2004; 40:245–248.
Article9. Alsheheri MA, Binitie OP. Acute epidural hematoma following restoration of ventriculoperitoneal shunt patency. Neurosciences (Riyadh). 2004; 9:312–314.10. Power D, Ali-Khan F, Drage M. Contralateral extradural haematoma after insertion of a programmable-valve ventriculoperitoneal shunt. J R Soc Med. 1999; 92:360–361.
Article11. Harkness W. Contralateral extradural haematoma after ventriculoperitoneal shunt insertion. J R Soc Med. 1999; 92:547.
Article12. Fujimoto Y, Aguiar PH, Carneiro JD, et al. Spontaneous epidural hematoma following a shunt in an infant with congenital factor X deficiency. Case report and literature review. Neurosurg Rev. 1999; 22:226–229.
Article13. Pereira CU, Porto MW, de Holanda RR, de Andrade WT. Epidural hematoma after ventriculoperitoneal shunt surgery. Report of two cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 1998; 56:629–632.
Article14. Baskin DS, Klein MS, Yang WC, Sachdev VP, Malis LI. Traumatic epidural hematoma in shunt dependent patients: a report of two cases. Surg Neurol. 1979; 11:135–139.15. Huang YH, Lee TC, Lee TH, Yang KY, Liao CC. Remote epidural hemorrhage after unilateral decompressive hemicraniectomy in brain-injured patients. J Neurotrauma. 2013; 30:96–101.
Article16. Xu GZ, Wang MD, Liu KG, Bai YA. A rare remote epidural hematoma secondary to decompressive craniectomy. J Craniofac Surg. 2014; 25:e17–e19.
Article17. Lourie H, Young RF. Posterior epidural hematoma following subfrontal tumor removal. Case report. J Neurosurg. 1974; 40:643–646.18. Sinar EJ, Lindsay KW. Distant extradural haematoma complicating removal of frontal tumours. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1986; 49:442–444.
Article19. Borkar SA, Sinha S, Sharma BS. Remote site extradural haematoma. J Clin Neurosci. 2009; 16:1097–1098.
Article20. Jin Y, Qiu Y, Zhang X. Postoperative complications of central neurocytoma. J Craniofac Surg. 2013; 24:e533–e537.
Article21. Cui Z, Zhong C, Zhang M, et al. Remote epidural haematoma and severe basal ganglia oedema complicating the removal of a central neurocytoma in the lateral ventricle: a case report and lessons learned. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2013; 115:365–367.
Article22. Bae KJ, Kim IM, Yim MB. Remote epidural hematoma following the removal of brain tumors: report of three cases. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2001; 30:366–370.23. Jeon JS, Chang IB, Cho BM, Lee HK, Hong SK, Oh SM. Immediate Postoperative Epidural Hematomas Adjacent to the Craniotomy Site. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2006; 39:335–339.24. Wolfsberger S, Gruber A, Czech T. Multiple supratentorial epidural haematomas after posterior fossa surgery. Neurosurg Rev. 2004; 27:128–132.
Article25. Pandey P, Madhugiri VS, Sattur MG, Devi BI. Remote supratentorial extradural hematoma following posterior fossa surgery. Childs Nerv Syst. 2008; 24:851–854.
Article26. Avci E, Dagtekin A, Baysal Z, Karabag H. Intraoperative supratentorial epidural haematoma during removal of a huge posterior fossa dermoid cyst. Neurol Neurochir Pol. 2010; 44:609–613.
Article27. Lim JW, Yang SH, Lee JS, Song SH. Multiple remote epidural hematomas following pineal gland tumor resection. J Pediatr Neurosci. 2010; 5:79–81.
Article28. Paiva WS, Oliveira AM, de Andrade AF, Brock RS, Teixeira MJ. Remote postoperative epidural hematoma after subdural hygroma drainage. Case Rep Med. 2010; 2010:417895.
Article29. Yacubian EM, de Andrade MM, Jorge CL, Valério RM. Cerebellar hemorrhage after supratentorial surgery for treatment of epilepsy: report of three cases. Neurosurgery. 1999; 45:159–162.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Remote Epidural Hematoma Following the Removal of Brain Tumors: Report of Three Cases
- Postoperative Contralateral Supra- and Infratentorial Acute Epidural Hematoma after Decompressive Surgery for an Acute Subdural Hematoma: A Case Report
- Acute and Delayed Epidural Hematoma After Total Spondylectomy for a Metastatic Spinal Tumor: A Case Report
- Supratentorial Epidural Hematoma as a Complication of Acoustic Neurinoma Surgery
- The Operation of Acute Epidural Hematoma Through Small Craniotomy: Technical Note