J Korean Soc Radiol.
2011 Feb;64(2):109-112. 10.3348/jksr.2011.64.2.109.
Acute Cerebral Infarction after FK 506 Administration in a Kidney Transplantation Recipient: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, College of Medicine, Yeungnam University, Daegu, Korea. wmbyun@med.yu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2097924
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/jksr.2011.64.2.109
Abstract
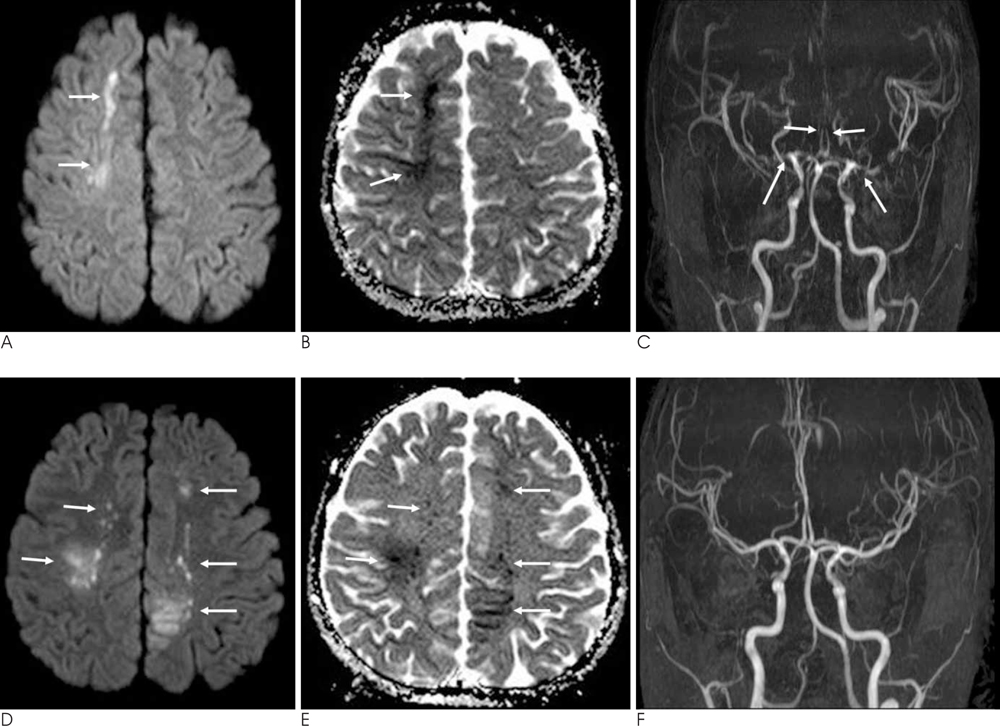
- FK506 is widely used as a potent immunosuppressive agent following organ transplantation. However, the use of FK506 is associated with a wide spectrum of neurotoxicity. FK506-induced cerebral infarctions have rarely been reported. We report here on a case of the acute cerebral infarction caused by vasospasm after FK506 administration in a kidney transplantation recipient. There were areas with increased signal intensity on the diffusion-weighted image. The areas showing increased signal intensity on the diffusion- and T2-weighted images demonstrated decreased signal intensity on the apparent diffusion coefficient mapping. MR angiography showed diffuse stenosis in both the anterior and middle cerebral arteries.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Gijtenbeek JM, van den Bent MJ, Vecht CJ. Cyclosporine neurotoxicity: a review. J Neurol. 1999; 246:339–346.2. Basic-Jukic N, Basic-Kes V, Kes P, Furic-Cunko V, Bacic-Baronica K. Neurological complications in renal transplant recipients. Acta Med Croatica. 2008; 62:Suppl 1. 76–81.3. Ahn KJ, Lee JW, Hahn ST, Yang DW, Kim PS, Kim HJ, et al. Diffusion-weighted MRI and ADC mapping in FK506 neurotoxicity. Br J Radiol. 2003; 76:916–919.4. Kinoshita T, Moritani T, Shrier DA, Hiwatashi A, Wang HZ, Numaguchi Y, et al. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of posterior reversible leukoencephalopathy syndrome: a pictorial essay. Clin Imaging. 2003; 27:307–315.5. Keenan RJ, Konishi H, Kawai A, Paradis IL, Nunley DR, Iacono AT, et al. Clinical trial of tacrolimus versus cyclosporine in lung transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 1995; 60:580–584.6. Eidelman BH, Abu-Elmagd K, Wilson J, Fung JJ, Alessiani M, Jain A, et al. Neurologic complications of FK 506. Transplant Proc. 1991; 23:3175–3178.7. Junna MR, Rabinstein AA. Tacrolimus induced leukoencephalopathy presenting with status epilepticus and prolonged coma. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2007; 78:1410–1411.8. Kilinc M, Benli S, Can U, Yilmaz A, Karakayali H, Colak T, et al. FK 506-induced fulminant leukoencephalopathy after kidney transplantation: case report. Transplant Proc. 2002; 34:1182–1184.9. Curro G, Baccarani U, Adani GL, Lorenzin D, Bresadola F. Transient ischemic attack after rizatriptan administration in a liver transplant recipient: a case report. Transplant Proc. 2006; 38:3138–3139.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Effect of FK 506 on the cornea: use of topical FK 506 in corneal transplantation in a guinea pig-rat model
- The Effect of Combined Immunosuppressive Treatment with FK 506-Cyclophosphamide on Surgical Angiogenesis
- Clinical manifestations of delayed COVID-19 pneumonia in kidney transplant recipients
- The Effects of Cyclosporin A and FK-506 on the Cytokine Production of Lymphocytes in Atopic Dermatitis
- The Effect of FK-506 and Cyclosporine A on Survival of Skin Allograft in Mice