Korean J Radiol.
2014 Jun;15(3):376-380. 10.3348/kjr.2014.15.3.376.
Extramedullary Pulmonary Hematopoiesis Causing Pulmonary Hypertension and Severe Tricuspid Regurgitation Detected by Technetium-99m Sulfur Colloid Bone Marrow Scan and Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/CT
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Diagnostic Radiology, Khoo Teck Puat Hospital, Singapore 768828, Republic of Singapore. syed.zama@gmail.com
- KMID: 2078648
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2014.15.3.376
Abstract
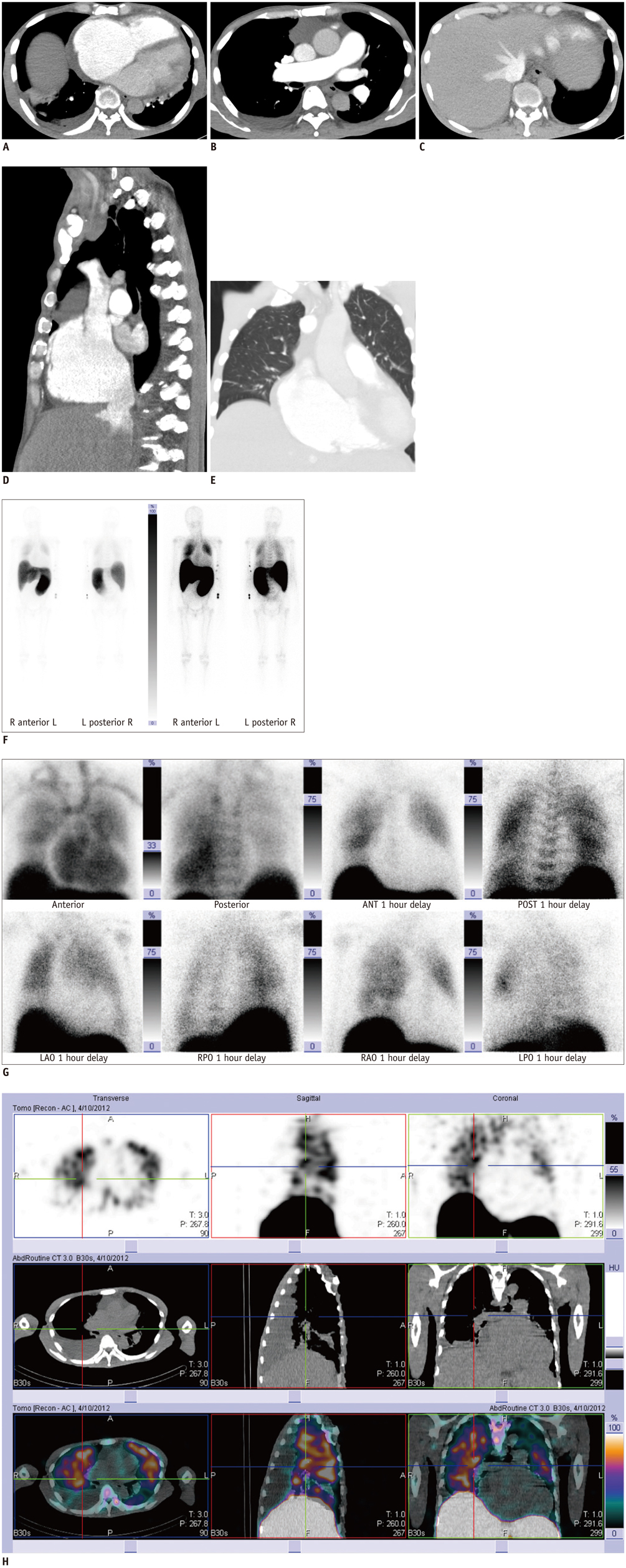
- Extramedullary pulmonary hematopoiesis is a rare entity with a limited number of case reports in the available literature only. We report the case of a 66-year-old man with known primary myelofibrosis, in whom a Technetium-99m sulfur colloid bone marrow scan with single-photon emission computed tomography (SPECT)/CT revealed a pulmonary hematopoiesis as the cause of pulmonary hypertension and severe tricuspid regurgitation. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first description of Technetium-99m sulfur colloid SPECT/CT imaging in this rare condition.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Aged
Bone Marrow/*radionuclide imaging
*Hematopoiesis, Extramedullary
Humans
Hypertension, Pulmonary/*etiology/radionuclide imaging
Lung/*radionuclide imaging
Male
Primary Myelofibrosis/complications
Technetium Tc 99m Sulfur Colloid/diagnostic use
Tomography, Emission-Computed, Single-Photon/methods
Tomography, X-Ray Computed
Tricuspid Valve Insufficiency/*etiology/radionuclide imaging
Technetium Tc 99m Sulfur Colloid
Figure
Reference
-
1. García-Manero G, Schuster SJ, Patrick H, Martinez J. Pulmonary hypertension in patients with myelofibrosis secondary to myeloproliferative diseases. Am J Hematol. 1999; 60:130–135.2. Dingli D, Utz JP, Krowka MJ, Oberg AL, Tefferi A. Unexplained pulmonary hypertension in chronic myeloproliferative disorders. Chest. 2001; 120:801–808.3. Georgiades CS, Neyman EG, Francis IR, Sneider MB, Fishman EK. Typical and atypical presentations of extramedullary hemopoiesis. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002; 179:1239–1243.4. Trow TK, Argento AC, Rubinowitz AN, Decker R. A 71-year-old woman with myelofibrosis, hypoxemia, and pulmonary hypertension. Chest. 2010; 138:1506–1510.5. Schwarz C, Bittner R, Kirsch A, Loddenkemper C, Mairinger T, Schonfeld N, et al. A 62-year-old woman with bilateral pleural effusions and pulmonary infiltrates caused by extramedullary hematopoiesis. Respiration. 2009; 78:110–113.6. Rumi E, Passamonti F, Boveri E, De Amici M, Astori C, Braschi M, et al. Dyspnea secondary to pulmonary hematopoiesis as presenting symptom of myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia. Am J Hematol. 2006; 81:124–127.7. Bajwa AA, Usman F, Wolfson D, Laos LF, Cury JD. A 62-year-old woman with dyspnea, leukocytosis, and diffuse ground-glass opacities. Chest. 2010; 137:1470–1473.8. Jacobson AF, Marks MA, Kaplan WD. Increased lung uptake on technetium-99m-sulfur colloid liver-spleen scans in patients with hepatic venoocclusive disease following bone marrow transplantation. J Nucl Med. 1990; 31:372–374.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Periportal Extramedullary Hematopoiesis
- Focal Increased Tc-99m MDP Uptake in the Nutrient Foramen of the Femoral Diaphysis on Bone SPECT/CT
- Nuclear Medicine Imaging in Rheumatic Diseases
- Clinical Applications of Technetium-99m Quantitative Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography/Computed Tomography
- The Clinical Significance of Bone Scan in Orbital Wall Fracture