Korean J Pain.
2013 Oct;26(4):368-373. 10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.368.
Bertolotti Syndrome: A Diagnostic and Management Dilemma for Pain Physicians
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Anesthesia, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India. anuj.jain.mln@gmail.com
- 2Department of Nuclear Medicine, Sanjay Gandhi Postgraduate Institute of Medical Sciences, Lucknow, India.
- KMID: 2074045
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2013.26.4.368
Abstract
- BACKGROUND
Bertolotti's syndrome (BS), a form of lumbago in lumbosacral transitional vertebrae, is an important cause of low back pain in young patients. The purpose of this study was to assess the etiology of low back pain and the efficacy of treatment offered to patients with BS.
METHODS
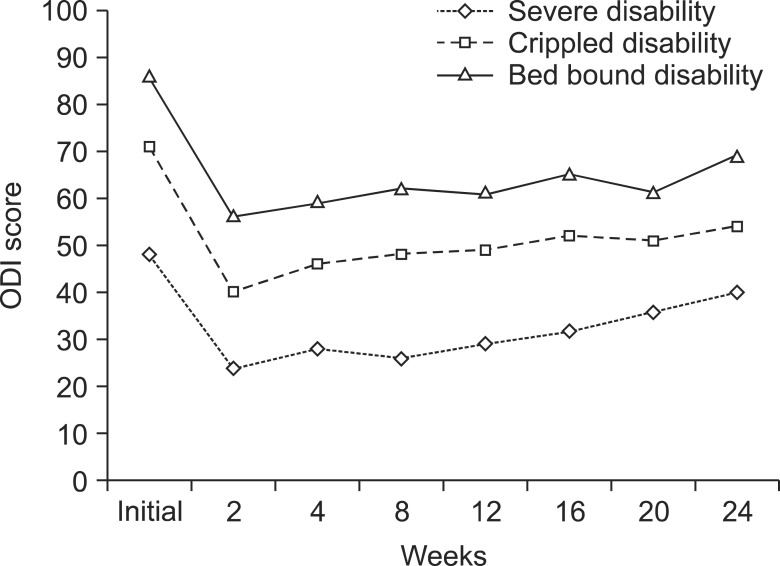
All patients of BS Castellvi type1a during a period of 6 months were enrolled in the study. The patients underwent interventional pain procedures for diagnosis and pain relief. Response to the therapy was assessed based on VAS and ODI scores. A 50% decrease in VAS score or a VAS score less than 3 would be considered adequate pain relief.
RESULTS
All 20 patients diagnosed with BS during the 6-month observation period had scoliosis. Common causes of back pain were the ipsilateral L5-S1 facet joint, neoarticulation, the SI joint, and disc degeneration. Responses to various interventions for pain relief were different and inconsistent from patient to patient. In particular, responses to interventions for neoarticular pain were generally poor.
CONCLUSIONS
Pain in patients with BS does not usually respond to interventional pain treatment. A very dynamic treatment approach must be pursued while managing BS patients, and the treatment plan must be individualized at various stages in order to obtain satisfactory pain relief.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Predictors of discogenic pain in magnetic resonance imaging: a retrospective study of provocative discography performed by posterolateral approach
Anuj Jain, Suruchi Jain, Swapnil Kumar Barasker, Amit Agrawal
Korean J Pain. 2021;34(4):447-453. doi: 10.3344/kjp.2021.34.4.447.
Reference
-
1. Aihara T, Takahashi K, Ogasawara A, Itadera E, Ono Y, Moriya H. Intervertebral disc degeneration associated with lumbosacral transitional vertebrae: a clinical and anatomical study. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2005; 87:687–691. PMID: 15855373.2. Tae HS, Kim SD, Park JY, Kim SH, Lim DJ, Suh JK. Gray ramus communicans nerve block: a useful therapeutic adjuvant for painful osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2003; 34:505–508.3. Simopoulos TT, Malik AB, Sial KA, Elkersh M, Bajwa ZH. Radiofrequency lesioning of the L2 ramus communicans in managing discogenic low back pain. Pain Physician. 2005; 8:61–65. PMID: 16850044.4. Manchikanti L, Helm S, Singh V, Benyamin RM, Datta S, Hayek SM, et al. An algorithmic approach for clinical management of chronic spinal pain. Pain Physician. 2009; 12:E225–E264. PMID: 19668283.5. Henley C, Wollam K, Springs C. Sacroiliac pain: a physical therapy perspective. Post-Polio Health. 2006; 22:1–3.6. Marks RC, Thulbourne T. Infiltration of anomalous lumbosacral articulations. Steroid and anesthetic injections in 10 back-pain patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1991; 62:139–141. PMID: 1826584.
Article7. Santavirta S, Tallroth K, Ylinen P, Suoranta H. Surgical treatment of Bertolotti's syndrome. Follow-up of 16 patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 1993; 112:82–87. PMID: 8457417.8. Nakamura SI, Takahashi K, Takahashi Y, Yamagata M, Moriya H. The afferent pathways of discogenic low-back pain. Evaluation of L2 spinal nerve infiltration. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1996; 78:606–612. PMID: 8682829.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Bertolotti’s Syndrome Requiring Intervention for Lower Back Pain: Two Cases Suspected as Ankylosing Spondylitis
- Bertolotti’s Syndrome Misdiagnosed as Juvenile Idiopathic Arthritis in an Adolescent Girl with Low Back Pain
- Multimodal Treatment for Various Clinical Features in Bertolotti’s Syndrome
- Unusual Lower Back Pain on the Non-Articulated Side in Patient with Bertolotti’s Syndrome
- Case Development on Nurses' Ethical Dilemmas with Physicians' and Nurses' Decision Making