Effects of Erythropoietin on Memory Deficits and Brain Oxidative Stress in the Mouse Models of Dementia
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences and Drug Research, Punjabi University, Patiala (Punjab), PIN-147002, India. nirmal_puru@rediffmail.com
- KMID: 2071704
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4196/kjpp.2010.14.5.345
Abstract
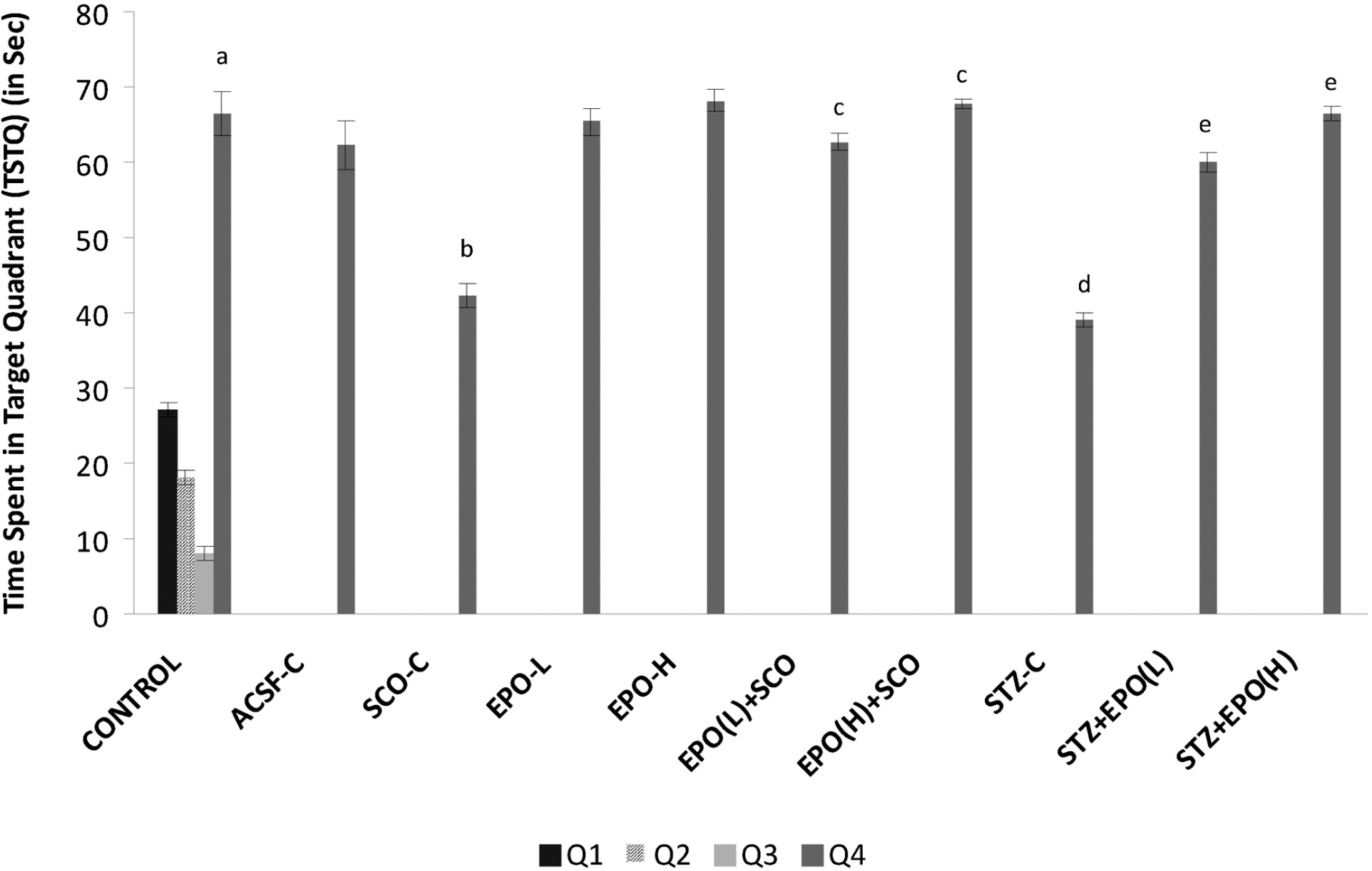
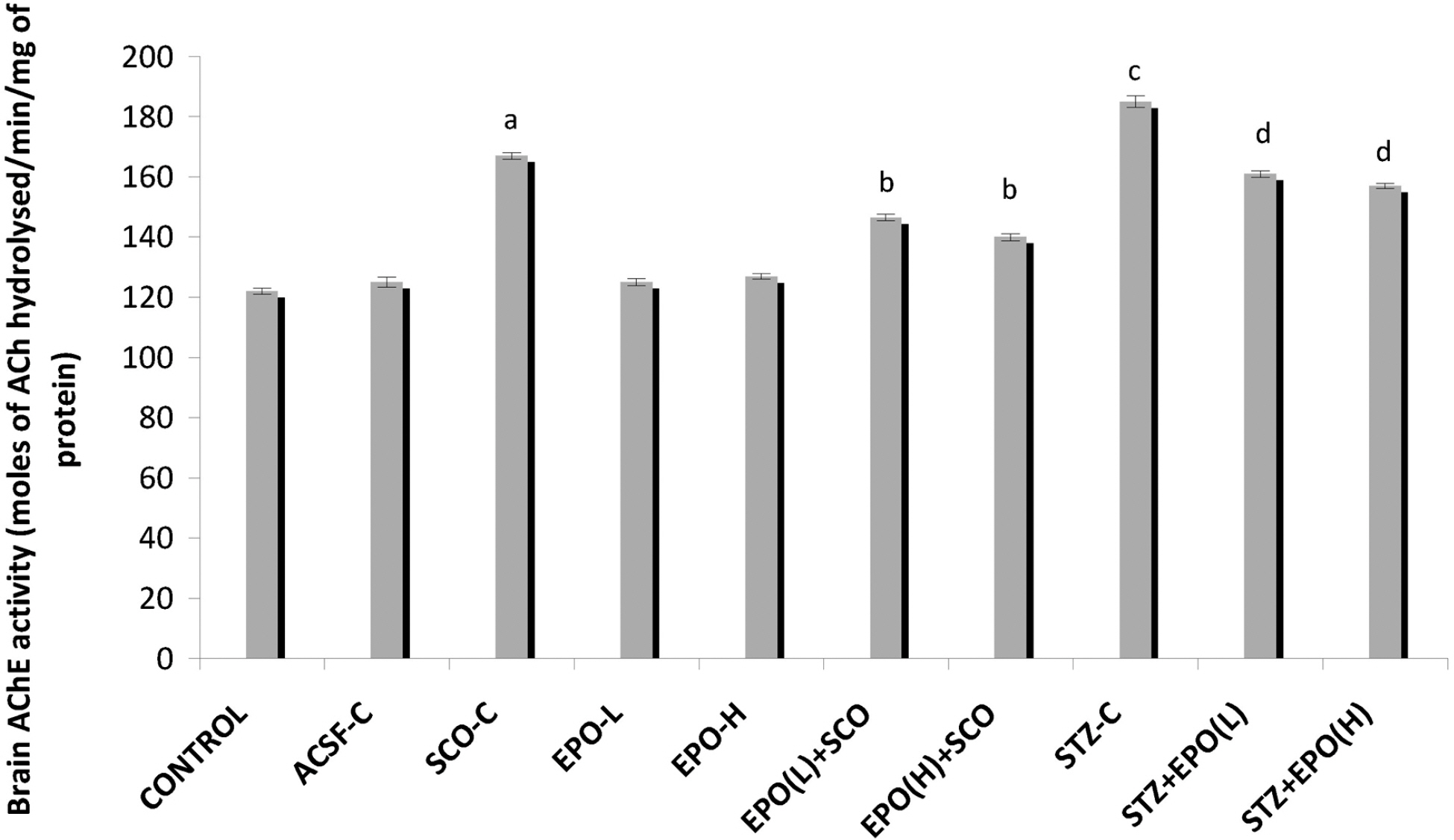
- The present study was undertaken to explore the potential of erythropoietin in memory deficits of mice. Memory impairment was produced by scopolamine (0.5 mg/kg, i.p.) and intracerebroventricular streptozotocin (i.c.v STZ, 3 mg/kg, 10 microliter, 1st and 3rd day) in separate groups of animals. Morris water-maze test was employed to assess learning and memory. The levels of brain thio-barbituric acid reactive species (TBARS) and reduced glutathione (GSH) were estimated to assess degree of oxidative stress. Brain acetylcholinesterase enzyme (AChE) activity was also measured. Scopolamine/streptozotocin administration induced significant impairment of learning and memory in mice as indicated by marked decrease in Morris water-maze performance. Scopolamine/streptozotocin administration also produced a significant enhancement of brain AChE activity and brain oxidative stress (an increase in TBARS and a decrease in GSH) levels. Treatment of erythropoietin (500 and 1,000 IU/Kg i.p.) significantly reversed scopolamine- as well as streptozotocin-induced learning and memory deficits along with attenuation of those-induced rise in brain AChE activity and brain oxidative stress levels. It may be concluded that erythropoietin exerts a beneficial effect in memory deficits of mice possibly through its multiple actions including potential anti-oxidative effect.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
-
Acetylcholinesterase
Animals
Brain
Dementia
Erythropoietin
Glutathione
Learning
Memory
Memory Disorders
Mice
Oxidative Stress
Scopolamine Hydrobromide
Streptozocin
Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances
Acetylcholinesterase
Erythropoietin
Glutathione
Scopolamine Hydrobromide
Streptozocin
Thiobarbituric Acid Reactive Substances
Figure
Cited by 3 articles
-
Phellodendron amurense and Its Major Alkaloid Compound, Berberine Ameliorates Scopolamine-Induced Neuronal Impairment and Memory Dysfunction in Rats
Bombi Lee, Bongjun Sur, Insop Shim, Hyejung Lee, Dae-Hyun Hahm
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2012;16(2):79-89. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2012.16.2.79.Ameliorative Effect of a Selective Endothelin ETA Receptor Antagonist in Rat Model of L-Methionine-induced Vascular Dementia
Gautamjeet S Mangat, Amteshwar S Jaggi, Nirmal Singh
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2014;18(3):201-209. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2014.18.3.201.Effects of cinnamic acid on memory deficits and brain oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
Ali Asghar Hemmati, Soheila Alboghobeish, Akram Ahangarpour
Korean J Physiol Pharmacol. 2018;22(3):257-267. doi: 10.4196/kjpp.2018.22.3.257.
Reference
-
References
Adamcio B., Sargin D., Stradomska A., Medrihan L., Gertler C., Theis F., Zhang M., Müller M., Hassouna I., Hannke K., Sperling S., Radyushkin K., El-Kordi A., Schulze L., Ronnenberg A., Wolf F., Brose N., Rhee JS., Zhang W., Ehrenreich H. Erythropoietin enhances hippocampal long-term potentiation and memory. BMC Biol. 2008. 6:37.
ArticleAgrawal R., Tyagi E., Shukla R., Nath C. Effect of insulin and melatonin on acetylcholinestrase activity in the brain of amnesic mice. Behav Brain Res. 2008. 189:381–386.Bartus RT., Dean RT., Beer B., Lippa AS. The cholinergic hypothesis of geriatric memory dysfunction. Science. 1982. 217:408–417.
ArticleBecker R. Therapy of cognitive deficit of Alzheimer's disease: the cholinergic system in cholinergic basis for Alzheimer therapy. Becker R, Giacobini E, eds. Boston: Birkhauser. 1991. pp.22.Beutler RG., Duron O., Kelly B. Reduced glutathion estimation. J Lab Clinical Med. 1963. 61:82.Blokland A. Acetylcholine: a neurotransmitter for learning and memory? Brain Res Rev. 1995. 21:285–300.
ArticleBraak H., Del Tredici K., Schultz C., Braak E. Vulnerability of select neuronal types of Alzheimer's disease. Ann N Y Acad Sci USA. 2000. 924:53–61.Brines ML., Ghezzi P., Keenan S., Agnello D., de Lanerolle NC., Cerami C., Itri LM., Cerami A. Erythropoietin crosses the blood-brain barrier to protect against experimental brain injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000. 97:10526–10531.
ArticleCampana WM., Misasi R., O'Brien JS. Identification of a neurotrophic sequence in erythropoietin. Int J Mol Med. 1998. 1:235–241.
ArticleChandel NS., Maltepe E., Goldwasser E., Mathieu CE., Simon MC., Schumacke PT. Mitochondrial reactive oxygen species trigger hypoxia-induced transcription. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 1998. 95:11715–11720.
ArticleCoyle JT., Price DL., Delong MR. Alzheimer's disease: a disorder of cortical cholinergic innervations. Science. 1983. 219:1184–1190.Dame C., Bratmann P., Wolber EM., Fahnenstich H., Hofman D., Fandrey J. Erythropoietin gene expression in different areas of the developing human central nervous system. Brain Res Dev Brain Res. 2000. 125:69–74.
ArticleDeutsch JA., Rocklin KW. Amnesia induced by scopolamine and its temporal variations. Nature. 1967. 216:89–90.
ArticleDeutsch JA. The cholinergic synapse and the site of memory. Science. 1971. 174:788–794.
ArticleEl-Kordi A., Radyushkin K., Ehrenreich H. Erythropoietin improves operant conditioning and stability of cognitive performance in mice. BMC Biol. 2009. 7:37.
ArticleEllman GL., Courtney DK., Andres V., Feathstone RM. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinestrase activity. Biochem Pharmacol. 1961. 7:88–95.El-Sherbiny DA., Khalifa AE., Attia AS., Eldenshary ED. Hypericum perforatum extract demonstrates anti oxidant properties against elevated rat brain oxidative status induced by amnestic dose of scopolamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2003. 76:525–533.Feillet-Coudray C., Rock E., Coudray C., Grzelkowska K., Azais-Braesco V., Dardevet D. Lipid peroxidation and anti oxidant status in experimental diabetes. Clin Chim Acta. 1999. 284:31–43.Genc S., Koroglu TF., Genc K. Erythropoietin and the nervous system. Brain Res. 2004. 1000:19–31.
ArticleGranic I., Dolga AM., Nijholt IM., Van Dijk G., Eisel UL. Inflammation and NF-kappaB in Alzheimer's disease and diabetes. J Alzheimers Dis. 2009. 16:809–821.Grünblatt E., Salkovic-Petrisic M., Osmanovic J., Riederer P., Hoyer S. Brain insulin system dysfunction in streptozotocin intrace-rebroventricularly treated rats generates hyperphosphorylated tau protein. J Neurochem. 2007. 101:757–770.
ArticleHaley TJ., McCormick WG. Pharmacological effects produced by intracerebral injection of drugs in the conscious mice. Br J Pharmacol Chemother. 1957. 12:12–15.Hoyer S. The aging brain. Changes in the neuronal insulin / insulin receptor signal transduction cascade trigger late onset sporadic Alzheimer's disease (SAD). A mini review. J Neural Transm. 2000a. 109:991–1002.Hoyer S. The brain insulin signal transduction system and sporadic (type II) Alzheimer's disease: an update. J Neural Transm. 2000b. 109:341–360.Juul S. Erythropoietin in the central nervous system, and its use to prevent hypoxic-ischemic brain damage. Acta Paediatr Suppl. 2002. 91:36–42.
ArticleJuul SE., Yachnis AT., Rojiani AM., Christensen RD. Immunohistochemical localization of erythropoietin and its receptor in the developing human brain. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 1999. 2:148–158.
ArticleKaur B., Singh N., Jaggi AS. Exploring mechanism of pioglitazone-induced memory restorative effect in experimental dementia. Fundam Clin Pharmacol. 2009. 23:557–566.
ArticleKhalifa AE. Pro oxidant activity of Zuclopenthixol in vivo: Differential effect of the drug on brain oxidative status of scopolamine treated rats. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2004. 23:439–445.Konishi Y., Chui DH., Hirose H., Kunishita T. Trophic effect of erythropoietin and other hematopoietic factors on central cholinergic neurons in vitro and in vivo. Brain Res. 1993. 609:29–35.
ArticleLannert H., Hoyer S. Intracerebroventricular administration of Streptozotocin causes long term diminutions in learning and memory abilities and in cerebral energy metabolism in adult rats. Behav Neurosci. 1998. 112:1199–1208.Lewczuk P., Hasselblatt M., Kamrowski-Kruck H., Heyer A., Unzicker C., Siren AL. Survival of hippocampal neurons in culture upon hypoxia: effect of erythropoietin. Neuroreport. 2000. 11:3485–3488.Liu X., Xie W., Liu P., Duan M., Jia Z., Li W. Mechanism of the cardioprotection of rhEPO pretreatment on suppressing the inflammatory response in ischemia-reperfusion. Life Sci. 2006. 78:2255–2264.
ArticleLowry OH., Rosenbrough NJ., Farr AL., Randall RJ. Protein measurement with folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951. 193:265–275.Marti HH., Wenger RH., Rivas LA., Straumann U., Dicicaylioglu M., Henn V. Erythropoietin gene expression in human, monkey and murine brain. Eur J Neurosci. 1996. 8:666–676.
ArticleMasuda S., Okano M., Yamagishi K., Nagao M., Ueda M., Sasaki R. A novel site of erythropoietin production: oxygen-dependent production in cultured rat astrocytes. J Biol Chem. 1994. 269:19488–19493.
ArticleMayer G., Nitsch R., Hoyer S. Effects of changes in peripheral and cerebral glucose metabolism on locomotor activity, learning and memory in adult male rats. Brain Res. 1990. 532:95–100.
ArticleMorishita E., Masuda S., Nagao M., Yasuda Y., Sasaki R. Erythropoietin receptor is expressed in rat hippocampal and cerebral cortical neurons and erythropoietin prevents in vitro glutamate-induced neuronal death. Neuroscience. 1997. 76:105–116.
ArticleMorris RGM. Developments of a water maze producer for studying spatial learning in the rats. J Neurosci Meth. 1984. 11:47–60.Ohkawa H., Ohishi N., Yagi K. Assay for lipid peroxides in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem. 1979. 95:351–358.
ArticlePackard MG., Teather LA., Bazan NG. Effect of intra-striated injections of platelet-activating factor and PAF antagonist BN 52021 on memory. Neurobiol Learn Mem. 1996. 66:176–182.Parle M., Singh N. Animal models of testing memory. Asia pacific J Pharmacol. 2004. 16:101–120.Parle M., Singh N. Reversal of memory deficits by atorvastatin and simvastatin in rats. Yakugaku Zasshi. 2007. 127:1125–1137.
ArticleReagan LP., Magariños AM., Yee DK., Swzeda LI., Van Bueren A., McCall AL., McEwen BS. Oxidative stress and HNE conjugation of GLUT3 are increased in the hippocampus of diabetic rats subjected to stress. Brain Res. 2000. 862:292–300.
ArticleRui T., Feng Q., Lie M., Peng T., Zhang J., Xu M. Erythropoietin prevents the acute myocardial inflammatory response induced by ischemia/reperfusion via induction of AP-1. Cardiovasc Res. 2005. 65:719–727.
ArticleSakurada T., Sakurada S., Katsuyama S., Sakurada C., No KT., Terenius L. Noceceptin (1–7) antagonizes noceceptin induced hyperalgesia in mice. Br J Pharmacol. 1999. 128:941–944.Salkovic-Petrisic M., Tribl F., Schmidt M., Hoyer S., Riederer P. Alzheimer-like changes in protein kinase B and glycogen synthase kinase-3 in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus after damage to the insulin signalling pathway. J Neurochem. 2006. 96:1005–1015.
ArticleSalminen A., Ojala J., Kauppinen A., Kaarniranta K., Suuronen T. Inflammation in Alzheimer's disease: amyloid-beta oligomers trigger innate immunity defence via pattern recognition receptors. Prog Neurobiol. 2009. 87:181–194.Sharma B., Singh N., Singh M., Jaggi AS. Exploitation of HIV protease inhibitor indinavir as a memory restorative agent in experimental dementia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2008b. 89:535–545.
ArticleSharma B., Singh N., Singh M. Modulation of celecoxib and Streptozotocin induced experimental dementia of Alzheimer's disease type by pitavastatin and donepezil. J Psychopharmacol. 2008a. 22:162–171.Sharma M., Gupta YK. Effect of chronic treatment of melatonin on learning, memory and oxidative deficiencies induced by intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2001. 70:325–331.
ArticleShoham S., Bejar C., Kovalev E., Weinstock M. Intracerebroventricular injection of streptozotocin causes neurotoxicity to myelin that contributesto spatial memory deficits in rats. Exp Neurol. 2003. 184:1043–1052.Signore AP., Weng Z., Hastings T., Van Laar AD., Liang Q., Lee YJ. Erythropoietin protects against 6-hydroxydopamine induced dopaminergic cell death. J Neurochem. 2006. 96:428–443.Siren AL., Enrenreich H. Erythropoietin a novel concept for neuroprotection. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci. 2001. 251:179–184.Siren AL., Fratelli M., Brines M., Goemans C., Casagrande S., Lewczuk P., Keenan S., Gleiter C., Pasquali C., Capobianco A., Mennini T., Heumann R., Cerami A., Ehrenreich H., Ghezzi P. Erythropoietin prevents neuronal apoptosis after cerebral ischemia and in metabolically stressed neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2001. 98:4044–4049.Siren AL., Knerlich F., Poser W., Gleiter CH., Bruck W., Ehrenreich H. Erythropoietin and erythropoietin receptor in human ischemic/ hypoxic brain. Acta Neuropathol. 2001. 101:271–276.Smith KJ., Kapoor R., Felts PA. Demyelination: the role of reactive oxygen and nitrogen species. Brain Patho. 1999. 9:69–92.
ArticleTabira T., Konishi Y., Gallyas F Jr. Neurotrophic effect of hematopoietic cytokines on cholinergic and other neurons in vitro. Int J Dev Neurosci. 1995. 13:241–252.Torre DLJ., Aliev G., Perry G. Drug therapy in Alzheimer's disease. N Engl J Med. 2004. 351:1911–1913.Viviani B., Bartesaghi S., Corsini E., Villa P., Ghezzi P., Garau A., Galli CL., Marinovich M. Erythropoietin protects primary hippocampal neurons increasing the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor. J Neurochem. 2005. 93:412–421.
ArticleVoss G., Sachsse K. Red cell and plasma cholinesterase activities in microsamples of human and animal blood determined simultaneously by a modified acetylcholine/DTNB procedure. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 1970. 16:764–772.Wang ZY., Shen LJ., Tu L., Hu DN., Liu GY., Zhou ZL., Lin Y., Chen LH., Qu J. Erythropoietin protects retinal pigment epithelial cells from oxidative damage. Free Radic Biol Med. 2009. 46:1032–1041.
ArticleXue YQ., Zhao LR., Guo WP., Duan WM. Intrastriatal administration of erythropoietin protects dopaminergic neurons and improves neurobehavioral outcome in a rat model of Parkinson's disease. Neuroscience. 2007. 146:1245–1258.
ArticleYamamoto M., Koshimura K., Kawaquchi M., Sohmiya M., Murakami Y., Kato Y. Stimulating effect of Erythropoietin on the release of dopamine and acetylcholine from the rat brain slice. Neurosci Lett. 2000. 292:131–133.
ArticleYamazaki M., Matsuoka N., Maeda N., Kuratani K., Ohkubo Y., Yamaguchi I. FR121196: a potential anti dementia drug ameliorates the impaired memory of rats in Morris water maze. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1995. 272:256–263.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- The memory ameliorating effects of novel N‑benzyl pyridine‑2‑one derivatives on scopolamine‑induced cognitive deficits in mice
- Ameliorative effects of Moringa on cuprizone-induced memory decline in rat model of multiple sclerosis
- Secondary hypoxic ischemia alters neurobehavioral outcomes, neuroinflammation, and oxidative stress in mice exposed to controlled cortical impact
- Effects of cinnamic acid on memory deficits and brain oxidative stress in streptozotocin-induced diabetic mice
- Strategic Infarct Dementia after Bilateral Anterior Fornix Infarction