Clin Orthop Surg.
2015 Mar;7(1):1-7. 10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.1.
Achilles Tendinosis: Treatment Options
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopedic Surgery, Konkuk University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. jungfoot@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2069868
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4055/cios.2015.7.1.1
Abstract
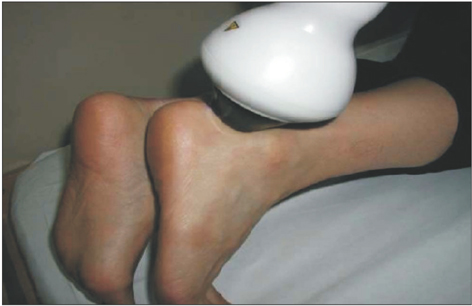
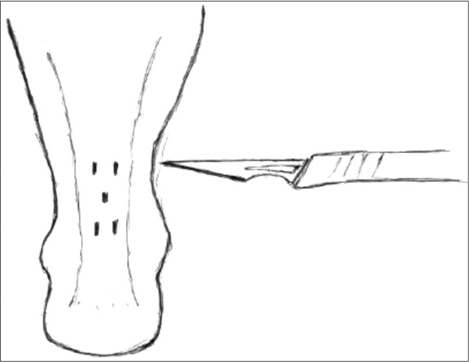
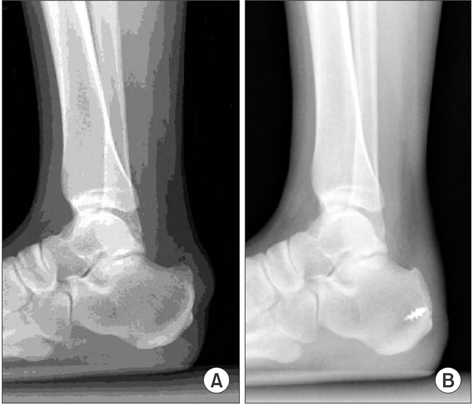
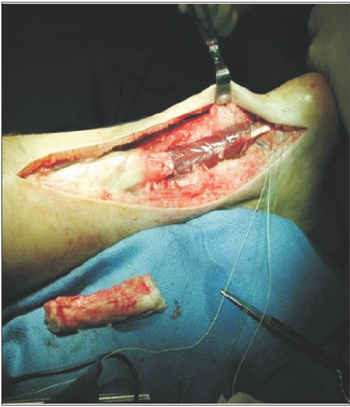
- Athletes usually complain of an ongoing or chronic pain over the Achilles tendon, but recently even non-athletes are experiencing the same kind of pain which affects their daily activities. Achilles tendinosis refers to a degenerative process of the tendon without histologic or clinical signs of intratendinous inflammation. Treatment is based on whether to stimulate or prevent neovascularization. Thus, until now, there is no consensus as to the best treatment for this condition. This paper aims to review the common ways of treating this condition from the conservative to the surgical options.
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lake JE, Ishikawa SN. Conservative treatment of Achilles tendinopathy: emerging techniques. Foot Ankle Clin. 2009; 14(4):663–674.2. Leadbetter WB. Cell-matrix response in tendon injury. Clin Sports Med. 1992; 11(3):533–578.3. Kvist M. Achilles tendon injuries in athletes. Sports Med. 1994; 18(3):173–201.4. Holmes GB, Lin J. Etiologic factors associated with symptomatic Achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Int. 2006; 27(11):952–959.5. Astrom M, Westlin N. No effect of piroxicam on Achilles tendinopathy: a randomized study of 70 patients. Acta Orthop Scand. 1992; 63(6):631–634.6. Smidt N, van der Windt DA, Assendelft WJ, Deville WL, Korthals-de Bos IB, Bouter LM. Corticosteroid injections, physiotherapy, or a wait-and-see policy for lateral epicondylitis: a randomised controlled trial. Lancet. 2002; 359(9307):657–662.7. DaCruz DJ, Geeson M, Allen MJ, Phair I. Achilles paratendonitis: an evaluation of steroid injection. Br J Sports Med. 1988; 22(2):64–65.8. Gill SS, Gelbke MK, Mattson SL, Anderson MW, Hurwitz SR. Fluoroscopically guided low-volume peritendinous corticosteroid injection for Achilles tendinopathy: a safety study. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2004; 86(4):802–806.9. Alfredson H, Pietila T, Jonsson P, Lorentzon R. Heavy-load eccentric calf muscle training for the treatment of chronic Achilles tendinosis. Am J Sports Med. 1998; 26(3):360–366.10. Shalabi A, Kristoffersen-Wiberg M, Aspelin P, Movin T. Immediate Achilles tendon response after strength training evaluated by MRI. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2004; 36(11):1841–1846.11. Alfredson H, Ohberg L, Forsgren S. Is vasculo-neural ingrowth the cause of pain in chronic Achilles tendinosis? An investigation using ultrasonography and colour Doppler, immunohistochemistry, and diagnostic injections. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003; 11(5):334–338.12. Fahlstrom M, Jonsson P, Lorentzon R, Alfredson H. Chronic Achilles tendon pain treated with eccentric calf-muscle training. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2003; 11(5):327–333.13. Furia JP. High-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a treatment for insertional Achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med. 2006; 34(5):733–740.14. Furia JP. High-energy extracorporeal shock wave therapy as a treatment for chronic noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36(3):502–508.15. Boesen MI, Torp-Pedersen S, Koenig MJ, et al. Ultrasound guided electrocoagulation in patients with chronic non-insertional Achilles tendinopathy: a pilot study. Br J Sports Med. 2006; 40(9):761–766.16. Murrell GA. Using nitric oxide to treat tendinopathy. Br J Sports Med. 2007; 41(4):227–231.17. Osadnik R, Redeker J, Kraemer R, Vogt PM, Knobloch K. Microcirculatory effects of topical glyceryl trinitrate on the Achilles tendon microcirculation in patients with previous Achilles tendon rupture. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010; 18(7):977–981.18. Hunte G, Lloyd-Smith R. Topical glyceryl trinitrate for chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Clin J Sport Med. 2005; 15(2):116–117.19. Paoloni JA, Murrell GA. Three-year followup study of topical glyceryl trinitrate treatment of chronic noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy. Foot Ankle Int. 2007; 28(10):1064–1068.20. Kane TP, Ismail M, Calder JD. Topical glyceryl trinitrate and noninsertional Achilles tendinopathy: a clinical and cellular investigation. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36(6):1160–1163.21. Orchard J, Massey A, Rimmer J, Hofman J, Brown R. Delay of 6 weeks between aprotinin injections for tendinopathy reduces risk of allergic reaction. J Sci Med Sport. 2008; 11(5):473–480.22. Capasso G, Maffulli N, Testa V, Sgambato A. Preliminary results with peritendinous protease inhibitor injections in the management of Achilles tendinitis. J Sports Traumatol Rel Res. 1993; 15(1):37–43.23. Stergioulas A, Stergioula M, Aarskog R, Lopes-Martins RA, Bjordal JM. Effects of low-level laser therapy and eccentric exercises in the treatment of recreational athletes with chronic achilles tendinopathy. Am J Sports Med. 2008; 36(5):881–887.24. Sweeting K, Yelland M. Achilles tendinosis: how does prolotherapy compare to eccentric loading exercises? J Sci Med Sport. 2009; 12:Supplement. S19.25. Magnussen RA, Dunn WR, Thomson AB. Nonoperative treatment of midportion Achilles tendinopathy: a systematic review. Clin J Sport Med. 2009; 19(1):54–64.26. de Jonge S, de Vos RJ, Weir A, et al. One-year follow-up of platelet-rich plasma treatment in chronic Achilles tendinopathy: a double-blind randomized placebo-controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2011; 39(8):1623–1629.27. Maffulli N, Testa V, Capasso G, et al. Surgery for chronic Achilles tendinopathy yields worse results in nonathletic patients. Clin J Sport Med. 2006; 16(2):123–128.28. Maffulli N, Testa V, Capasso G, et al. Surgery for chronic Achilles tendinopathy produces worse results in women. Disabil Rehabil. 2008; 30(20-22):1714–1720.29. Testa V, Capasso G, Benazzo F, Maffulli N. Management of Achilles tendinopathy by ultrasound-guided percutaneous tenotomy. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2002; 34(4):573–580.30. Maffulli N, Testa V, Capasso G, Bifulco G, Binfield PM. Results of percutaneous longitudinal tenotomy for Achilles tendinopathy in middle- and long-distance runners. Am J Sports Med. 1997; 25(6):835–840.31. Maffulli N, Longo UG, Spiezia F, Denaro V. Minimally invasive surgery for Achilles tendon pathologies. Open Access J Sports Med. 2010; 1:95–103.32. Longo UG, Ramamurthy C, Denaro V, Maffulli N. Minimally invasive stripping for chronic Achilles tendinopathy. Disabil Rehabil. 2008; 30(20-22):1709–1713.33. Steenstra F, van Dijk CN. Achilles tendoscopy. Foot Ankle Clin. 2006; 11(2):429–438.34. Maquirriain J. Surgical treatment of chronic achilles tendinopathy: long-term results of the endoscopic technique. J Foot Ankle Surg. 2013; 52(4):451–455.35. Murphy GA. Surgical treatment of non-insertional Achilles tendinitis. Foot Ankle Clin. 2009; 14(4):651–661.36. Schon LC, Shores JL, Faro FD, Vora AM, Camire LM, Guyton GP. Flexor hallucis longus tendon transfer in treatment of Achilles tendinosis. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2013; 95(1):54–60.