J Cerebrovasc Endovasc Neurosurg.
2015 Sep;17(3):173-179. 10.7461/jcen.2015.17.3.173.
Endovascular Treatment for Acute Ischemic Stroke Patients over 80 Years of Age
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Regional Caridocerebrovascular Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea. storynlemon@gmail.com
- 2Department of Neurology, Regional Caridocerebrovascular Center, Seoul National University Bundang Hospital, Seongnam, Korea.
- KMID: 2069240
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.7461/jcen.2015.17.3.173
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
We evaluated the effect of endovascular treatment (EVT) for acute ischemic stroke in patients over 80 years of age.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
The records of 156 acute stroke patients aged over 80 years who were considered as candidates for EVT were analyzed. Fifty-six patients (35.9%, EVT group) underwent EVT and 100 patients (64.1%, non-EVT group) did not. Outcomes, in terms of functional outcomes and rates of symptomatic hemorrhage, in-hospital morbidity and mortality, were compared between groups. Each comparison was adjusted for age, time from onset, initial National Institute of Health Stroke Scale, and pre-stroke modified Rankin Scale (mRS).
RESULTS
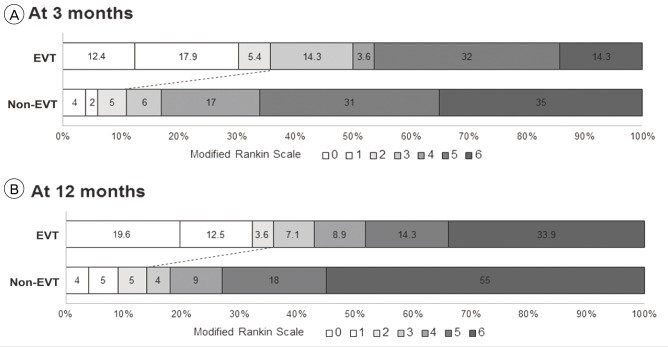
More patients in the EVT group achieved good outcomes (mRS score of 0-2) at 3 months (35.7% vs. 11.0%, adjusted odds ratio [OR] 4.779 [95% confidence interval 1.972-11.579], p = 0.001) and 12 months (35.7% vs. 14.0%, adjusted OR 3.705 [1.574-8.722], p = 0.003) after stroke. During admission, rates of hospital-acquired infection including pneumonia (12.5% vs. 29.0%, adjusted OR 0.262 [0.098-0.703], p = 0.008) and urinary tract infection (16.0% vs. 34.0%, adjusted OR 0.256 [0.099-0.657], p = 0.005) were significantly lower in the EVT group. More symptomatic hemorrhages (10.7% vs. 2.0%, adjusted OR 6.859 [1.139-41.317], p = 0.036) occurred in the EVT group, but no significant difference was observed in in-hospital mortality rate (12.5% vs. 8.0%, adjusted OR 1.380 [0.408-4.664], p = 0.604).
CONCLUSION
EVT improved functional outcome and reduced the risk of hospital-acquired infections in acute stroke patients over 80 years of age without increasing the risk of in-hospital mortality, although symptomatic hemorrhage occurred more frequently after EVT.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Alshekhlee A, Mohammadi A, Mehta S, Edgell RC, Vora N, Feen E, et al. Is thrombolysis safe in the elderly?: analysis of a national database. Stroke. 2010; 10. 41(10):2259–2264. PMID: 20829516.2. Aslanyan S, Weir CJ, Diener HC, Kaste M, Lees KR. GAIN International Steering Committee and Investigators. Pneumonia and urinary tract infection after acute ischaemic stroke: a tertiary analysis of the GAIN International trial. Eur J Neurol. 2004; 1. 11(1):49–53. PMID: 14692888.
Article3. Bang JS, Oh CW, Jung C, Park SQ, Hwang KJ, Kang HS, et al. Intracranial stent placement for recanalization of acute cerebrovascular occlusion in 32 patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 8. 31(7):1222–1225. PMID: 20360342.
Article4. Bateman BT, Schumacher HC, Boden-Albala B, Berman MF, Mohr JP, Sacco RL, et al. Factors associated with in-hospital mortality after administration of thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke patients: an analysis of the nationwide inpatient sample 1999 to 2002. Stroke. 2006; 2. 37(2):440–446. PMID: 16397164.5. Berkhemer OA, Fransen PS, Beumer D, van den Berg LA, Lingsma HF, Yoo AJ, et al. A randomized trial of intraarterial treatment for acute ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 1. 372(1):11–20. PMID: 25517348.6. Bonita R, Anderson CS, Broad JB, Jamrozik KD, Stewart-Wynne EG, Anderson NE. Stroke incidence and case fatality in Australasia. A comparison of the Auckland and Perth population-based stroke registers. Stroke. 1994; 3. 25(3):552–557. PMID: 8128506.
Article7. Davenport RJ, Dennis MS, Warlow CP. Gastrointestinal hemorrhage after acute stroke. Stroke. 1996; 3. 27(3):421–424. PMID: 8610306.
Article8. Derex L, Nighoghossian N. Thrombolysis, stroke-unit admission and early rehabilitation in elderly patients. Nat Rev Neurol. 2009; 9. 5(9):506–511. PMID: 19652651.
Article9. Di Carlo A, Baldereschi M, Gandolfo C, Candelise L, Ghetti A, Maggi S, et al. Stroke in an elderly population: incidence and impact on survival and daily function. The Italian Longitudinal Study on Aging. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2003; 2. 16(2):141–150. PMID: 12792172.10. Finlayson O, Kapral M, Hall R, Asllani E, Selchen D, Saposnik G. Risk factors, inpatient care, and outcomes of pneumonia after ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2011; 10. 77(14):1338–1345. PMID: 21940613.
Article11. Furlan A, Higashida R, Wechsler L, Gent M, Rowley H, Kase C, et al. Intra-arterial prourokinase for acute ischemic stroke. The PROACT II study: a randomized controlled trial. Prolyse in Acute Cerebral Thromboembolism. JAMA. 1999; 12. 282(21):2003–2011. PMID: 10591382.12. Goyal M, Demchuk AM, Menon BK, Eesa M, Rempel JL, Thornton J, et al. Randomized assessment of rapid endovascular treatment of ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 3. 372(11):1019–1030. PMID: 25671798.13. Group TNt-PSS. Generalized efficacy of t-PA for acute stroke. Subgroup analysis of the NINDS t-PA Stroke Trial. Stroke. 1997; 11. 28(11):2119–2125. PMID: 9368551.14. Hacke W, Donnan G, Fieschi C, Kaste M, von Kummer R, Broderick JP, et al. Association of outcome with early stroke treatment: pooled analysis of ATLANTIS, ECASS, and NINDS rt-PA stroke trials. Lancet. 2004; 3. 363(9411):768–774. PMID: 15016487.15. Hacke W, Kaste M, Fieschi C, Toni D, Lesaffre E, von Kummer R, et al. Intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute hemispheric stroke. The European Cooperative Acute Stroke Study (ECASS). JAMA. 1995; 10. 274(13):1017–1025. PMID: 7563451.
Article16. Heuschmann PU, Kolominsky-Rabas PL, Roether J, Misselwitz B, Lowitzsch K, Heidrich J, et al. Predictors of in-hospital mortality in patients with acute ischemic stroke treated with thrombolytic therapy. JAMA. 2004; 10. 292(15):1831–1838. PMID: 15494580.
Article17. Hussein HM, Georgiadis AL, Vazquez G, Miley JT, Memon MZ, Mohammad YM, et al. Occurrence and predictors of futile recanalization following endovascular treatment among patients with acute ischemic stroke: a multicenter study. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2010; 3. 31(3):454–458. PMID: 20075087.
Article18. Hwang G, Oh CW, Bang JS, Jung CK, Kwon OK, Kim JE, et al. Superficial temporal artery to middle cerebral artery bypass in acute ischemic stroke and stroke in progress. Neurosurgery. 2011; 3. 68(3):723–729. discussion 729-30PMID: 21311299.
Article19. Jauch EC, Saver JL, Adams HP Jr, Bruno A, Connors JJ, Demaerschalk BM, et al. Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke. 2013; 3. 44(3):870–947. PMID: 23370205.20. Jovin TG, Chamorro A, Cobo E, de Miquel MA, Molina CA, Rovira A, et al. Thrombectomy within 8 hours after symptom onset in ischemic stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 6. 372(24):2296–2306. PMID: 25882510.
Article21. Kang DH, Hwang YH, Kim YS, Park J, Kwon O, Jung C. Direct thrombus retrieval using the reperfusion catheter of the penumbra system: forced-suction thrombectomy in acute ischemic stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2011; 2. 32(2):283–287. PMID: 21087940.
Article22. Kass-Hout T, Amuluru K, Al-Derazi Y, Singh P, Prestigiacomo CJ, Gandhi CD. Endovascular therapy for acute ischemic stroke: time to enter a new era in stroke management. World Neurosurg. 2015; 6. 83(6):951–953. PMID: 25845715.
Article23. Kim D, Ford GA, Kidwell CS, Starkman S, Vinuela F, Duckwiler GR, et al. Intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute stroke in patients 80 and older: a comparison of results in patients younger than 80 years. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2007; 1. 28(1):159–163. PMID: 17213448.24. Marini C, Baldassarre M, Russo T, De Santis F, Sacco S, Ciancarelli I, et al. Burden of first-ever ischemic stroke in the oldest old: evidence from a population-based study. Neurology. 2004; 1. 62(1):77–81. PMID: 14718701.
Article25. Mazighi M, Labreuche J, Meseguer E, Serfaty JM, Laissy JP, Lavallee PC, et al. Impact of a combined intra-venous/intra-arterial approach in octogenarians. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2011; 6. 31(6):559–565. PMID: 21487220.26. Mono ML, Romagna L, Jung S, Arnold M, Galimanis A, Fischer U, et al. Intra-arterial thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke in octogenarians. Cerebrovasc Dis. 2012; 2. 33(2):116–122. PMID: 22179504.
Article27. O'Donnell MJ, Kapral MK, Fang J, Saposnik G, Eikelboom JW, Oczkowski W, et al. Gastrointestinal bleeding after acute ischemic stroke. Neurology. 2008; 8. 71(9):650–655. PMID: 18685137.28. Park H, Hwang GJ, Jin SC, Jung CK, Bang JS, Han MK, et al. A retrieval thrombectomy technique with the Solitaire stent in a large cerebral artery occlusion. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 2011; 8. 153(8):1625–1631. PMID: 21479799.
Article29. Poisson SN, Johnston SC, Josephson SA. Urinary tract infections complicating stroke: mechanisms, consequences, and possible solutions. Stroke. 2010; 4. 41(4):e180–e184. PMID: 20167905.30. Qureshi AI, Suri MF, Georgiadis AL, Vazquez G, Janjua NA. Intra-arterial recanalization techniques for patients 80 years or older with acute ischemic stroke: pooled analysis from 4 prospective studies. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 6. 30(6):1184–1189. PMID: 19342542.
Article31. Rocco A, Pasquini M, Cecconi E, Sirimarco G, Ricciardi MC, Vicenzini E, et al. Monitoring after the acute stage of stroke: a prospective study. Stroke. 2007; 4. 38(4):1225–1228. PMID: 17322080.32. Saver JL, Goyal M, Bonafe A, Diener HC, Levy EI, Pereira VM, et al. Stent-Retriever Thrombectomy after Intravenous t-PA vs. t-PA Alone in Stroke. N Engl J Med. 2015; 6. 372(24):2285–2295. PMID: 25882376.
Article33. Stott DJ, Falconer A, Miller H, Tilston JC, Langhorne P. Urinary tract infection after stroke. QJM. 2009; 4. 102(4):243–249. PMID: 19233882.
Article34. Vargas M, Horcajada JP, Obach V, Revilla M, Cervera A, Torres F, et al. Clinical consequences of infection in patients with acute stroke: is it prime time for further antibiotic trials? Stroke. 2006; 2. 37(2):461–465. PMID: 16385093.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Endovascular Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke
- Intravenous Thrombolysis and Endovascular Thrombectomy in Acute Ischemic Stroke with Minor Symptom
- Rescue Endovascular Treatment to Prevent Neurological Deterioration in Acute Symptomatic Bilateral Vertebral Artery Occlusion
- Reperfusion therapy in acute ischemic stroke
- Endovascular Mechanical Thrombectomy for Acute Ischemic Stroke: A New Standard of Care