Infect Chemother.
2015 Sep;47(3):190-193. 10.3947/ic.2015.47.3.190.
FDG PET-CT in the Diagnosis of Takayasu Arteritis Presenting as Fever of Unknown Origin: A Case Report
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, Seoul National University Hospital, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mdohmd@snu.ac.kr
- KMID: 2068985
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3947/ic.2015.47.3.190
Abstract
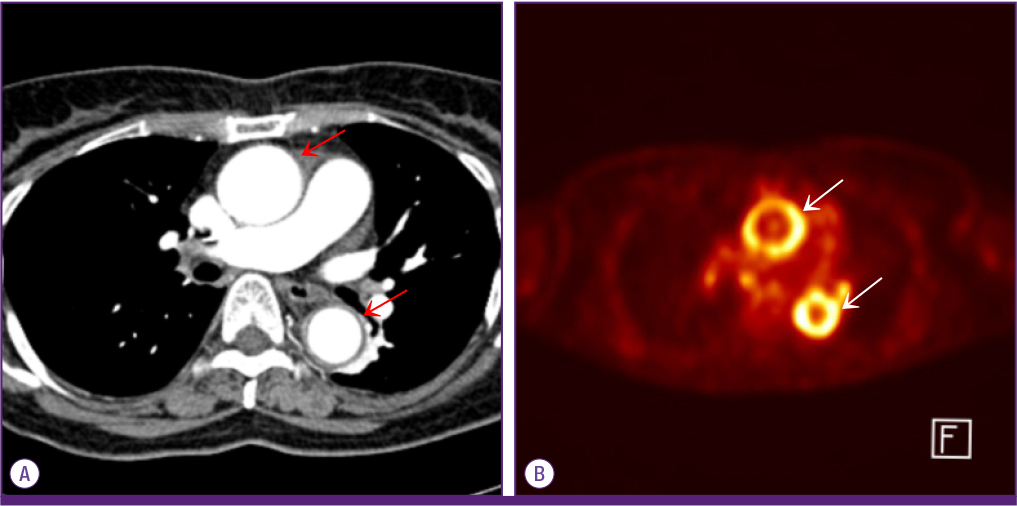
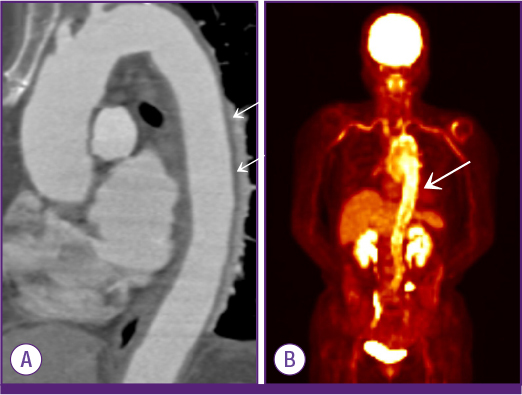
- Takayasu arteritis is a chronic vasculitis involving the large vessels. At diagnosis, ischemic symptom are usually present in the affected vessels. However, fever of unknown origin (FUO) is rare as an initial presentation and renders the condition difficult to diagnose. In this case report, we describe a patient who presented with a fever of unknown origin. A 68-year-old female was diagnosed with Takayasu arteritis after fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) positron-emission tomography-computed tomography (PET-CT) was performed at the prepulseless stage. FDG PET-CT can assist in the early diagnosis of Takayasu arteritis patients with FUO and can improve the prognosis of such patients.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 2 articles
-
Utility of Magnetic Resonance Imaging and Positron Emission Tomography in Rheumatic Diseases
Eun Hye Park, Chong-Hyeon Yoon, Eun Ha Kang, Han Joo Baek
J Rheum Dis. 2020;27(3):136-151. doi: 10.4078/jrd.2020.27.3..Outcome in Patients with Fever of Unknown Origin whose 18Fluoro-Deoxyglucose Positron Emission Tomography/Computerized Tomography Finding is Non-Diagnostic
Tark Kim, Jin Park, Eun Ju Choo, Hyemin Jeong, Chan Hong Jeon, Jae Pil Hwang, Jung Mi Park
Infect Chemother. 2018;50(1):43-47. doi: 10.3947/ic.2018.50.1.43.
Reference
-
1. Johnston SL, Lock RJ, Gompels MM. Takayasu arteritis: a review. J Clin Pathol. 2002; 55:481–486.
Article2. Arend WP, Michel BA, Bloch DA, Hunder GG, Calabrese LH, Edworthy SM, Fauci AS, Leavitt RY, Lie JT, Lightfoot RW Jr, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Mills JA, Stevens MB, Wallace SL, Zvaifler NJ. The American College of Rheumatology 1990 criteria for the classification of Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1990; 33:1129–1134.
Article3. Arnaud L, Haroche J, Mathian A, Gorochov G, Amoura Z. Pathogenesis of Takayasu's arteritis: a 2011 update. Autoimmun Rev. 2011; 11:61–67.
Article4. Kerr GS, Hallahan CW, Giordano J, Leavitt RY, Fauci AS, Rottem M, Hoffman GS. Takayasu arteritis. Ann Intern Med. 1994; 120:919–929.
Article5. Wu YJ, Martin B, Ong K, Klein NC, Cunha BA. Takayasu's arteritis as a cause of fever of unknown origin. Am J Med. 1989; 87:476–477.
Article6. Oh MD, Ko EM, Suh C, Choi SJ, Choe KW. Fever of undetermined origin (FUO) as a presenting symptom of Takayasu arteritis. J Korean Med Assoc. 1986; 29:1018–1022.7. Keidar Z, Gurman-Balbir A, Gaitini D, Israel O. Fever of unknown origin: the role of 18F-FDG PET/CT. J Nucl Med. 2008; 49:1980–1985.
Article8. Becerra Nakayo EM, García Vicente AM, Soriano Castrejón AM, Mendoza Narváez JA, Talavera Rubio MP, Poblete García VM, Cordero García JM. Analysis of cost-effectiveness in the diagnosis of fever of unknown origin and the role of 18F-FDG PET-CT: a proposal of diagnostic algorithm. Rev Esp Med Nucl Imagen Mol. 2012; 31:178–186.
Article9. Akin E, Coen A, Momeni M. PET-CT findings in large vessel vasculitis presenting as FUO, a case report. Clin Rheumatol. 2009; 28:737–738.
Article10. Tatò F, Weiss M, Hoffmann U. Takayasu's arteritis without manifest arterial stenoses as a cause of fever of unknown origin. Dtsch Med Wochenschr. 2006; 131:1727–1730.
Article11. Meller J, Strutz F, Siefker U, Scheel A, Sahlmann CO, Lehmann K, Conrad M, Vosshenrich R. Early diagnosis and follow-up of aortitis with [18F]FDG PET and MRI. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 2003; 30:730–736.
Article12. Ohigashi H, Haraguchi G, Konishi M, Tezuka D, Kamiishi T, Ishihara T, Isobe M. Improved prognosis of Takayasu arteritis over the past decade--comprehensive analysis of 106 patients. Circ J. 2012; 76:1004–1011.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- A Case of Atypical Giant Cell Arteritis Presenting as a Fever of Unknown Origin
- Non-Specific Disease Mimicking Malignancy: Two Cases of FDG Uptake in the Extremities
- A Case Report of Takayaeu's Arteritis Associated with, a Retinopathy
- Takayasu's Arteritis: report of 2 cases and review of literature
- A Case of Acute Q Fever Hepatitis Diagnosed by F-18 FDG PET/CT