Hip Pelvis.
2013 Jun;25(2):135-140. 10.5371/hp.2013.25.2.135.
Etanercept Treatment in Ankylosing Spondylitis Hip Lesions
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Orthopaedic Surgery, Haeundae Paik Hospital, College of Medicine, Inje University, Busan, Korea. moonsw1106@gmail.com
- KMID: 2054151
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5371/hp.2013.25.2.135
Abstract
- PURPOSE
To evaluate the efficacy of etanercept in patients with an ankylosing spondylitis hip lesion.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Between March 2008 and December 2011, this study evaluated 13 patients with hip lesions who were refractory to conventional therapy. The general improvement was evaluated by the Harris hip score, Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI), ESR, CRP, and complications.
RESULTS
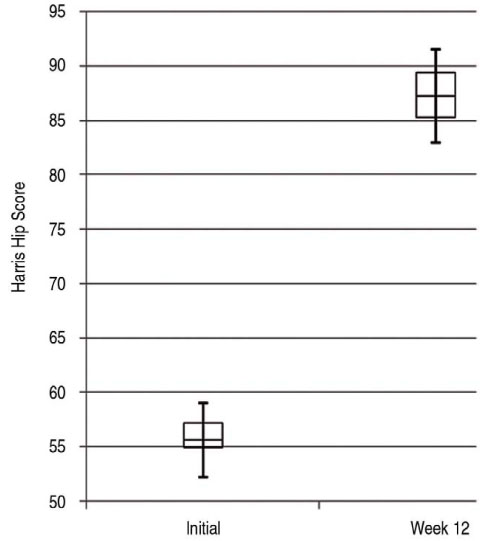
The mean Harris hip score changed from 55.6+/-3.4 to 87.2+/-4.3(P=0.01). The mean BASDAI/ BASFI decreased from 6.8+/-1.7/6.8+/-1.6 before treatment to 4.4+/-1.8(P=0.02)/4.3+/-1.1(P=0.02) after treatment. The mean ESR/CRP changed from 48.4+/-31.5/5.8+/-5.1 to 20.8+/-19.7(P=0.06)/3.1+/-4.2(P=0.03). No complications were encountered.
CONCLUSION
These results suggest that etanercept can induce significant pain improvement in most ankylosing spondylitis hip lesions.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Diagnosis and Treatment of Inflammatory Joint Disease
Yeesuk Kim, Hyun-Cheol Oh, Jang Won Park, In-Sung Kim, Jun-Young Kim, Ki-Choul Kim, Dong-Sik Chae, Woo-Lam Jo, Joo-Hyoun Song
Hip Pelvis. 2017;29(4):211-222. doi: 10.5371/hp.2017.29.4.211.
Reference
-
1. Braun J, Brandt J, Listing J, Rudwaleit M, Sieper J. Biologic therapies in the spondyloarthritis: new opportunities, new challenges. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2003; 15:394–407.
Article2. Braun J, de Keyser F, Brandt J, Mielants H, Sieper J, Veys E. New treatment options in spondyloarthropathies: increasing evidence for significant efficacy of anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Curr Opin Rheumatol. 2001; 13:245–249.
Article3. Davis JC Jr, van der Heijde DM, Braun J, et al. Efficacy and safety of up to 192 weeks of etanercept therapy in patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2008; 67:346–352.
Article4. Calin A, Elswood J. The relationship between pelvic, spinal and hip involvement in ankylosing spondylitis--one disease process or several. Br J Rheumatol. 1988; 27:393–395.
Article5. Sturrock RD, Hart FD. Double-blind cross-over comparison of indomethacin, flurbiprofen, and placebo in ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 1974; 33:129–131.
Article6. Davis JC Jr. Understanding the role of tumor necrosis factor inhibition in ankylosing spondylitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 34:668–677.
Article7. Gorman JD, Sack KE, Davis JC Jr. Treatment of ankylosing spondylitis by inhibition of tumor necrosis factor alpha. N Engl J Med. 2002; 346:1349–1356.
Article8. Calin A, Dijkmans BA, Emery P, et al. Outcomes of a multicentre randomised clinical trial of etanercept to treat ankylosing spondylitis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2004; 63:1594–1600.
Article9. van der Heijde D, Dijkmans B, Geusens P, et al. Efficacy and safety of infliximab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a randomized, placebo-controlled trial (ASSERT). Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52:582–591.
Article10. Gratacós J, Collado A, Filella X, et al. Serum cytokines (IL-6, TNF-alpha, IL-1 beta and IFN-gamma) in ankylosing spondylitis: a close correlation between serum IL-6 and disease activity and severity. Br J Rheumatol. 1994; 33:927–931.11. Toussirot E, Lafforgue P, Boucraut J, et al. Serum levels of interleukin 1-beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, soluble interleukin 2 receptor and soluble CD8 in seronegative spondylarthropathies. Rheumatol Int. 1994; 13:175–180.
Article12. Grom AA, Murray KJ, Luyrink L, et al. Patterns of expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha, tumor necrosis factor beta, and their receptors in synovia of patients with juvenile rheumatoid arthritis and juvenile spondylarthropathy. Arthritis Rheum. 1996; 39:1703–1710.
Article13. Cañete JD, Llena J, Collado A, et al. Comparative cytokine gene expression in synovial tissue of early rheumatoid arthritis and seronegative spondyloarthropathies. Br J Rheumatol. 1997; 36:38–42.
Article14. Braun J, Bollow M, Neure L, et al. Use of immunohistologic and in situ hybridization techniques in the examination of sacroiliac joint biopsy specimens from patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Arthritis Rheum. 1995; 38:499–505.
Article15. Crew MD, Effros RB, Walford RL, Zeller E, Cheroutre H, Brahn E. Transgenic mice expressing a truncated Peromyscus leucopus TNF-alpha gene manifest an arthritis resembling ankylosing spondylitis. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 1998; 18:219–225.
Article16. Lord PA, Farragher TM, Lunt M, Watson KD, Symmons DP, Hyrich KL. Predictors of response to anti-TNF therapy in ankylosing spondylitis: results from the British Society for Rheumatology Biologics Register. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2010; 49:563–570.
Article17. van der Heijde D, Kivitz A, Schiff MH, et al. Efficacy and safety of adalimumab in patients with ankylosing spondylitis: results of a multicenter, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2006; 54:2136–2146.
Article18. Brandt J, Marzo-Ortega H, Emery P. Ankylosing spondylitis: new treatment modalities. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:559–570.
Article19. Law LA, Haftel HM. Shoulder, knee, and hip pain as initial symptoms of juvenile ankylosing spondylitis: a case report. J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 1998; 27:167–172.
Article20. Amor B, Santos RS, Nahal R, Listrat V, Dougados M. Predictive factors for the longterm outcome of spondyloarthropathies. J Rheumatol. 1994; 21:1883–1887.21. Akkoc N, van der Linden S, Khan MA. Ankylosing spondylitis and symptom-modifying vs disease-modifying therapy. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol. 2006; 20:539–557.
Article22. Davis JC Jr, Van Der Heijde D, Braun J, et al. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor receptor (etanercept) for treating ankylosing spondylitis: a randomized, controlled trial. Arthritis Rheum. 2003; 48:3230–3236.
Article23. Balandraud N, Guis S, Meynard JB, Auger I, Roudier J, Roudier C. Long-term treatment with methotrexate or tumor necrosis factor alpha inhibitors does not increase epstein-barr virus load in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007; 57:762–767.
Article24. Ehlers S. Why does tumor necrosis factor targeted therapy reactivate tuberculosis? J Rheumatol Suppl. 2005; 74:35–39.25. Wolfe F. Comparative usefulness of C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rate in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol. 1997; 24:1477–1485.26. Choi CB, Kim TJ, Park HJ, et al. Safety and clinical responses in ankylosing spondylitis after three months of etanercept therapy. J Korean Med Sci. 2008; 23:852–856.
Article27. Son JH, Cha SW. Anti-TNF-alpha therapy for ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Orthop Surg. 2010; 2:28–33.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- TNF Inhibitors and Uveitis in Ankylosing Spondylitis
- A Case of Ankylosing Spondylitis Accompanying Sarcoidosis
- IgA nephropathy in a patient with ankylosing spondylitis well controlled with etanercept
- A Case of Tumor Necrosis Factor-alpha Inhibitors-induced Pustular Psoriasis
- A Case of Ankylosing Spondylitis with Cricoarytenoid Arthritis