Tuberc Respir Dis.
2012 Nov;73(5):288-291. 10.4046/trd.2012.73.5.288.
A Case of Typhlitis Developed after Chemotherapy with Irinotecan and Cisplatin in a Patient with Small Cell Lung Carcinoma
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Internal Medicine, The Catholic University of Korea College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. mdlee@catholic.ac.kr
- KMID: 2050683
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.4046/trd.2012.73.5.288
Abstract
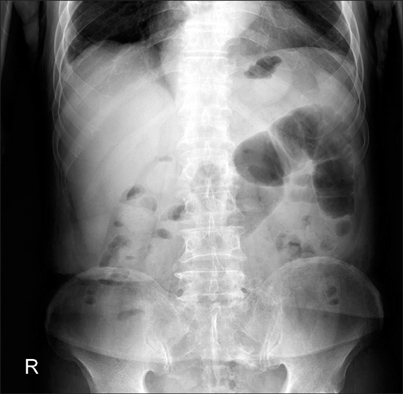
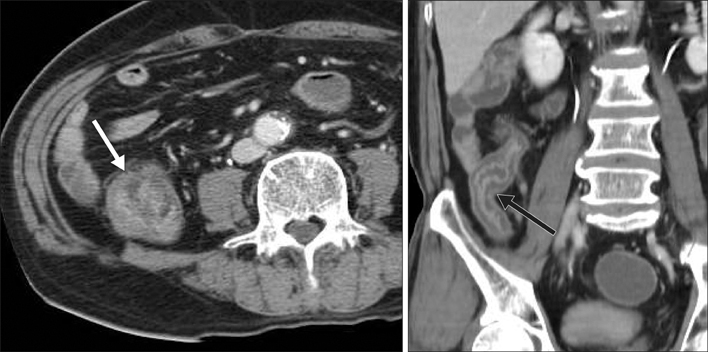
- Typhlitis is a necrotizing colitis that usually occurs in neutropenic patients and develops most often in patients with hematologic malignancies such as leukemia and lymphoma. Typhlitis may proceed to bowel perforation, peritonitis and sepsis, which requires immediate treatment. Irinotecan is a semisynthetic analogue of the natural alkaloid camptothecin which prevents DNA from unwinding by inhibition of topoisomerase I. It is mainly used in colon cancer and small cell lung carcinoma (SCLC), of which the most common adverse effects are gastrointestinal toxicities. To the best of our knowledge, no case of typhlitis after chemotherapy with a standard dose of irinotecan in a solid tumor has been reported in the literature. We, herein, report the first case of typhlitis developed after chemotherapy combining irinotecan and cisplatin in a patient with SCLC.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Noda K, Nishiwaki Y, Kawahara M, Negoro S, Sugiura T, Yokoyama A, et al. Irinotecan plus cisplatin compared with etoposide plus cisplatin for extensive small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2002. 346:85–91.2. Bleiberg H, Cvitkovic E. Characterisation and clinical management of CPT-11 (irinotecan)-induced adverse events: the European perspective. Eur J Cancer. 1996. 32A:Suppl 3. S18–S23.3. Gorschlüter M, Mey U, Strehl J, Ziske C, Schepke M, Schmidt-Wolf IG, et al. Neutropenic enterocolitis in adults systematic analysis of evidence quality. Eur J Haematol. 2005. 75:1–13.4. Keidan RD, Fanning J, Gatenby RA, Weese JL. Recurrent typhlitis: a disease resulting from aggressive chemotherapy. Dis Colon Rectum. 1989. 32:206–209.5. Oh YS, Yoo JH, Kim YR, Hahn CW, Park CW, Shin WS, et al. Four cases of typhlitis in patients with acute leukemia. Korean J Med. 1995. 49:550–555.6. Cartoni C, Dragoni F, Micozzi A, Pescarmona E, Mecarocci S, Chirletti P, et al. Neutropenic enterocolitis in patients with acute leukemia: prognostic significance of bowel wall thickening detected by ultrasonography. J Clin Oncol. 2001. 19:756–761.7. Kim YB, Lee SJ, Lee YH, Lee YK, Sin SK, Kim JS, et al. A case of typhlitis developed after anticancer chemotherapy in a patient with solid tumor. Korean J Med. 2002. 62:657–660.8. Tiseo M, Gelsomino F, Bartolotti M, Barili MP, Ardizzoni A. Typhlitis during second-line chemotherapy with pemetrexed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC): A case report. Lung Cancer. 2009. 65:251–253.9. Rodriguez-Galindo C, Crews KR, Stewart CF, Furman W, Panetta JC, Daw NC, et al. Phase I study of the combination of topotecan and irinotecan in children with refractory solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 2006. 57:15–24.10. Hahn KK, Wolff JJ, Kolesar JM. Pharmacogenetics and irinotecan therapy. Am J Health Syst Pharm. 2006. 63:2211–2217.11. Shamberger RC, Weinstein HJ, Delorey MJ, Levey RH. The medical and surgical management of typhlitis in children with acute nonlymphocytic (myelogenous) leukemia. Cancer. 1986. 57:603–609.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment of Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Chemotherapy for Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Adjuvant Chemotherapy in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
- Acute myelogenous leukemia following etoposide and cisplatin combination chemotherapy for small cell carcinoma of the lung
- Phase II Study of Irinotecan Plus Cisplatin as First Line therapy in Extensive Small-Cell Lung Cancer