Ann Lab Med.
2015 Jul;35(4):469-471. 10.3343/alm.2015.35.4.469.
Identification of Mixed Lineage Leukemia Gene (MLL)/MLLT10 Fusion Transcripts by Reverse Transcription-PCR and Sequencing in a Case of AML With a FISH-Negative Cryptic MLL Rearrangement
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Laboratory Medicine, Kangbuk Samsung Hospital, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea.
- 2Department of Laboratory Medicine and Genetics, Samsung Medical Center, Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. sunnyhk@skku.edu
- KMID: 2045874
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3343/alm.2015.35.4.469
Abstract
- No abstract available.
MeSH Terms
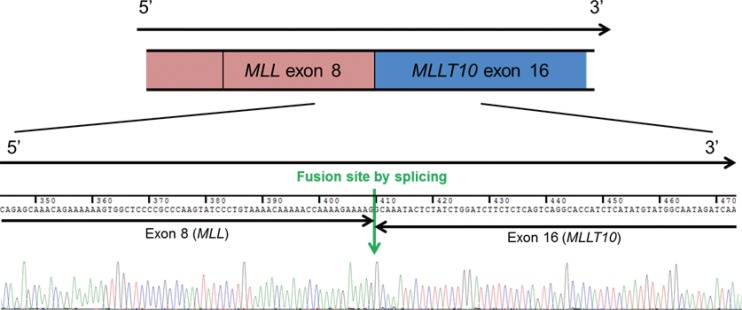
Figure
Reference
-
1. de Boer J, Walf-Vorderwülbecke V, Williams O. In focus: MLL-rearranged leukemia. Leukemia. 2013; 27:1224–1228. PMID: 23515098.
Article2. Morerio C, Rapella A, Rosanda C, Lanino E, Lo Nigro L, Di Cataldo A, et al. MLL-MLLT10 fusion in acute monoblastic leukemia: variant complex rearrangements and 11q proximal breakpoint heterogeneity. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2004; 152:108–112. PMID: 15262427.
Article3. Stasevich I, Utskevich R, Kustanovich A, Litvinko N, Savitskaya T, Chernyavskaya S, et al. Translocation (10;11)(p12;q23) in childhood acute myeloid leukemia: incidence and complex mechanism. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 2006; 169:114–120. PMID: 16938568.
Article4. Van Limbergen H, Poppe B, Janssens A, De Bock R, De Paepe A, Noens L, et al. Molecular cytogenetic analysis of 10;11 rearrangements in acute myeloid leukemia. Leukemia. 2002; 16:344–351. PMID: 11896537.
Article5. Yang JJ, Marschalek R, Meyer C, Park TS. Diagnostic usefulness of genomic breakpoint analysis of various gene rearrangements in acute leukemias: a perspective of long distance- or long distance inverse-PCR-based approaches. Ann Lab Med. 2012; 32:316–318. PMID: 22779077.
Article6. Choi HJ, Kim HR, Shin MG, Kook H, Kim HJ, Shin JH, et al. Spectra of chromosomal aberrations in 325 leukemia patients and implications for the development of new molecular detection systems. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:886–892. PMID: 21738341.
Article7. Kim MJ, Choi JR, Suh JT, Lee HJ, Lee WI, Park TS. Diagnostic standardization of leukemia fusion gene detection system using multiplex reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction in Korea. J Korean Med Sci. 2011; 26:1399–1400. author reply 1401. PMID: 22022200.8. Watanabe N, Kobayashi H, Ichiji O, Yoshida MA, Kikuta A, Komada Y, et al. Cryptic insertion and translocation or nondividing leukemic cells disclosed by FISH analysis in infant acute leukemia with discrepant molecular and cytogenetic findings. Leukemia. 2003; 17:876–882. PMID: 12750700.
Article9. Meyer C, Hofmann J, Burmeister T, Gröger D, Park TS, Emerenciano M, et al. The MLL recombinome of acute leukemias in 2013. Leukemia. 2013; 27:2165–2176. PMID: 23628958.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Rapid Detection of Prognostically Significant Fusion Transcripts in Acute Leukemia Using Simplified Multiplex Reverse Transcription Polymerase Chain Reaction
- Systematic Classification of Mixed-Lineage Leukemia Fusion Partners Predicts Additional Cancer Pathways
- Acute Monocytic Leukemia with t(11;17)(q23;q21) Involving a Rearrangement of Mixed Lineage Leukemia Gene
- Prevalence and Clinical Implication of Partial Tandem Duplication of the Mixed Lineage Leukemia Gene in Pediatric Acute Leukemia
- Acute Monoblastic Leukemia with t(11;17)(q23;q21): Fusion of the KMT2A(MLL) and MLLT6(AF17) Genes