J Korean Neurotraumatol Soc.
2011 Oct;7(2):103-107. 10.13004/jknts.2011.7.2.103.
Two Cases of Secondary Intracranial Hypotension
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Kangdong Sacred Heart Hospital, Hallym University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea. nschbm@hanmail.net
- KMID: 2019923
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.13004/jknts.2011.7.2.103
Abstract
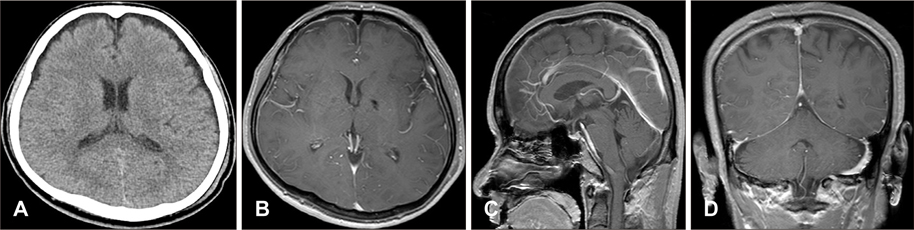
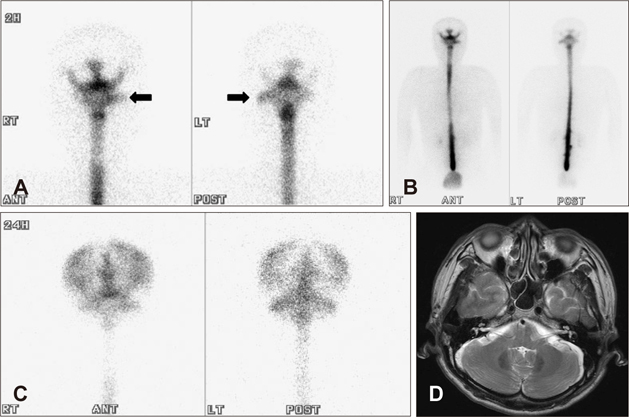
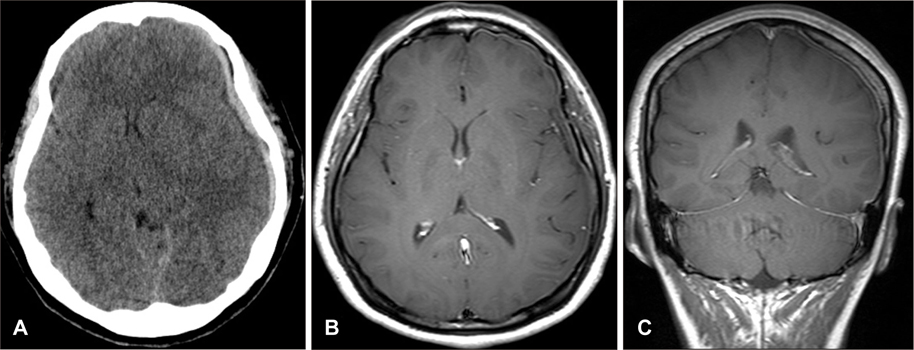
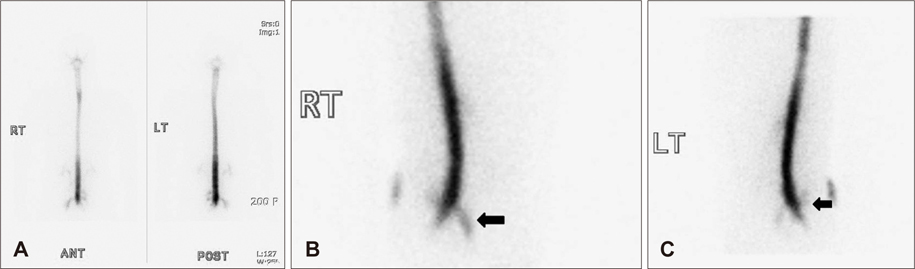
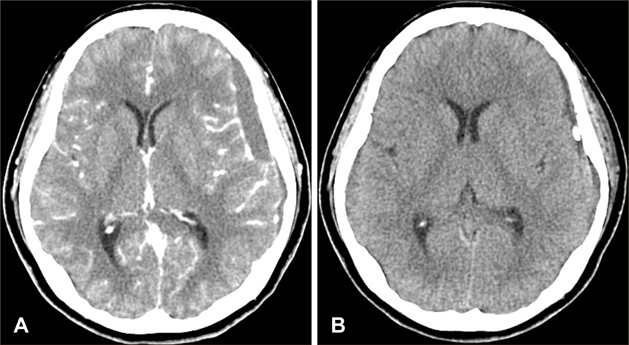
- Intracranial hypotension (IH) is a clinical syndrome which leads to orthostatic headache due to low cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) volume. Severe cases are present with nausea, vomiting, photophobia, and rarely, decreased level of consciousness and coma. The various modalities for diagnosing CSF leakage have been used, such as radionuclide cisternography (RNC), CT myelography and MRI myelography. Despites of the various modalities, the actual location of leakage is hard to find. We present two patients who underwent RNC for suspected CSF leakage after trauma and lumbar puncture. One case, site of CSF leakage was misidentified. The other case, we performed burr hole trephination with closed drainage due to progressive subdural hematoma (SDH) after epidural blood patch (EBP). This report emphasizes that intracranial hypotension presents with various clinical presentation and neuroimaging findings.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
Cervical Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage Concomitant with a Thoracic Spinal Intradural Arachnoid Cyst
Sanghyun Han, Seung-Won Choi, Bum-Soo Park, Jeong-Wook Lim, Seon-Hwan Kim, Jin-Young Youm
Korean J Neurotrauma. 2019;15(2):214-220. doi: 10.13004/kjnt.2019.15.e31.
Reference
-
1. Berroir S, Loisel B, Ducros A, Boukobza M, Tzourio C, Valade D, et al. Early epidural blood patch in spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Neurology. 2004; 63:1950–1951.
Article2. Fujimaki H, Saito N, Tosaka M, Tanaka Y, Horiguchi K, Sasaki T. Cerebrospinal fluid leak demonstrated by three-dimensional computed tomographic myelography in patients with spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Surg Neurol. 2002; 58:280–284. discussion 284-285.
Article3. Headache Classification Subcommittee of the International Headache Society. The International Classification of Headache Disorders: 2nd edition. Cephalalgia. 2004; 24:Suppl 1. 9–160.4. Kantor D, Silberstein SD. Cervical epidural blood patch for low CSF pressure headaches. Neurology. 2005; 65:1138.
Article5. Li L, Gao FQ, Zhang B, Luo BN, Yang ZY, Zhao J. Overdosage of intrathecal gadolinium and neurological response. Clin Radiol. 2008; 63:1063–1068.
Article6. Mikawa S, Ebina T. [Spontaneous intracranial hypotension complicating subdural hematoma: unilateral oculomotor nerve palsy caused by epidural blood patch]. No Shinkei Geka. 2001; 29:747–753.7. Mokri B. Headaches caused by decreased intracranial pressure: diagnosis and management. Curr Opin Neurol. 2003; 16:319–326.
Article8. Mokri B, Low PA. Orthostatic headaches without CSF leak in postural tachycardia syndrome. Neurology. 2003; 61:980–982.
Article9. Morioka T, Aoki T, Tomoda Y, Takahashi H, Kakeda S, Takeshita I, et al. Cerebrospinal fluid leakage in intracranial hypotension syndrome: usefulness of indirect findings in radionuclide cisternography for detection and treatment monitoring. Clin Nucl Med. 2008; 33:181–185.
Article10. Paldino M, Mogilner AY, Tenner MS. Intracranial hypotension syndrome: a comprehensive review. Neurosurg Focus. 2003; 15:ECP2.
Article11. Raskin NH. Lumbar puncture headache: a review. Headache. 1990; 30:197–200.
Article12. Schievink WI. Misdiagnosis of spontaneous intracranial hypotension. Arch Neurol. 2003; 60:1713–1718.
Article13. Schoffer KL, Benstead TJ, Grant I. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension in the absence of magnetic resonance imaging abnormalities. Can J Neurol Sci. 2002; 29:253–257.
Article14. Takeuchi S, Takasato Y, Masaoka H, Hayakawa T, Otani N, Yoshino Y, et al. Progressive subdural hematomas after epidural blood patch for spontaneous intracranial hypotension. J Anesth. 2010; 24:315–316.
Article15. Watanabe A, Horikoshi T, Uchida M, Koizumi H, Yagishita T, Kinouchi H. Diagnostic value of spinal MR imaging in spontaneous intracranial hypotension syndrome. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009; 30:147–151.
Article16. Winter SC, Maartens NF, Anslow P, Teddy PJ. Spontaneous intracranial hypotension due to thoracic disc herniation. Case report. J Neurosurg. 2002; 96:343–345.17. Yoo HM, Kim SJ, Choi CG, Lee DH, Lee JH, Suh DC, et al. Detection of CSF leak in spinal CSF leak syndrome using MR myelography: correlation with radioisotope cisternography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:649–654.
Article18. Yoon SH, Chung YS, Yoon BW, Kim JE, Paek SH, Kim DG. Clinical experiences with spontaneous intracranial hypotension: a proposal of a diagnostic approach and treatment. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2011; 113:373–379.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Treatment with Epidural Blood Patch for Iatrogenic Intracranial Hypotension after Spine Surgery
- A Case of Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension: Detection of Cerebrospinal Fluid Leakage by Early Dynamic Radionuclide Cisternography
- Intracranial Hypotension Leading to Intracranial Hypertension with Ocular Manifestations
- Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension Secondary to Lumbar Disc Herniation
- Intracranial Hypertension Following Epidural Blood Patch in a Patient With Spontaneous Intracranial Hypotension