J Korean Neurosurg Soc.
2014 Nov;56(5):400-404. 10.3340/jkns.2014.56.5.400.
Quantitative Analysis of Factors Affecting Cobalt Alloy Clip Artifacts in Computed Tomography
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Neurosurgery, Inje University Seoul Paik Hospital, Seoul, Korea. lessordi@naver.com
- 2Department of Radiology, National Medical Center, Seoul, Korea.
- KMID: 2018098
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.3340/jkns.2014.56.5.400
Abstract
OBJECTIVE
Clip artifacts limit the visualization of intracranial structures in CT scans from patients after aneurysmal clipping with cobalt alloy clips. This study is to analyze the parameters influencing the degree of clip artifacts.
METHODS
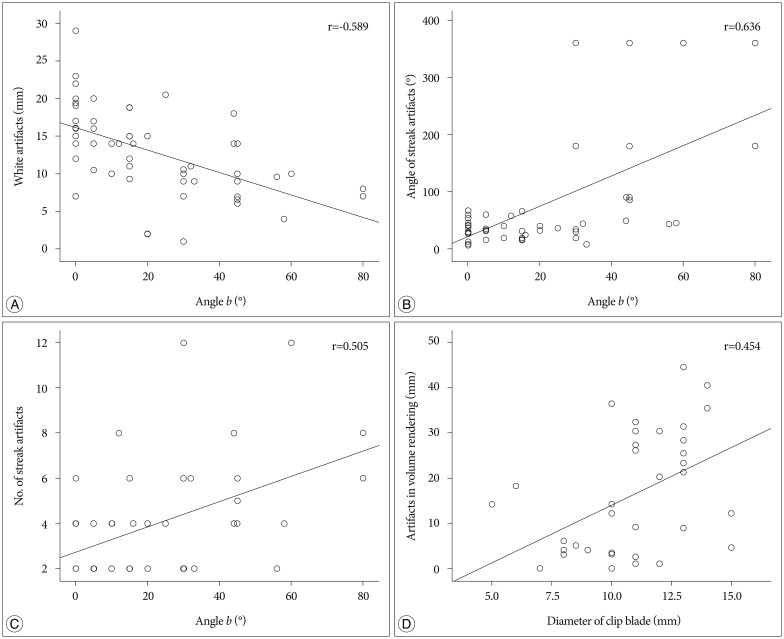
Postoperative CT scans of 60 patients with straight cobalt alloy-clipped aneurysms were analyzed for the maximal diameter of white artifacts and the angle and number of streak artifacts in axial images, and the maximal diameter of artifacts in three-dimensional (3-D) volume-rendered images. The correlation coefficient (CC) was determined between each clip artifact type and the clip blade length and clip orientation to the CT scan (angle a, lateral clip inclination in axial images; angle b, clip gradient to scan plane in lateral scout images).
RESULTS
Angle b correlated negatively with white artifacts (r=-0.589, p<0.001) and positively with the angle (r=0.636, p<0.001) and number (r=0.505, p<0.001) of streak artifacts. Artifacts in 3-D images correlated with clip blade length (r=0.454, p=0.004). Multiple linear regression analysis revealed that angle b was the major parameter influencing white artifacts and the angle and number of streak artifacts in axial images (p<0.001), whereas clip blade length was a major factor in 3-D images (p=0.034).
CONCLUSION
Use of a clip orientation perpendicular to the scan gantry angle decreased the amount of white artifacts and allowed better visualization of the clip site.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Brown JH, Lustrin ES, Lev MH, Ogilvy CS, Taveras JM. Reduction of aneurysm clip artifacts on CT angiograms : a technical note. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1999; 20:694–696. PMID: 10319984.2. Dandy WE. Intracranial aneurysm of the internal carotid artery : cured by operation. Ann Surg. 1938; 107:654–659. PMID: 17857170.
Article3. Kato Y, Sano H, Katada K, Ogura Y, Ninomiya T, Okuma I, et al. Effects of new titanium cerebral aneurysm clips on MRI and CT images. Minim Invasive Neurosurg. 1996; 39:82–85. PMID: 8892287.
Article4. Klingebiel R, Busch M, Bohner G, Zimmer C, Hoffmann O, Masuhr F. Multi-slice CT angiography in the evaluation of patients with acute cerebrovascular disease--a promising new diagnostic tool. J Neurol. 2002; 249:43–49. PMID: 11954867.
Article5. Kovács A, Flacke S, Tschampa H, Hadizadeh D, Greschus S, Clusmann H, et al. Gated multidetector computed tomography. A technique to reduce intracranial aneurysm clip and coil artifacts. Clin Neuroradiol. 2010; 20:99–107. PMID: 20490439.6. Mamourian AC, Erkmen K, Pluta DJ. Nonhelical acquisition CT angiogram after aneurysmal clipping : in vitro testing shows diminished artifact. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:660–662. PMID: 18184847.
Article7. Mamourian AC, Pluta DJ, Eskey CJ, Merlis AL. Optimizing computed tomography to reduce artifacts from titanium aneurysm clips : an in vitro study. Technical note. J Neurosurg. 2007; 107:1238–1243. PMID: 18077966.
Article8. Nagatani T, Shibuya M, Ooka K, Suzuki Y, Takayasu M, Yoshida J. Titanium aneurysm clips : mechanical characteristics and clinical trial. Neurol Med Chir Tokyo. 1998; 38(Suppl):39–44. PMID: 10234976.9. Otawara Y, Ogasawara K, Ogawa A, Sasaki M, Takahashi K. Evaluation of vasospasm after subarachnoid hemorrhage by use of multislice computed tomographic angiography. Neurosurgery. 2002; 51:939–942. discussion 942-943. PMID: 12234400.
Article10. Pechlivanis I, König M, Engelhardt M, Scholz M, Heuser L, Harders A, et al. Evaluation of clip artefacts in three-dimensional computed tomography. Cent Eur Neurosurg. 2009; 70:9–14. PMID: 19191202.
Article11. Sagara Y, Kiyosue H, Hori Y, Sainoo M, Nagatomi H, Mori H. Limitations of three-dimensional reconstructed computerized tomography angiography after clip placement for intracranial aneurysms. J Neurosurg. 2005; 103:656–661. PMID: 16266048.
Article12. van der Schaaf I, van Leeuwen M, Vlassenbroek A, Velthuis B. Minimizing clip artifacts in multi CT angiography of clipped patients. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2006; 27:60–66. PMID: 16418357.13. Vannier MW, Hildebolt CF, Conover G, Knapp RH, Yokoyama-Crothers N, Wang G. Three-dimensional dental imaging by spiral CT. A progress report. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1997; 84:561–570. PMID: 9394390.14. von Holst H, Bergström M, Möller A, Steiner L, Ribbe T. Titanium clips in neurosurgery for elimination of artefacts in computer tomography (CT) a technical note. Acta Neurochir (Wien). 1977; 101–109. PMID: 899893.15. Watanabe Y, Kashiwagi N, Yamada N, Higashi M, Fukuda T, Morikawa S, et al. Subtraction 3D CT angiography with the orbital synchronized helical scan technique for the evaluation of postoperative cerebral aneurysms treated with cobalt-alloy clips. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2008; 29:1071–1075. PMID: 18372416.
Article16. Zachenhofer I, Cejna M, Schuster A, Donat M, Roessler K. Image quality and artefact generation post-cerebral aneurysm clipping using a 64-row multislice computer tomography angiography (MSCTA) technology : a retrospective study and review of the literature. Clin Neurol Neurosurg. 2010; 112:386–391. PMID: 20189713.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Comparison of Aneurysmal Clip-induced Artifacts in 64- and 16-row Multislice Computed Tomography Angiograms
- Reoperation due to Slippage of Titanium Aneurysm Clip: Case Report
- A study of artifacts in MR imaging induced by metalic aneurysm clips
- Comparison of the Cobalt Alloy and Stainless Steel Core(r) Stent in a Porcine Coronary Restenosis Model
- Assessment of the efficiency of a pre- versus post-acquisition metal artifact reduction algorithm in the presence of 3 different dental implant materials using multiple CBCT settings: An in vitro study