J Korean Acad Conserv Dent.
2008 Jan;33(1):20-27. 10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.020.
In vitro evaluation of the consistency of two electronic apex locators
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Conservative Dentistry, School of Dentistry, Yonsei University, Korea. sjlee@yuhs.ac
- KMID: 1986746
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5395/JKACD.2008.33.1.020
Abstract
- The purpose of this study was to evaluate the consistency of two electronic apex locators in vitro model.
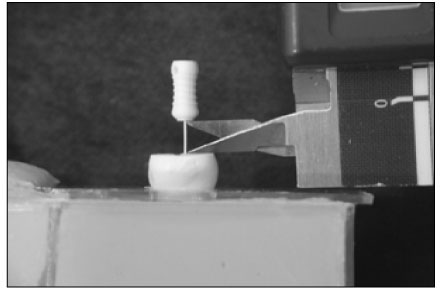
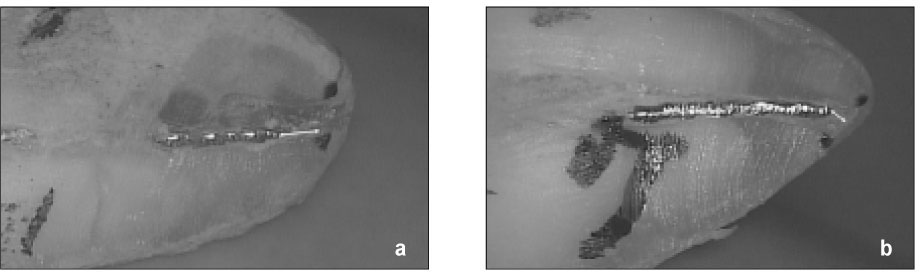
Materials consisted of fifty two extracted premolars and two electronic apex locators; Root ZX (J. Morita, Osaka, Japan) and E-Magic Finder Deluxe (S-Denti, Cheonan, Korea). After access preparation, the teeth were embedded in a saline-mixed alginate model. Canal lengths of each tooth were measured at "0.5" and "Apex" mark of the apex locators, respectively so that each tooth had two measurements from 0.5 and Apex points. The file was fixed at final measurement using a glass ionomer cement. The apical 4 mm from the apex was exposed to measure the distance from the file tip to the major apical foramen of each tooth. Average distances and standard deviations were used to evaluate the consistency.
Results
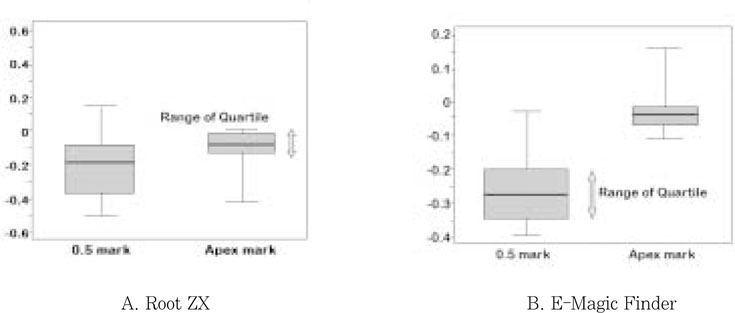
showed that all measurements of both Root ZX and E-Magic Finder located the major foramen the range of +/- 0.5 mm level. Both apex locators showed better consistency at Apex mark than at 0.5 mark. The average distance of file tip-major foramen was - 0.18 mm at 0.5 mark and - 0.07 mm at Apex mark in Root ZX, - 0.25 mm at 0.5 mark and - 0.02 mm at Apex mark in E-Magic Finder. Standard deviation was 0.21 at 0.5 mark and 0.12 at Apex mark in Root ZX, 0.12 at 0.5 mark and 0.09 at Apex mark in E-Magic Finder.
MeSH Terms
Figure
Cited by 1 articles
-
In vivo evaluation of accuracy and consistency of two electronic apex locators
Chien-Yun Pi, Euiseong Kim, Il-Young Jung, Seung-Jong Lee
J Korean Acad Conserv Dent. 2010;35(6):453-460. doi: 10.5395/JKACD.2010.35.6.453.
Reference
-
1. Seltzer S, Soltanoff W, Sinai I, Goldenberg A, Bender IB. Biologic aspects of endodontics. Part III. Periapical tissue reactions to root canal instrumentation. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1968. 26:534–546. 694–705.
Article2. Kuttler Y. Microscopic investigation of root apexes. J Am Dent Assoc. 1955. 50:544–552.
Article3. Lee SJ, Nam KC, Kim YJ, Kim DW. Clinical accuracy of a new apex locator with an automatic compensation circuit. J Endod. 2002. 28:706–709.
Article4. Sunada I. New method for the measuring the length of the root canal. J Dent Res. 1962. 41:375–387.
Article5. Inoue N. An audiometric method for determining the length of root canals. J Can Dent Assoc (Tor). 1973. 39:630–636.6. Frank AL, Torabinejad M. An in vivo evaluation of Endex electronic apex locator. J Endod. 1993. 19:177–179.7. Kobayashi C, Okiji T, Kaqwashima N, Suda H, Sunada I. A basic study on the electronic root canal length measurement: Part 3. Newly designed electronic root canal length measuring device using division method. Jpn J Conservative Dent. 1991. 34:1442–1448.8. Kobayashi C, Suda H. New electronic canal measuring device based on the ratio method. J Endod. 1994. 20:111–114.
Article9. Kobayashi C. Electronic canal length measurement. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod. 1995. 79:226–231.
Article10. Kaufman AY, Keila S, Yoshpe M. Accuracy of a new apex locator: an in vitro study. Int Endod J. 2002. 35:186–192.11. Fouad AF, Rivera EM, Krell KV. Accuracy of the Endex with variations in canal irrigants and foramen size. J Endod. 1993. 19:63–67.
Article12. Riccuci D, Langeland K. Apical limit of root canal instrumentation and obturation. Int Endod J. 1998. 31:394–409.13. Dummer PM, McGinn JH, Rees DG. Theposition and topography of the apical canal constriction and apical foramen. Int Endod J. 1984. 17:192–198.
Article14. Green D. Stereomicroscopic study of 700 root apices of maxillary and mandibular posterior teeth. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1960. 13:728–733.
Article15. Dunlap CA, Remeikis NA, BeGole EA, Rauschenberger CR. An in vivo evaluation of an electronic apex locator that uses the ratio method. J Endod. 1998. 24:48–50.
Article16. Pagavino G, Pace R, Baccetti T. A SEM study of in vivo accuracy of the Root ZX electronic apex locator. J Endod. 1998. 24:438–441.17. Tselnik M, Baumgartner CJ, Marshall GJ. An evaluation of Root ZX and Elements Diagnostic Apex Locators. J Endod. 2005. 31:507–509.
Article
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- In vitro evaluation of accuracy and consistency of four different electronic apex locators
- Evaluating Accuracy according to the Evaluator and Equipment Using Electronic Apex Locators
- An accuracy of the several electronic apex locators on the mesial root canal of the mandibular molar
- In vivo evaluation of accuracy and consistency of two electronic apex locators
- In vitro comparison of measurement accuracy in pre-enlarged and enlarged canals with four apex locators