J Korean Assoc Oral Maxillofac Surg.
2014 Apr;40(2):87-90. 10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.2.87.
Treatment of dental implant-related maxillary sinusitis with functional endoscopic sinus surgery in combination with an intra-oral approach
- Affiliations
-
- 1Department of Dentistry, Keimyung University Dongsan Medical Center, Keimyung University School of Medicine, Daegu, Korea. nkyp@dsmc.or.kr
- KMID: 1960960
- DOI: http://doi.org/10.5125/jkaoms.2014.40.2.87
Abstract
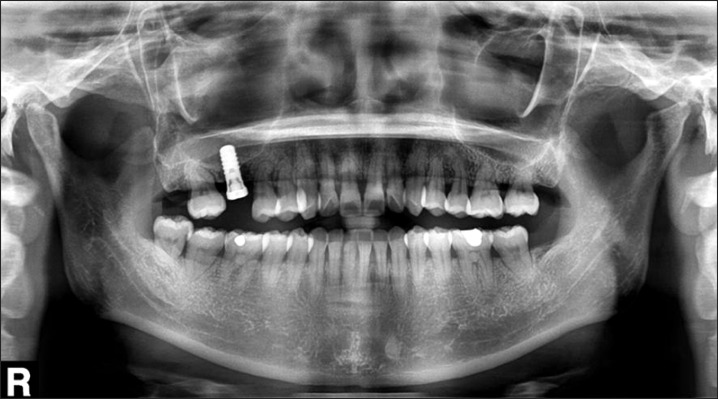
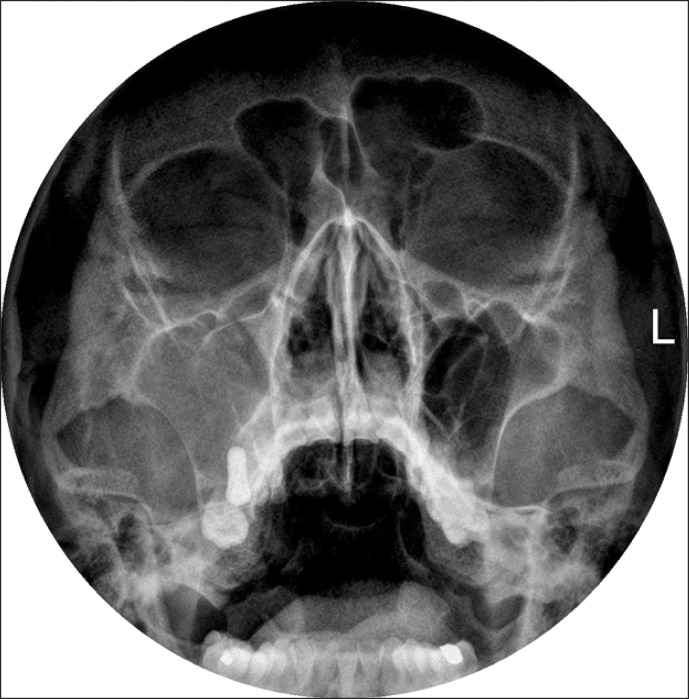
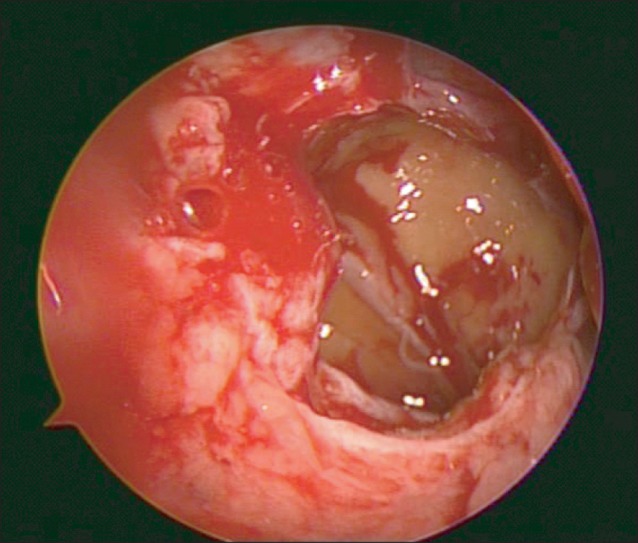
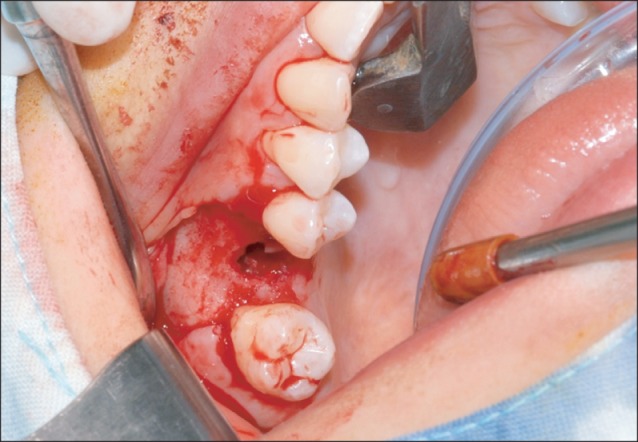
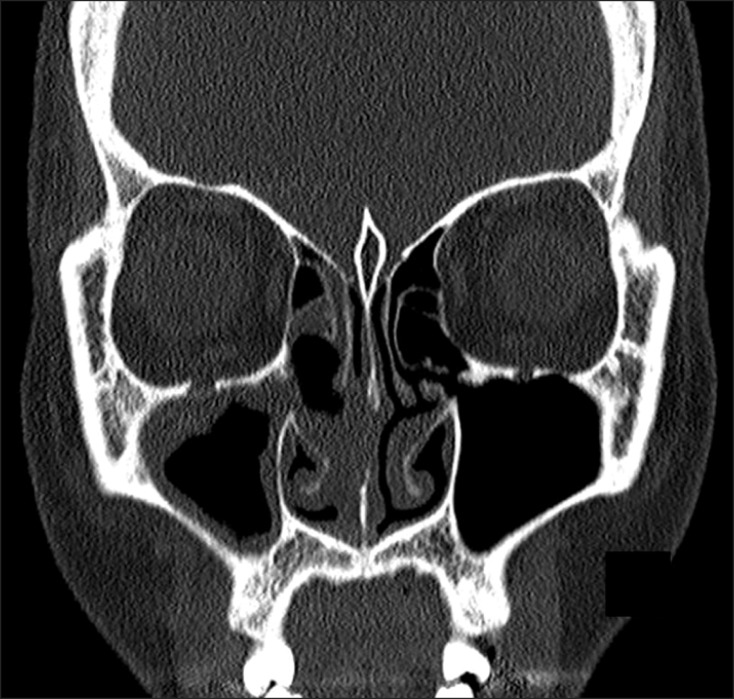
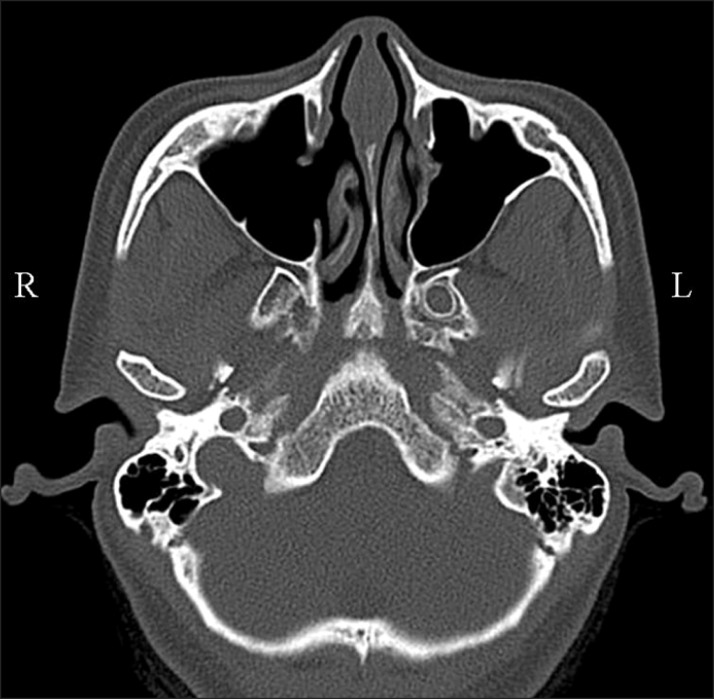
- The present report describes the case of a patient who underwent maxillary sinusitis right after dental implant installation with sinus lifting. Computed tomography scan revealed a dental implant (#16) was protruded inside the right maxillary sinus and confirmed the obstruction of ostium. A symptom remission was gained with the dual approaches combined by functional endoscopic sinus surgery and an intra-oral approach. Fully recovered function and healing of sinus were identified after 10 months follow-up. We report the case of sinusitis caused by protrusion of implants with sinus floor lift procedures and propose that practitioners should be aware of the possible its complications and management.
Keyword
MeSH Terms
Figure
Reference
-
1. Lee JK, Um HS, Chang BS. Retrospective study on the survival rate of the sinus perforated implants. J Korean Acad Periodontol. 2006; 36:891–900.2. Ueda M, Kaneda T. Maxillary sinusitis caused by dental implants: report of two cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 1992; 50:285–287. PMID: 1542071.
Article3. Quiney RE, Brimble E, Hodge M. Maxillary sinusitis from dental osseointegrated implants. J Laryngol Otol. 1990; 104:333–334. PMID: 2370457.
Article4. Galindo P, Sánchez-Fernández E, Avila G, Cutando A, Fernandez JE. Migration of implants into the maxillary sinus: two clinical cases. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implants. 2005; 20:291–295. PMID: 15839124.5. Felisati G, Lozza P, Chiapasco M, Borloni R. Endoscopic removal of an unusual foreign body in the sphenoid sinus: an oral implant. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2007; 18:776–780. PMID: 17868385.
Article6. Chen YW, Huang CC, Chang PH, Chen CW, Wu CC, Fu CH, et al. The characteristics and new treatment paradigm of dental implant-related chronic rhinosinusitis. Am J Rhinol Allergy. 2013; 27:237–244. PMID: 23710961.
Article7. Chiapasco M, Felisati G, Zaniboni M, Pipolo C, Borloni R, Lozza P. The treatment of sinusitis following maxillary sinus grafting with the association of functional endoscopic sinus surgery (FESS) and an intra-oral approach. Clin Oral Implants Res. 2013; 24:623–629. PMID: 22404380.
Article8. Timmenga NM, Raghoebar GM, van Weissenbruch R, Vissink A. Maxillary sinusitis after augmentation of the maxillary sinus floor: a report of 2 cases. J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2001; 59:200–204. PMID: 11213989.
Article9. Pignataro L, Mantovani M, Torretta S, Felisati G, Sambataro G. ENT assessment in the integrated management of candidate for (maxillary) sinus lift. Acta Otorhinolaryngol Ital. 2008; 28:110–119. PMID: 18646572.10. Yang SN. The Inflammatory disease of the maxillary sinus associated with tooth extraction and implant. J Korean Dent Assoc. 2008; 46:727–733.11. Raghoebar GM, van Weissenbruch R, Vissink A. Rhino-sinusitis related to endosseous implants extending into the nasal cavity. A case report. Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg. 2004; 33:312–314. PMID: 15287319.
- Full Text Links
- Actions
-
Cited
- CITED
-
- Close
- Share
- Similar articles
-
- Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for a Patient with Maxillary Sinusitis Occurring after Implant Placement
- Functional endoscopic sinus surgery for odontogenic maxillary sinusitis; A case report
- Delayed Occurrence of Maxillary Sinusitis after Simultaneous Maxillary Sinus Augmentation and Implant: A Case Report and Literature Review
- A Case of Acute Unilateral Maxillary Sinusitis Developed after Dental Implant
- Management of Sinus Infection After Immediate Implant Placement with Sinus Lift (Lateral Approach): Case Report